Interesting Science Videos
Anthrone Test Definition
Anthrone test is a group test for carbohydrates that provides a rapid and convenient method for quantification of carbohydrates that are either free or bound to any lipids or proteins.
Objectives of Anthrone Test
- To detect the presence of carbohydrates in a given solution.
- To quantify the concentration of free and bound carbohydrates in a solution.
Principle of Anthrone Test
If carbohydrate is present in the form of free carbohydrate as poly- or monosaccharide or bound as in a glycoprotein or a glycolipid, the concentrated acid in the Anthrone reagent first hydrolyses it into component monosaccharide. Similarly, the concentrated acid then catalyzes the dehydration of the monosaccharides to form furfural (from pentoses) or hydroxyl furfural (from hexoses). The furfural or hydroxyl furfural formed condenses with two molecules of naphthol from the Anthrone reagent to form a blue-green complex. The complex can then be quantified by measuring the absorbance of 620 nm wavelength in a spectrophotometer or in a red filter colorimeter.
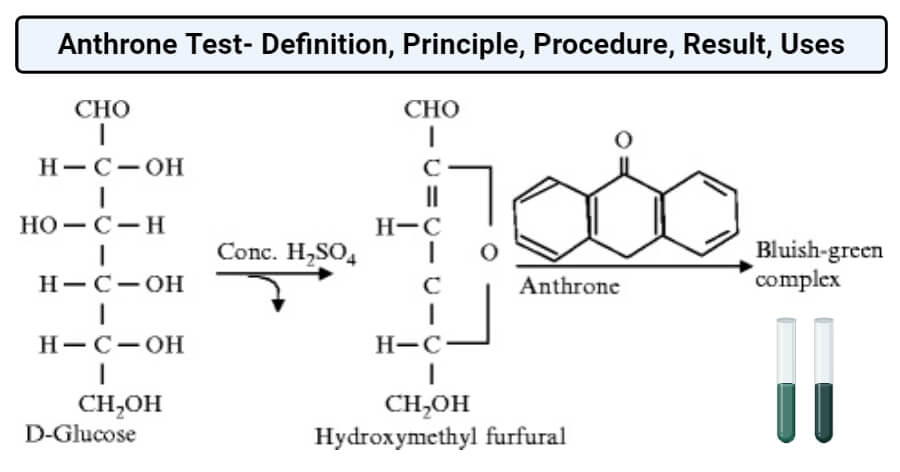
Image Source: Rajan Katoch.
Reaction
1. Hydrolysis of polysaccharides to monosaccharide
Polysaccharide → Monosaccharides
2. Dehydration of monosaccharides to furfural
Monosaccharide → Furfural
3. Reaction of furfural with naphthol
Furfural + Anthrone reagent (naphthol) → Blue-green complex
Requirements
1. Materials required
Equipment:
- UV Spectrophotometer
- Vortex mixer
- Mantle heater/Water Bath.
Chemicals/Reagents:
- Anthrone Reagent
- Glucose
- Other carbohydrates if desired
- Sample
Glasswares and other equipment:
- Test tubes, Test tube stand, Pipettes, Beaker, Ice Test tube caps, Tissue paper, Wash bottle.
2. Reagents
- Anthrone reagent: 2g of Anthrone is dissolved in 1 liter of concentrated H2SO4. The freshly prepared reagent should be used for the assay
- Glucose stock solution: 200µg glucose per mL distilled water stock solution of glucose is to be prepared from the stocked solution. Note: Other carbohydrates of the same concentration can be used as samples if desired.
Procedure of Anthrone Test
- Pipette out different volumes (50 µl, 100 µl, and so on) of glucose solution from the supplied stock solution (200µg /ml) into a series of test tubes and make up the volume to 1 mL with distilled water.
- Take a tube labeled as one as blank containing 1ml of just distilled water and the rest of the tubes labeled 2 to 9 for construction of a standard curve. Tubes 10-15 are for the unknown samples.
- Add 5 ml of the anthrone reagent To each tube and mix well by vortexing.
- Cool the tubes.
- Cover the tubes with caps on top and incubate at 90°C for 17 minutes or boiling water bath for 10 minutes.
- Cool the tubes to room temperature and measure the optical density of the solutions at 620 nm against a blank.
- Prepare a standard curve of absorbance against glucose concentration.
- Determine the amount of glucose in the unknown sample by plotting a standard curve of A620 on the Y-axis and concentration of Glucose on the X-axis.
Result and Interpretation of Anthrone Test
- The presence of a blue-green complex indicates the presence of carbohydrates in the given solution.
- From the graph, we can determine the concentration of unknown samples.
Uses of Anthrone Test
- Anthrone test is used for the detection and quantification of carbohydrates in various samples like blood serum, milk, and its variation, etc.
Limitations of Anthrone Test
- Anthrone test gives a negative result in samples that are carbohydrates like D-glucose phenylosazone and D-glucose phenylosotriaole but do not form furfural or hydroxyfurfural in the dehydration step.
References and Sources
- Am.(1950) Limitations of the Anthrone Test for Carbohydrates. Chem. Soc. 72. 8. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01164a521.
- Tiwari A. (2015). Practical Biochemistry. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
- 2% – https://allmedicalstuff.com/molischs-test/
- 2% – http://www.jbc.org/content/208/1/55.full.pdf
- 13% – https://www.iitg.ac.in/biotech/MTechLabProtocols/Carbohydrate%20estimation%20by%20Anthrone.pdf
- 1% – https://www.chem.purdue.edu/courses/chm224/Lab-Experiments/Experiment6_plus%20apparatus.pdf
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_curve
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Molisch%27s_test
- 1% – http://www.bcc.bas.bg/BCC_Volumes/Volume_48_Number_1_2016/BCC-48-1-2016-3863-X-li%20%20Wang-109-113.pdf

C’est intéressant comme document, mais est ce qu’on peut avoir la procédure pour les moustiques svp
More anthrone advantage and disadvantage
Thanks!
Very helpful document indeed
Very helpful document