Zoonotic diseases, or zoonoses, are infections that can be transmitted from animals (vertebrates) to humans or vice versa.
- Around 61% of the emerging human diseases are zoonotic, of which 70% originate from wildlife species.
- Zoonoses is derived from the Greek word “zoon”, meaning animal, and “nosos”, meaning illness.
- About a century ago, zoonotic diseases such as bubonic plague, bovine tuberculosis, and glanders caused millions of deaths before the establishment of hygiene protocols.
- Zoonoses become more prominent with environmental instability, which causes epidemics and pandemics.
- The transmission of pathogens from humans to animals is termed ‘reverse zoonosis’.
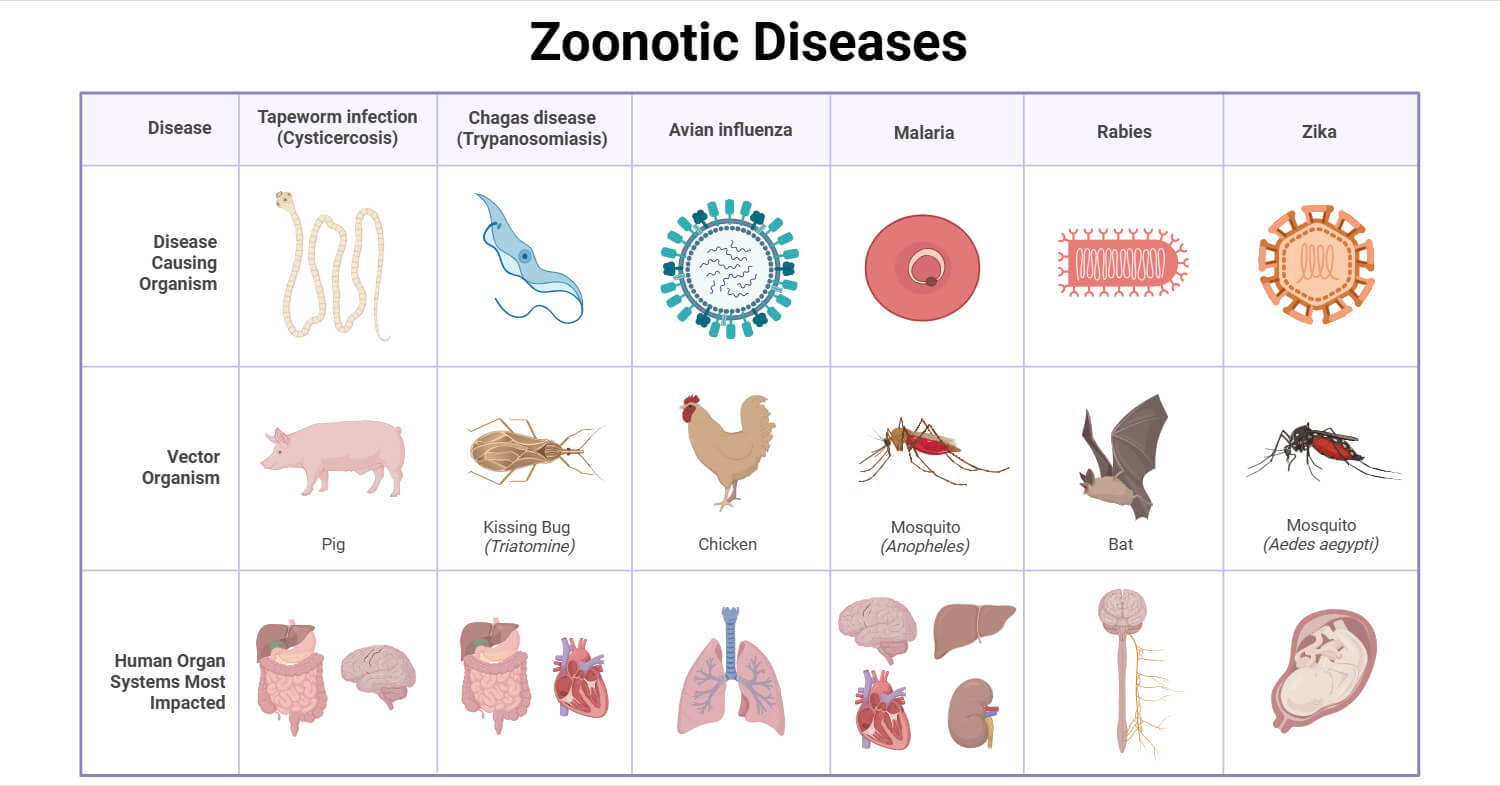
Classification of Zoonotic Diseases
Zoonotic pathogens are classified based on their etiology into bacterial zoonoses, viral zoonoses, fungal zoonoses, parasitic zoonoses, protozoal zoonoses, and mycoplasma zoonoses.
Bacterial Zoonoses
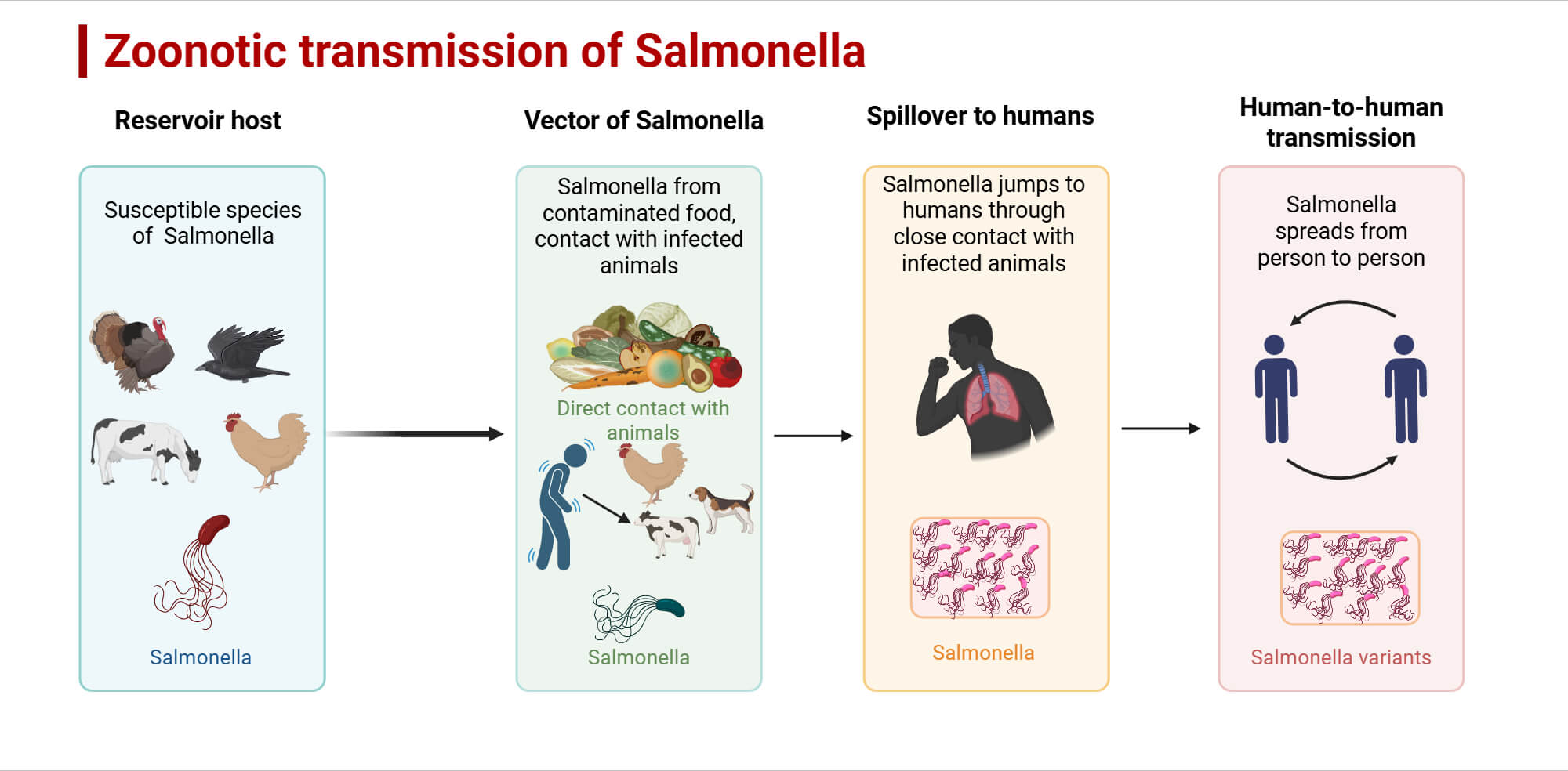
Bacterial zoonoses such as tuberculosis, anthrax, Salmonella, etc., release toxins which can be detrimental to humans. Both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria are known to cause zoonotic infections. They particularly re-emerge after eradication or control. Moreover, the excessive use of antibiotics has made it difficult to treat such bacterial pathogens.
Fungal Zoonoses
Fungal zoonoses or saprozoic transmission are considered to be a worldwide public health concern. They do not get much attention as bacterial or viral zoonoses, but they can be transferred through spores, proliferating on skin, subcutaneous membrane, lymph nodes or bone.
Viral Zoonoses
Viral zoonoses are caused by a wide range of virus families. They can be unapparent or fatal to humans. They usually replicate rapidly, mutating and adapting to the existing host environment.
Parasitic Zoonoses
Parasitic zoonoses are worms, protozoa, arthropods, and helminths that are transmitted between vertebrates and humans.
Protozoal Zoonoses
Protozoal zoonoses are caused by parasitic zoonoses, which infect host organisms, causing no symptoms until it transmits to humans.
| Disease | Etiology | Animal Host | Major Symptoms |
| Bacterial Zoonoses | |||
| Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium bovis | Sheep, cattle, boar, camels | Respiratory organs bone marrow |
| Salmonella | Salmonella enterica | Domestic animals, birds, and dogs | Enteritis |
| Bubonic Plague | Yersina pestis | Wood rats, rock squirrels, ground squirrels, chipmunks, rabbits, etc. | Fever, diarrhea, vomiting, and bleeding from the natural opening |
| Anthrax | Bacillus anthracis | Cattle, horses, pigs, dogs, goats, etc. | Skin, respiratory organs, or GI tract |
| Fungal Zoonoses | |||
| Ringworm infection | Microsporum spp. | Cattle, cats, and dogs | Skin lesions |
| Aspergillosis | Aspergillus spp. | Domestic animals and birds | Respiratory problems |
| Cryptococcosis | Cryptococcus neoformis | Cattle, dogs, cats, birds, horses, and wild animals | Meningitis, fever, cough, nausea photophobia |
| Histoplasmosis | Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum | Dogs, cats, rabbits, and rats | Fever, chest pain, weight loss (normally asymptomatic) |
| Viral Zoonoses | |||
| Rabies | Rabies virus | Cattle, horses, cats, bats, monkeys, dogs, wolves, etc. | Nervous system |
| Avian influenza | Influenza A virus | Chickens, ducks, dogs, cats, pigs, wild birds, etc. | Flu-like symptoms, pneumonia, diarrhea |
| Dengue virus | Dengue virus | Dogs and monkeys | High fever, skin rash, shock, hemorrhage |
| Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) | Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) | Monkeys and chimpanzees | Immunosuppression, fever, night sweats, fatigue, swollen lymph nodes |
| Parasitic Zoonoses | |||
| Trichinellosis | Trichinella spp. | Pigs, dogs, cats, rats, wild species | Vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Hyadatidosis | Echinococcus granulosus | Buffaloes, sheep, goats, adult and stray dogs | Hydatid cysts in the liver, lungs, bones, kidneys spleen |
| Fascioliasis | Fasciola hepatica, F. gigantica | Cattles | Intense internal bleeding, fever nausea, swollen liver, skin rashes |
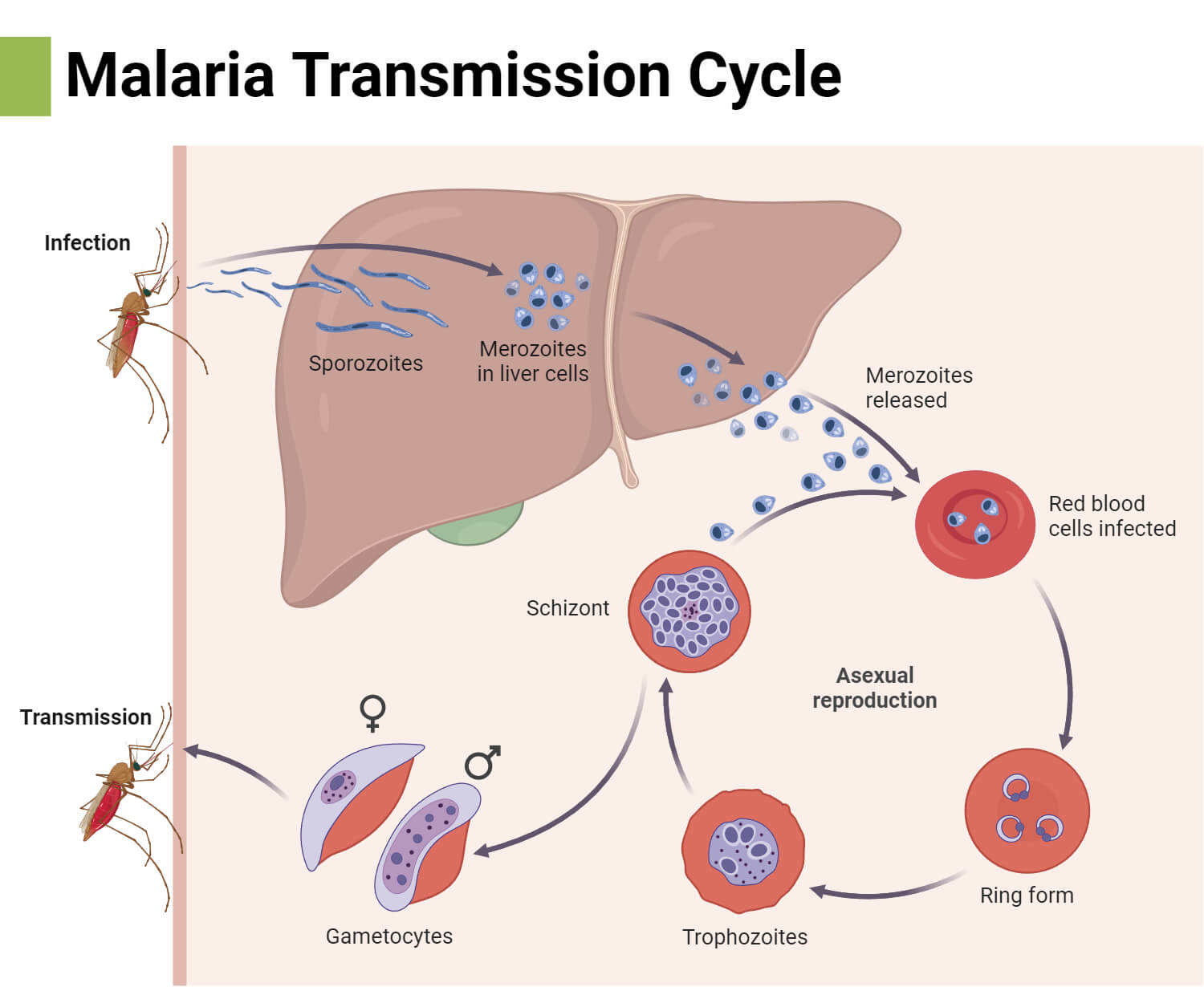
| Malaria | Plasmodium | Female Anopheles mosquito | Fever, headache, chills, fatigue, confusion, seizures, breathing difficulties. |
| Protozoal Zoonoses | |||
| Leishmaniasis | Leishmania infantum | Cats, dogs, horses, and bats | Skin lesions, hepatosplenomegaly |
| Giardiasis | Giardia lamblia | Ruminants, cats, dogs, and pigs | Diarrhea, malaise, abdominal cramping, anorexia |
| Toxoplasmosis | Toxoplasma gondii | Poultry, pigs, goats, sheep | Lymphadenopathy, fever, sore throat, malaise, night sweats, myalgia |
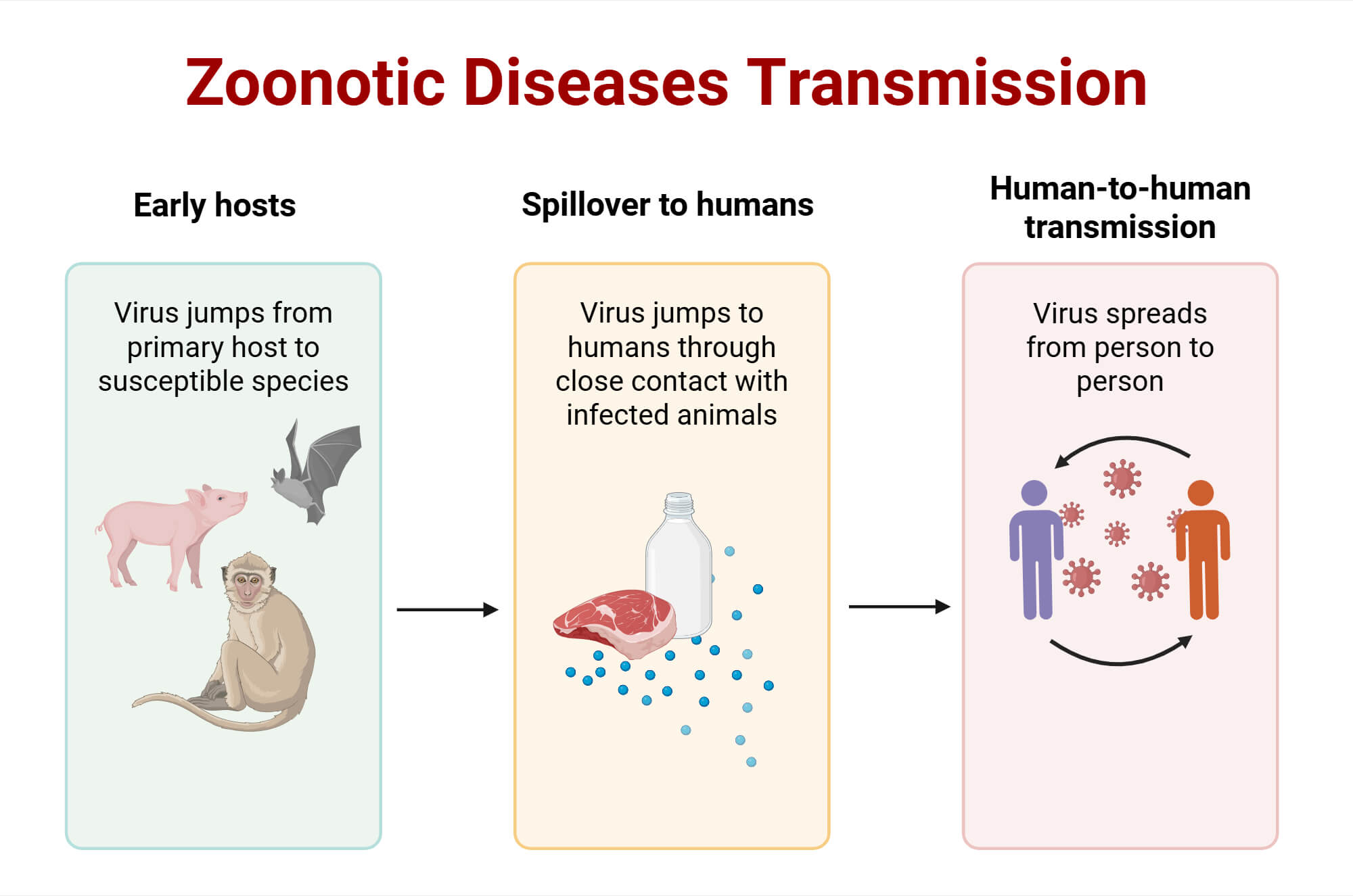
Causes of Zoonotic Diseases
- Infected animals, such as bats, dogs, cats, cattle, birds, and wild animals, carry zoonotic pathogens.
- The pathogens are then released through animal excretion, slaughter, or can even be vector-borne, such as malaria, dengue fever, etc.
- Once the pathogen is released, it must survive and move until it disseminates and eventually meets another host, usually humans.
- Therefore, zoonotic transmission occurs when an individual comes in contact with an infected animal, consumes animal products, or their derivatives. This has become more prominent because of the domestication of animals.
- Zoonotic transmission can happen in two ways: direct transmission and indirect transmission in a process known as a ‘spillover event’.
- Direct transmission to humans from an infected animal is rare. It can happen from hunting, consumption, and wildlife trading of infected animals.
- Indirect transmission or bridging host exposure occurs when an intermediate animal is infected from the original host animal and then transfers it to humans.
Factors Affecting Zoonotic Infection
- Host immunity: The intensity of infection depends on the immunity of the reservoir host. Animals with resistance can be immune or asymptomatic. Likewise, the transmission to humans is also determined by the defenses in the immune system. Immunocompromised individuals, pregnant women, children younger than 5, and older people are more prone to infections by opportunistic pathogens.
- Environmental factors: The environmental factors, such as rising temperature, rising sea level, decreased Arctic and Alpine snow and ice, have forced living organisms to move to higher altitudes and closer to the Earth’s poles. This affects the migration of bats, birds, insects, and such, which can potentially promote transmission of zoonotic diseases. Pathogens that were not seen in one part of the globe are slowly emerging for this reason.
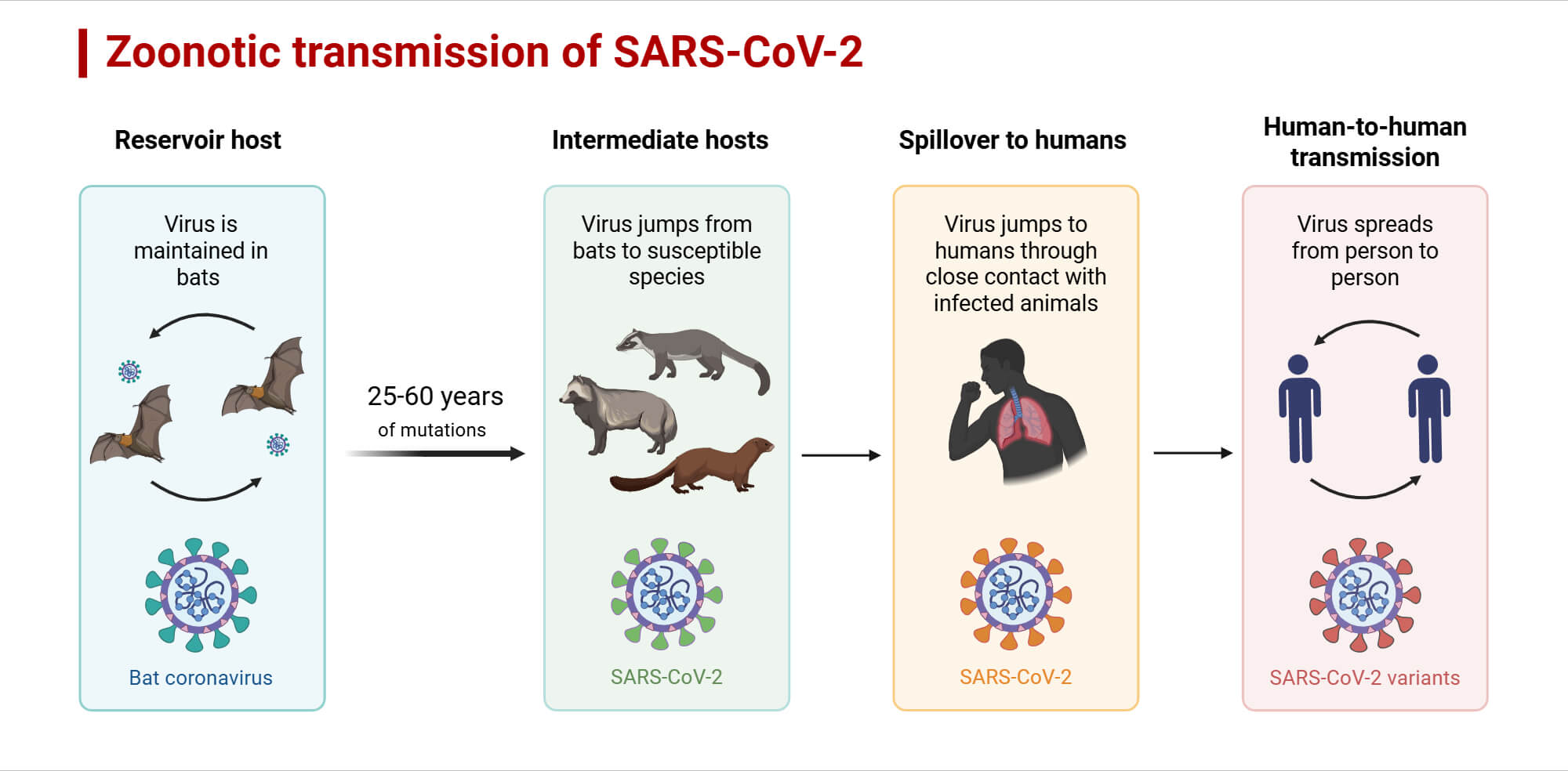
- Antigenic mutation: The antigenic mutation plays a significant role in the transmission of pathogens from one host species to another. To elaborate, coronaviruses such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) are known for their Spike (S) protein, which binds to DPP4 receptor in bats and primates, but not to ferrets and rodents because of 5 amino acid differences in its receptor.
- Spillover event: Spillover depends primarily on the host and its physiological habits, and the environmental changes. When stress is given to the host organism through environmental cues such as low food availability, climate change, and habitat loss, the hosts become increasingly more in contact with humans, which promotes unwanted spillover.
- Animal workers: People who are more in contact with animals, such as wildlife workers, hunters, butchers, veterinary, etc., are more prone to zoonotic infections.
Prevention of Zoonotic Diseases
- Proper sanitary practices: Washing your hands with clean, detergent soap and running water can stop the spread of germs.
- Vector control: Applying repellents, wearing long trousers and sleeves, and cleaning stagnant water areas can prevent vector-borne diseases such as malaria, dengue, yellow fever, etc. by largely stopping insect bites from mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas.
- Maintaining kitchen hygiene: Infections such as Salmonella can be prevented by preparing healthy food, ensuring hygiene by cleaning kitchenware, dishes, and pots. Salmonella infection can occur via eating raw eggs as well, which should be prevented.
- Safe dairy food products: Consumption of raw milk and milk products has a zoonotic risk; therefore, pasteurization and boiling are crucial to for potential infection.
- Domestication of animals: Domesticated animals such as pets and cattle should be regularly monitored and taken to the vet. Vaccines should be applied to pets before adopting them. They should be regularly cleaned and checked for changes in behavior.
- Vaccines: Vaccines are necessary for proper safety and wide prevention of the pathogen. This is especially true to prevent any kind of infection. Infants should be given all of the vaccines advised by the government. Likewise, adults should take available vaccines.
- Research: Proper research is essential before travelling to be aware of various zoonotic diseases.
Treatment of Zoonotic Diseases
- The treatment of zoonotic diseases depends on the pathogen. There are no specific medications for zoonotic pathogens, however, treatment might include:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotic intervention during the early stage of infection can eliminate bacterial zoonoses.
- Antifungals: Fungal zoonoses can be treated through antifungal creams or lotions.
- Antivirals: Antiviral medications assist in fighting against certain viral pathogens.
- Antiparasitic medications: Parasites can mostly be treated by the incorporation of antiparasitic medications.
- Surgery: Few pathogens are responsible for the development of cysts, which can be removed through surgery.
- Monoclonal antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies can be specifically engineered against specific pathogens for extremely hard-to-treat zoonotic diseases.
References
- Adebiyi, A. I., & and Oluwayelu, D. O. (2018). Zoonotic fungal diseases and animal ownership in Nigeria. Alexandria Journal of Medicine, 54(4), 397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2017.11.007
- Cantas, L., & Suer, K. (2014). Review: The Important Bacterial Zoonoses in “One Health” Concept. Frontiers in Public Health, 2, 144. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2014.00144
- CDC. (2024, May 16). About Zoonotic Diseases. One Health. https://www.cdc.gov/one-health/about/about-zoonotic-diseases.html
- Environmental Metamorphosis and Surging Zoonotic Diseases. (2020, June 8). Diplomatist. https://diplomatist.com/2020/06/08/environmental-metamorphosis-and-surging-zoonotic-diseases/
- Gérald, L. (2020, December 1). Chauves-souris et virus ou comment cohabiter en harmonie. Encyclopédie de l’environnement. https://www.encyclopedie-environnement.org/vivant/chauves-souris-virus-comment-cohabiter-en-harmonie/
- History’s Seven Deadliest Plagues. (n.d.). Retrieved March 30, 2025, from https://www.gavi.org/vaccineswork/historys-seven-deadliest-plagues
- Rahman, M. T., Sobur, M. A., Islam, M. S., Ievy, S., Hossain, M. J., El Zowalaty, M. E., Rahman, A. T., & Ashour, H. M. (2020). Zoonotic Diseases: Etiology, Impact, and Control. Microorganisms, 8(9), Article 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091405
- Zoonotic Diseases. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved March 28, 2025, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/zoonotic-diseases
