- Yeasts are unicellular eukaryotes and extensively studied model organism in molecular genetics.
- They are chemoorganotrophs as they utilize organic compounds as a source of energy.
- Yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD or YEPD) Growth Agar is used for the maintenance and propagation of yeasts including S. cerevisiae in various molecular microbiology procedures.
- YPD functions as a complete medium for yeast growth.
Interesting Science Videos
Composition of YEPD Agar
| Ingredients | Gms/liter |
| Peptone | 20.000 |
| Yeast extract | 10.000 |
| Dextrose | 20.000 |
| Agar | 15.000 |
Final pH (at 25°C): 6.5±0.2
Principle of YEPD Agar
- YEPD consists of yeast extract, peptone, and glucose or dextrose.
- Yeasts grow well on a minimal medium containing only dextrose and salts.
- The addition of protein and yeast cell extract hydrolysates allows faster growth so that during exponential or log-phase growth.
- Yeast extract supplies B-complex vitamins and it contains all the amino acids necessary for growth.
- Peptone acts as the source of nitrogen, vitamins, and minerals.
- Dextrose serves as the carbon source.
- This medium supports the vigorous growth of wild type as well as mutant strains of all kinds of budding yeast.
Preparation of YEPD Agar
- Suspend 65 grams of the powder in 1 liter of purified water.
- Mix thoroughly.
- Heat the agar medium with frequent agitation and boil for 1 minute to completely dissolve the powder.
- Autoclave the agar and broth media at 121°C for 15 minutes.
- Cool to 45-50ºC.
- Portion equally into Petri plates.
Result Interpretation on YEPD Agar
| Organisms | Growth |
| Kluyveromyces lactis | Luxuriant growth |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Luxuriant growth; smooth, moist, glistening colonies |
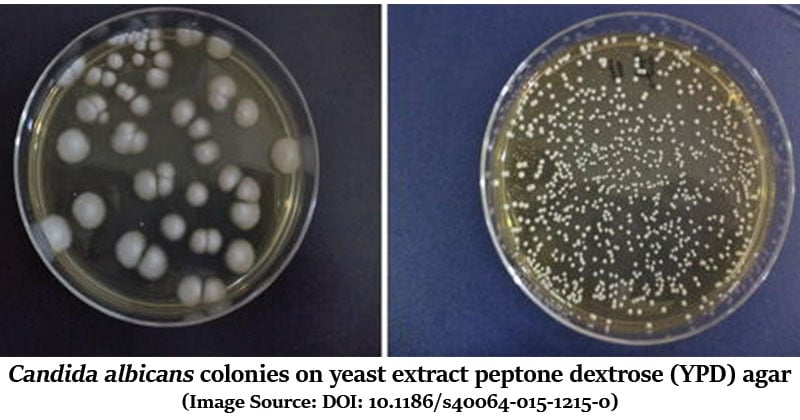
| Candida albicans | Luxuriant growth |
Uses of YEPD Agar
- YEPD is used as a growth medium to grow yeast cultures.
- It is used for the growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- This medium supports the growth of most heterotrophic microorganisms but due to their simple composition, they have been adopted as the basal media for the routine cultivation of yeasts.
- It is used for preparing culture media in molecular microbiology procedures.
Limitations of YEPD Agar
- It is a non-selective medium.
- By being a complete medium, YEPD cannot be used as a selection medium to test for auxotrophs.
References
- http://himedialabs.com/TD/ECG038CCL.pdf
- https://www.bd.com/europe/regulatory/Assets/IFU/Difco_BBL/242820.pdf
- http://himedialabs.com/TD/M1363.pdf
- http://cshprotocols.cshlp.org/content/2017/8/pdb.rec090563.full?text_only=true
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/y1500?lang=en®ion=US
- http://west2.amazonaws.com/owwfilespublic/8/88/DahlquistLab_YEPDliquidmedia.pdf
- https://www.fishersci.com/shop/products/bd-difco-dehydrated-culture-media-ypd-agar-2/p-4901518
