Interesting Science Videos
What is Widal Test?
Widal test is an agglutination test used for diagnosis of enteric fever (Typhoidal or Paratyphoidal fever) serologically in clinical/diagnostic laboratories. This tests measure agglutinating serum antibodies level produced against the O (somatic) and H (flagellar) antigen of Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi A, B, and C.
This test is widely used throughout the world as a major diagnostic tool for detecting enteric fever.
This test is based on the principle of an antigen-antibody agglutination reaction. Purified antigens of Salmonella causing enteric fevers are commercially available. The patient’s serum is tested against these commercial antigens and observed for visible agglutination reaction. If the serum agglutinates, the test is considered positive.
Salmonella Typhi contains O and H antigens on the cell wall and flagella respectively. Salmonella Paratyphi A and Paratyphi B contain AH and BH antigens on flagella respectively.
O antigen of Salmonella Paratyphi is not used because they cross-react with O antigens of Salmonella Typhi.
These antigens are immunogenic and when introduces to on host’s immune system, they induce the production of specific antibodies. Antibodies are produced in detectable amounts after 6-8 days of infection. These specific antibodies are tested in the Widal test following the principle of an agglutination reaction.
This test was introduced in 1896 by a French physician and bacteriologist Georges Fernand Isidor Widal (March 9, 1862, to January 14, 1929).
He originally described this test to diagnose Salmonella Paratyphi B infection. Later it was modified and used to diagnose all types of enteric fevers.
Widal Test Objectives
The objective of the Widal test is to detect the presence of serum antibodies Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi to diagnose enteric fever.
Widal Test Principle
Widal Test is based on the principle of antigen-antibody reaction of agglutination type. It can be stated as, when a homologous antibody reacts with a specific insoluble antigen, which induced its production, in presence of a specific electrolyte and at optimum temperature and pH, a visible clumping is formed.
Similarly in the case of the Widal test, when the antibodies in serum against O and H antigens of Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi react with insoluble O and H antigens present in the test reagent, then a visible clumping reaction (agglutination) occurs.
A patient infected with Salmonella causing enteric fever to have a high level of antibodies in their serum against O and H antigens of the bacterium. Antibodies levels against these antigens will reach a peak after 6-8 days of infection. The serum is extracted from the blood of the suspected patient and allowed to react with specifically prepared O and H antigens of Salmonella Typhi, and AH and BH antigens of Salmonella Paratyphi. If antibodies are present in serum, they specifically agglutinate the antigens and produce visible clumping.
Widal Test Requirements
- Blood sample of suspected patient or serum
- Widal test kit containing Salmonella antigens
- O-antigen of Salmonella Typhi
- H-antigen of Salmonella Typhi
- AH-antigen of Salmonella Paratyphi A
- BH-antigen of Salmonella Paratyphi B
- Positive control
- Widal test card (glass slide can be used in substitution of card)
- Applicator stick
Widal Test Procedures
Widal test is done by two methods; rapid slide agglutination method, and tube agglutination method. Slide agglutination may be either a qualitative or quantitative test. The tube method is more sensitive and accurate, but the slide agglutination method is widely used.
Preparation of Widal Antigens
Antigens can be prepared in the lab using a pure culture of Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi A and B. However, commercially available kits are used in most laboratories.
- For preparing H-antigens overnight broth culture of Salmonella is treated with 0.1% formalin solution
- For preparing O-antigens, Salmonella grown freshly on phenol agar is emulsified in a small volume of normal. 1 ml of the suspension is mixed with 20 ml of ethanol (absolute) and heated at 400 to 500 C and centrifuged.
- The antigens are treated with a preservative (chloroform) and stained with suitable dye.
Rapid Slide Agglutination Test
This test is performed on the Widal test card. This is the most widely performed test and is of two types, viz;
Qualitative Slide Test
This test is done to detect the presence or absence of antigens of Salmonella causing enteric fever. It is a simple and quick method, but we can’t measure antigen levels. It is performed in the following steps:
- Place a drop of sample serum in each reaction circle of the Widal test card labeled as O, H, AH, and BH.
- Place a drop of positive control reagent in reaction circle labeled as PC
- Place a drop of negative control reagent in reaction circle labeled as NC
- Add one-one drop of antigen solution H from the Widal test kit over positive control and negative control
- Add a drop each of antigen solution O, H, AH, and BH over sample serum in their respective reaction circle
- Mix the serum and antigen solution in each reaction circle uniformly using an applicator stick
- Rock the slide gently to rotate the reaction mixture in a circular motion within reaction circles
- Observe for macroscopic agglutination within a minute.
Quantitative (Semi-quantitative) Slide Test
This test is performed to measure the level of antigens present in the serum sample. This is only performed if the qualitative test is positive. It is performed in the following steps:
- Place a drop of normal saline into the first reaction circle
- Place 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 μl of the test sample (serum) in the remaining reaction circle respectively
- Add a drop of antigen suspension which showed positive test (i.e. agglutination) in the qualitative test in each of the reaction circles
- Mix the contents uniformly using applicator stick
- Rock the slide gently to rotate the reaction mixture in circular motion within reaction circles
- Observe for macroscopic agglutination within a minute.
Tube Agglutination Test (Quantitative Tube Test)
This test is performed in glass tubes. Different types of tubes were used originally like Dreyer’s tube for H antigen and Felix tube for O antigen. In modern test methods, Kahn tube or simple test tubes are used widely. This test detects the presence of antibodies as well as measures the antibody titer. The test is performed in the following steps:
- Arrange 4 sets of clean dry Khan Tube each set with 8 tubes labeled as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8.
- Add 1.9 ml of isotonic (0.85%) sterile saline solution in tube 1 of each set
- Add 1.0 ml of isotonic sterile saline in remaining tubes (2 – 8) of each set
- Add 0.1 ml of sample serum in tube 1 of each set and mix properly
- From tube 1 of each set, transfer 1.0 ml of diluted serum to each tube 2 of their respective set.
- From tube 2 of each set, transfer 1.0 ml of diluted serum to each tube 3 of their respective set.
- Continue this serial dilution process up to tube 7 of each set. From tube 7 of each set, discard 1.0 ml of dilution. (Never transfer to tube 8).
- Add 1 drop of Widal antigen-O in each tube of set 1, 1 drop of Widal antigen-H in each tube of set 2, 1 drop of Widal antigen-AH in each tube of set 3, and 1 drop of Widal antigen-BH in each tube of set 4.
- Mix the reaction mixture properly, cover the tubes and incubate at 370C for about 18 hours (overnight)
- Following incubation look for agglutination at the bottom of the tubes.
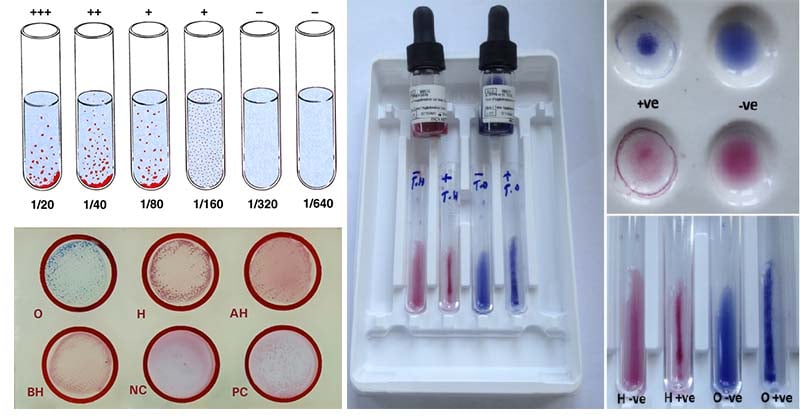
Widal Test Result Interpretation
Qualitative Slide Test Results
- Positive test (presence of Salmonella antigen) = Agglutination within a minute
- Negative test (absence of Salmonella antigen) = No agglutination
Quantitative (Semi-quantitative) Slide Test Results
The antibody titer of test serum is read as the highest serum dilution that gives a positive reaction (visible agglutination). Antibody titer greater than 1:80 is considered significant. The titer can be read accordingly to the table below;
| Reaction Circle | Volume of Serum | Antibody Titer |
| 2nd | 5μl | 1:320 |
| 3rd | 10 μl | 1:160 |
| 4th | 20 μl | 1:80 |
| 5th | 40 μl | 1:40 |
| 6th | 80 μl | 1:20 |
Tube Agglutination Test (Quantitative Tube Test) Results
The antibody titer is read as the highest serum dilution that gives a positive reaction (visible agglutination). Antibody titer greater than 1:80 is considered significant. The titer can be read accordingly to the table below;
| Tube Number | Antibody Titer |
| 1 | 1:20 |
| 2 | 1:40 |
| 3 | 1:80 |
| 4 | 1:160 |
| 5 | 1:320 |
| 6 | 1:640 |
| 7 | 1:1280 |
| 8 | Negative control |
Widal Test Applications
- Used for rapid diagnosis of enteric fever
- Used to identify serovar (Typhi, Paratyphi A, and Paratyphi B) of Salmonella causing enteric fever
Widal Test Limitations
- False-positive result in the vaccinated or previously infected person.
- Agglutinin appears in serum only after 6-8 days of infection and persists up to the 4th week of infection. So, the Widal test has low sensitivity and efficiency when tested before 1st week and after 4th week of infection.
- Considered a presumptive test, so need further investigations to confirm an enteric fever
- Cross-reactivity with antibody produced against typhus, malarial parasites, and non-enteric Salmonella infection.
- Quantitative tube tests require a longer time.
- Treatment with antibiotics reduces antibody responses. Similarly, the immune disorder may cause a low level of antibody production. These will give false-negative results.
- Agglutinin titer level for clinical significance is different in different places and is also differs from person to person.
References
- Kenneth E.Sanderson, Shu-LinLiu1, LeTang and Randal N.Johnston.(2015).Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi A. Molecular Medical Microbiology (2 eds.). (2):1275-1306.
- Song JH, Park M, Na DS, Moon HB, Pai CH. Detection of Salmonella typhi in the blood of patients with typhoid fever by PCR. J Clin Microbiol 1993;31:1439-1443.
- Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, White NJ, Farrar JJ. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002 (347); 22:1770-1782.
- Cheesbrough, M. (2005). District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries, Part 2.Cambridge University Press, 2000. Page 185.
- Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2022, January 10). Fernand-Isidore Widal. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Fernand-Isidore-Widal
- Acharya et. al. Baseline Widal Agglutination Titre in Apparently Healthy Nepalese Blood Donors. JHAS, 2013, Vol. 3, No. 1 P 27-30
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/widal-test-introduction-principle-procedure-interpretation-and-limitation/
- http://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/widal-test-introduction-principle-procedure-result-interpretation-applications-and-limitations/
- https://microbeonline.com/widal-test-principle-procedure-results/
- https://laboratoryinfo.com/widal-test-principle-procedure-result-interpretation-and-limitations

Thanks for the post, but I want to ask because I don’t understand this part, is the serum added to the positive and negative control? It’s kind of confusing to me.
Is a widal test with the following antigen positive?
H: 110,112,110,110
O: 110,110,110,110
Reaction Circle Volume of Serum Antibody Titer
2nd 5μl 1:320
3rd 10 μl 1:160
4th 20 μl 1:80
5th 40 μl 1:40
6th 80 μl 1:20 how prove given titre ? Sir
How I can get PDF of this?
Sorry to say that there is no PDF of this.
I’d like to thank you for efforts you made
just i wanna ask if any one could give me a hand in interpreting the results of that test if the titre of O antigen was less than 1/40 ( Negative) and H antigen was 1/160 (Positive) could we say it due post infection or due immunization against S.typhi ?
there more thing i think there’s a problem in this figure (https://163602-560839-raikfcquaxqncofqfm.stackpathdns.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Result-Interpretation-of-Widal-Test.jpg) , i think the tubes arrange is inverted !
Thanx Alot Dr 🙂
It really helpful ,keep updating us also on sign and symptom
Very helpful information on Widal, Kindly include reliable tests available for diagnosis of entric fevers like PCR… Tq so much
these notes are really helpful for us… can i get the PDF of these notes???
👌👌👌👌👌👌👌👌👌👌