Medical Disclaimer: The information presented on the website is only for academic and study purposes and must not be used for the purpose of treatment. If you are not feeling well, please consult with your physician or doctor.
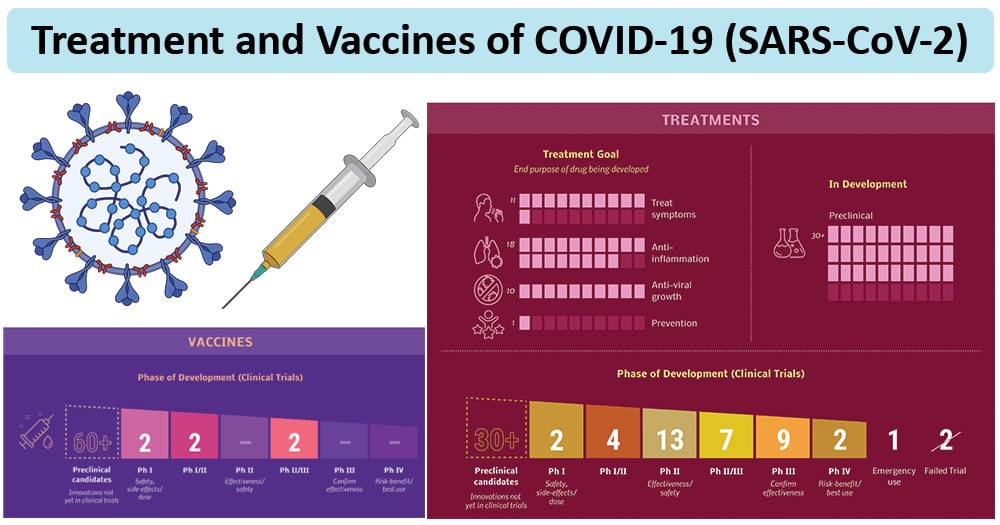
Image Source: Biorender and ARTIS Ventures
Interesting Science Videos
Current Therapies of COVID-19
- Currently, no specific antiviral treatment has been confirmed to be effective against COVID-19.
- Regarding patients infected with COVID-19, it has been recommended to apply appropriate symptomatic treatment and supportive care.
- Many of the patients have accepted oxygen therapy, and the WHO has recommended extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) to patients with refractory hypoxemia.
- Rescue treatment involving convalescent plasma and immunoglobulin G are also delivered to some critical cases according to their conditions.
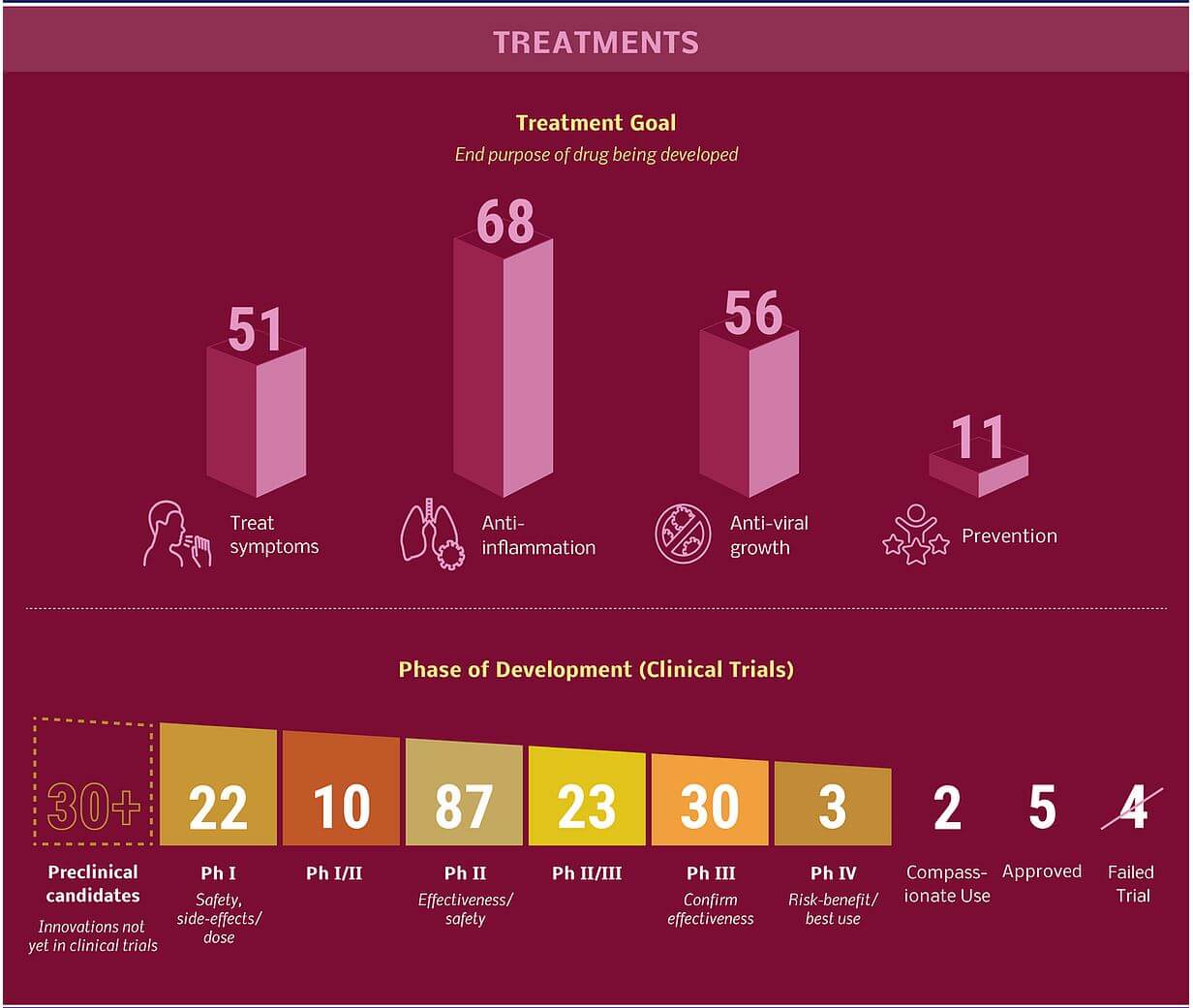
Image Source: ARTIS Ventures
Treatments options for COVID-19
- The only option available is using broad-spectrum antiviral drugs like Nucleoside analogs and also HIV-protease inhibitors that could alleviate virus infection until the specific antiviral becomes available.
- Furthermore, several other compounds are in development.
- These include the clinical candidate EIDD-2801 compound that has shown high therapeutic potential against seasonal and pandemic influenza virus infections and this represents another potential drug to be considered for the treatment of COVID-19 infection.
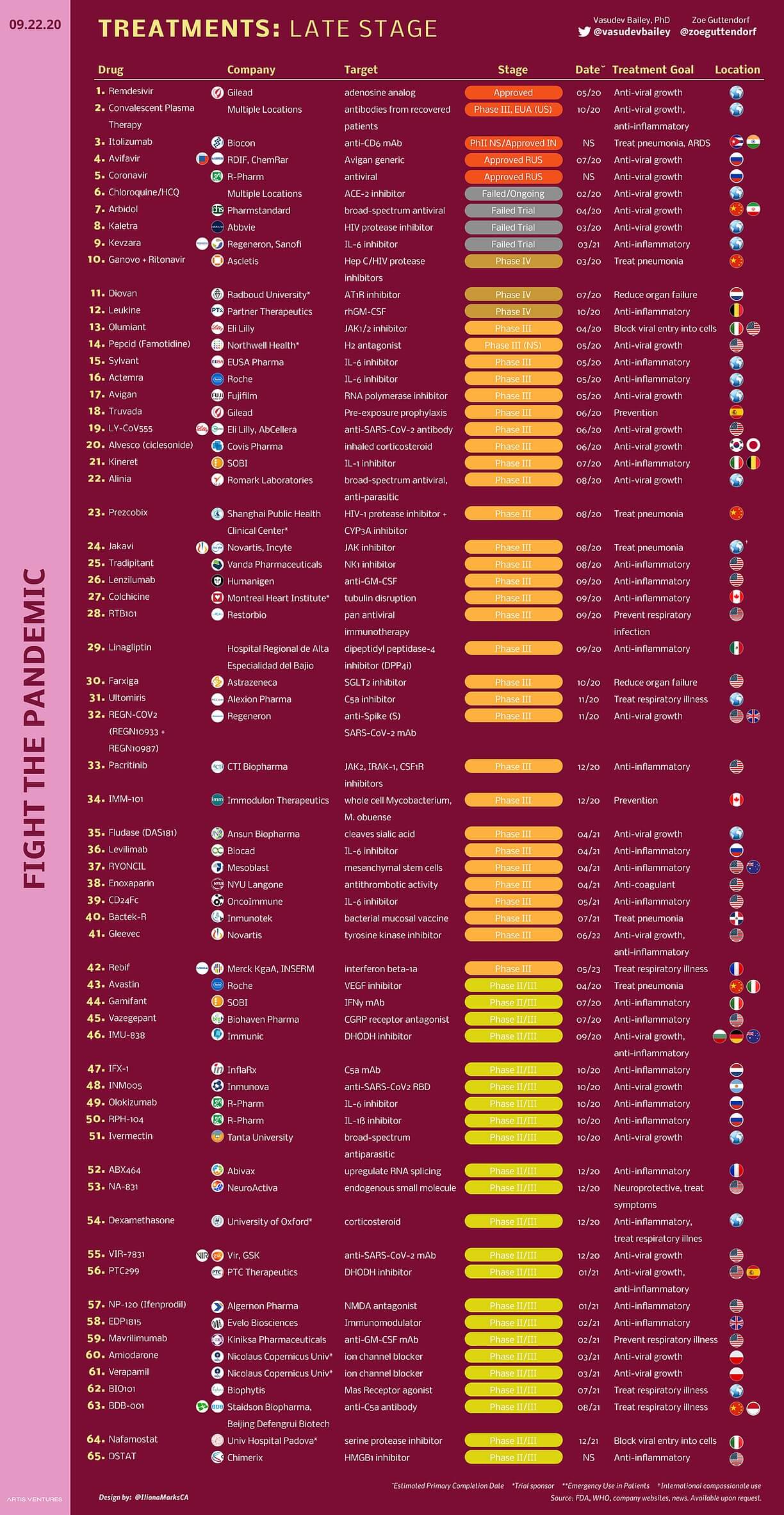
Image Source: ARTIS Ventures
Remdesivir
- Remdesivir has been reported to be used for the treatment of a few cases of COVID-19 successfully.
- Remdesivir is a 1′-cyano-substituted adenosine nucleotide analog prodrug and shows broad-spectrum antiviral activity against several RNA viruses.
Chloroquine (Hydroxychloroquine)
- Chloroquine (Hydroxychloroquine) is another repurposed drug that shows great potential for the treatment of COVID-19.
- Chloroquine has been in use for many years for the treatment of malaria, with a mechanism not well understood against some viral infections.
- It has been assumed that chloroquine can inhibit pH-dependent steps of the replication of several viruses, with a potent effect on infection and the spread of SARS-CoV-2.
- Moreover, chloroquine has immunomodulatory effects, suppressing the production/release of TNF-α and IL-6 and also works as a novel class of autophagy inhibitor, which may interfere with viral infection and replication.
- Several studies have found that chloroquine interfered with the glycosylation of cellular receptors of SARS-CoV and functioned at both entry and post-entry stages of the COVID-19 infection in Vero E6 cells.
- A combination of remdesivir and chloroquine was proven to inhibit the recently emerged SARS-CoV-2 in vitro effectively.
- The protease inhibitors, lopinavir, and ritonavir used to treat the infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV patients have been reported to significantly reduce the β-coronavirus viral loads of COVID-19 patients after treatment with these drugs.
Update: FDA Revokes Emergency Use Authorization for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine
Ivermectin
- Ivermectin is an FDA-approved broad-spectrum anti-parasitic agent that has shown to have antiviral activity against a broad range of viruses in vitro.
- Ivermectin is an inhibitor of the causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) able to effect ∼a 5000-fold reduction in viral RNA at 48 hours.
- Ivermectin has been confirmed to inhibit nuclear import and HIV-1 replication.
- It has been shown to inhibit the nuclear import of host and viral proteins in many RNA viruses like dengue virus (DENV), West Nile Virus, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV).
- This broad-spectrum activity is believed to be due to the involvement of IMPα/β1 during infection in the case of many different RNA viruses.
- It has been assumed that ivermectin acts through inhibiting IMPα/β1-mediated nuclear import of viral proteins, as shown for other RNA viruses.
- The confirmation of this mechanism in the case of SARS-CoV-2 and the identification of the specific SARS-CoV-2 and host components impacted is yet to be done.
- Ivermectin has an established safety profile for human use, and is FDA-approved for several parasitic infections and thus is worthy of further consideration as a possible SARS-CoV-2 antiviral.
Vaccines Update for COVID-19
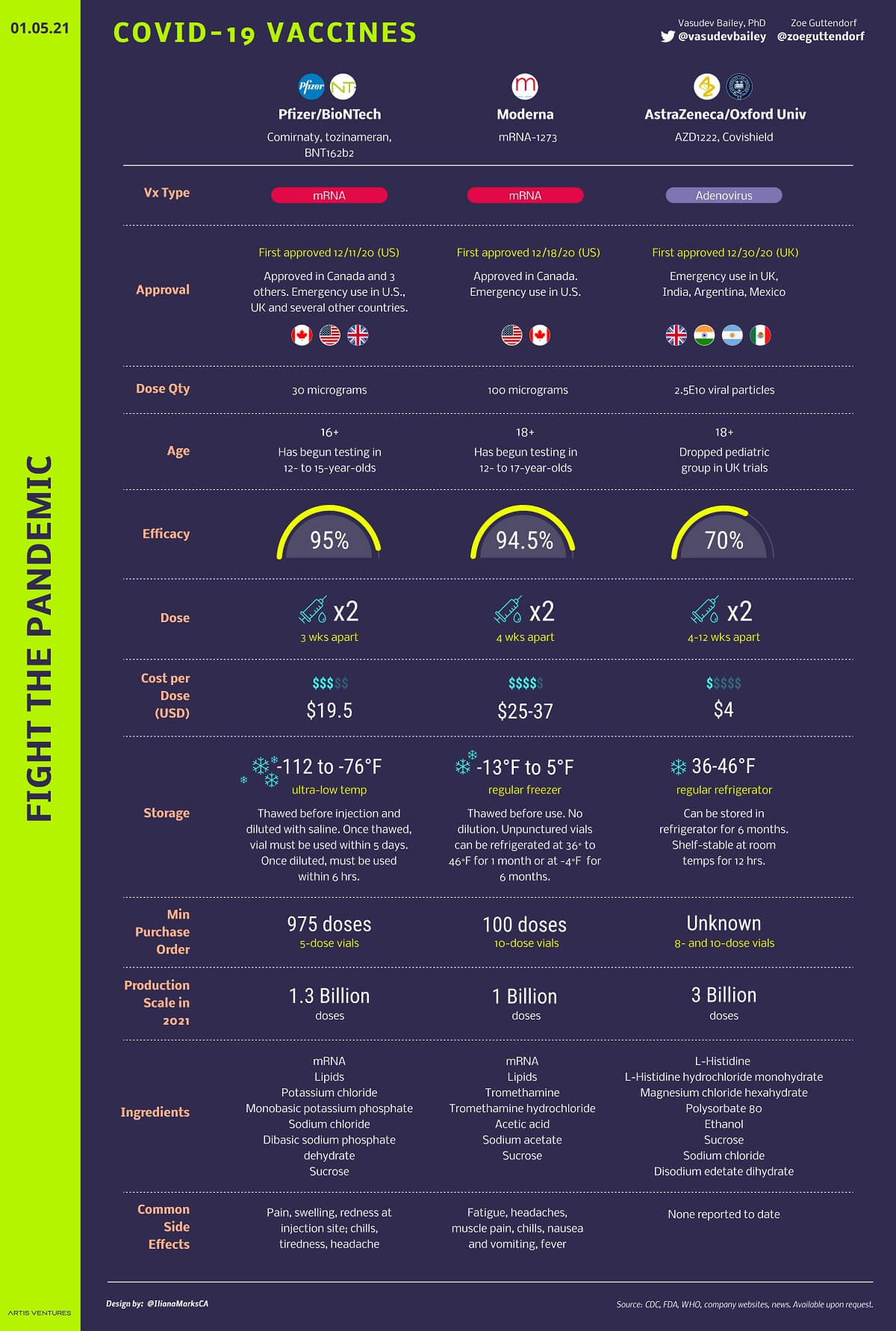
Image Source: ARTIS Ventures
- Currently, there is no vaccine available for this disease.
- However, as of April 6, 2020, there are 61 ongoing research efforts across the globe to develop a COVID-19 vaccine.
- Five vaccine candidates, for instance, have already started human testing in record timing.
- But it is believed to take at least a year to determine if any vaccine works against this virus.
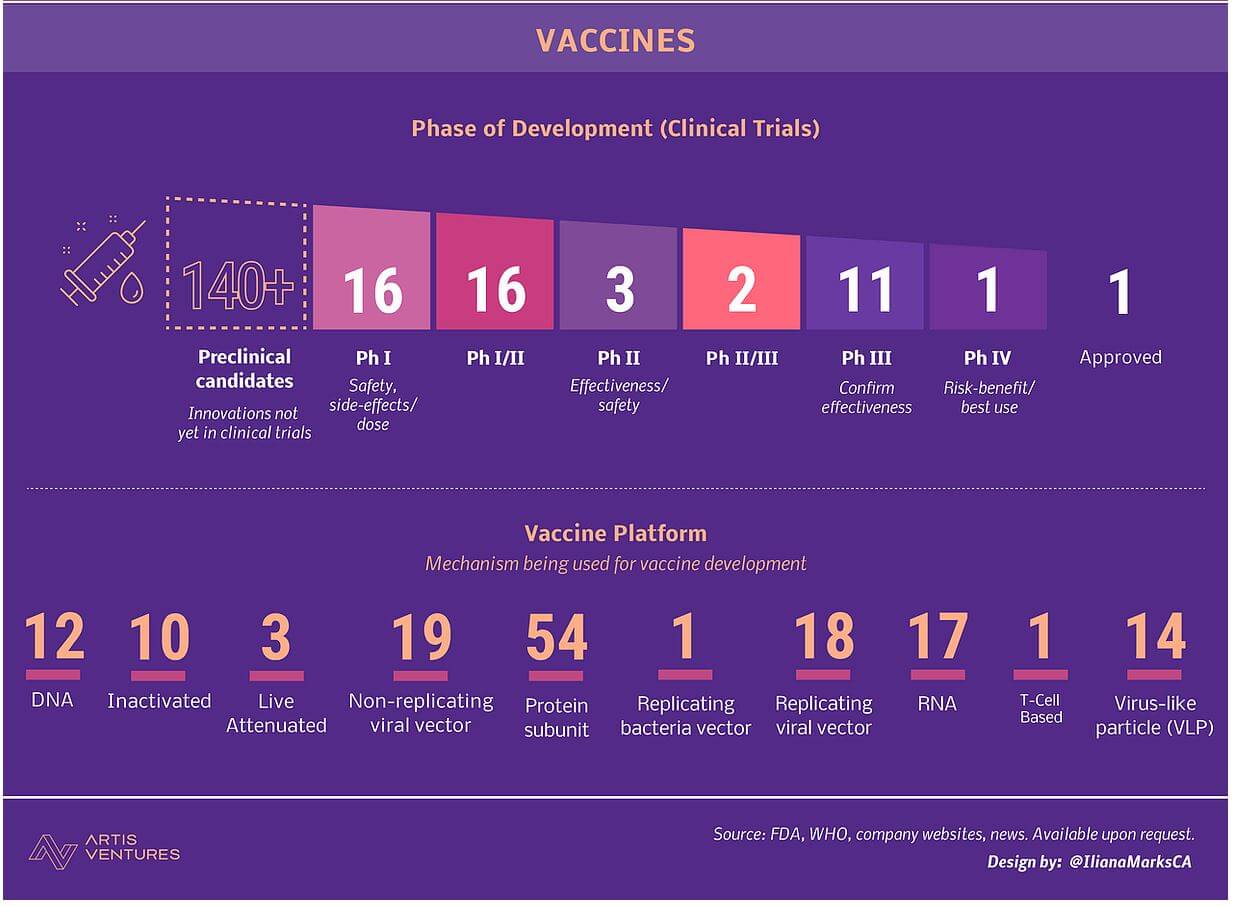
Image Source: ARTIS Ventures
References
- Caly L, Druce J, Catton M, Jans D and Wagstaff K. The FDA-approved Drug Ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Antiviral Research. 2020. 104787. ISSN 0166-3542, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166354220302011)
- Guo Y, Cae Q, Hong Z, et al. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak – an update on the status. Millitary Medical Reasearch. (2020) 7:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
- Rothan HA and Byrareddy SN. (2020). Journal of Autoimmunity, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433
- Adhikari et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infectious Diseases of Poverty. (2020) 9:29.
- Liu, C., Zhou, Q., Li, Y., Garner, L. V., Watkins, S. P., Carter, L. J., Smoot, J., Gregg, A. C., Daniels, A. D., Jervey, S., & Albaiu, D. (2020). Research and Development on Therapeutic Agents and Vaccines for COVID-19 and Related Human Coronavirus Diseases. ACS central science, 6(3), 315–331. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.0c00272
Sources
- 7% – https://mmrjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
- 4% – https://www.viewsbank.com/poll/covid-19-transmission-symptoms-therapeuticstreatment-options-and-other-useful-information
- 4% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0896841120300469
- 4% – https://www.businessinsider.com/coronavirus-vaccines-what-we-know-about-testing-and-availability-2020-4
- 4% – https://www.24hourcampfire.com/ubbthreads/ubbthreads.php/topics/14747129/the-fda-approved-drug-ivermectin-inhibits-the-replication-of-sars-cov-
- 3% – https://pharmafield.co.uk/pharma_news/study_shows_anti-parasitic_drug_ivermectin_kills_coronavirus/
- 2% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166354220302011
- 2% – https://www.newkerala.com/news/2020/58349.htm
- 2% – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520719/
- 2% – https://www.genengnews.com/virology/coronavirus/anti-parasitic-drug-halts-coronavirus-replication-in-lab-grown-cells-within-48-hours/
- 1% – https://www.truthorfiction.com/the-covid-19-chloroquine-controversy-explained/
- 1% – https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(03)00806-5/fulltext
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1473309903008065
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924857920300984
- 1% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338804522_Successful_Extracorporeal_Membrane_Oxygenation_Treatment_in_an_Acquired_Immune_Deficiency_Syndrome_AIDS_Patient_with_Acute_Respiratory_Distress_Syndrome_ARDS_Complicating_Pneumocystis_jirovecii_Pneumo
- 1% – https://www.medicinenet.com/chloroquine-oral/article.htm
- 1% – https://www.cdc.gov/sars/clinical/guidance.html
- 1% – https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/faq.html
- <1% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339161688_Therapeutic_options_for_the_2019_novel_coronavirus_2019-nCoV

Best