Interesting Science Videos
Seliwanoff’s test definition
Seliwanoff’s test is used to differentiate between sugars that have a ketone group (ketose) and sugars that have an aldehyde group (aldoses). This test is a timed color reaction specific to ketohexoses.
Objectives of Seliwanoff’s test
- To detect the presence of ketohexoses in a given sample.
- To distinguish ketoses from aldoses.
Principle of Seliwanoff’s test
- The reagent of this test consists of resorcinol and concentrated HCl.
- The acid hydrolysis of polysaccharides and oligosaccharides yields simpler sugars.
- Ketoses are more rapidly dehydrated than aldoses.
- Ketoses undergo dehydration in the presence of concentrated acid to yield 5-hydroxymethyl furfural.
- The dehydrated ketose reacts with two equivalents of resorcinol in a series of condensation reactions to produce a complex (not a precipitate), termed xanthenoid, with deep cherry red color.
- Aldoses may react slightly to produce a faint pink to cherry red color if the test is prolonged.
- The product and reaction time of the oxidation reaction helps to distinguish between carbohydrates.
- Other carbohydrates like sucrose and inulin also give a positive result for this test as these are hydrolyzed by acid to give fructose.
Reaction
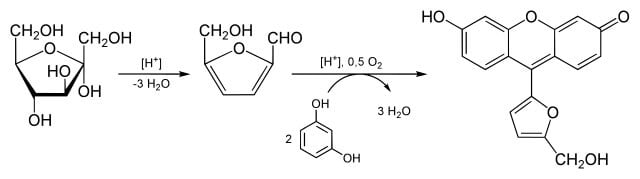
Figure: Seliwanoff’s test with fructose as an example. Image Source: Yikrazuul.
Requirements
Reagent
- Seliwanoff’s reagent: add 0.05% resorcinol (m-hydroxybenzene) in 3 N HCl. Dissolve 50 mg resorcinol in 33 ml concentrated HCl and make it 100 ml with water.
- Test sample
- Distilled water
Materials required
- Test tubes
- Test tube stand
- Pipettes
Equipment
- Water bath
Procedure of Seliwanoff’s test
- Take two clean, dry test tubes and add 1 ml of the test sample in one test tube and 1 ml of distilled water in another as blank.
- Add 2 ml of Seliwanoffs’ reagent to both the test tubes.
- Keep both the test tubes in a water bath for 1 min.
- Observe the formation of color and note it down.
Result and Interpretation of Seliwanoff’s test
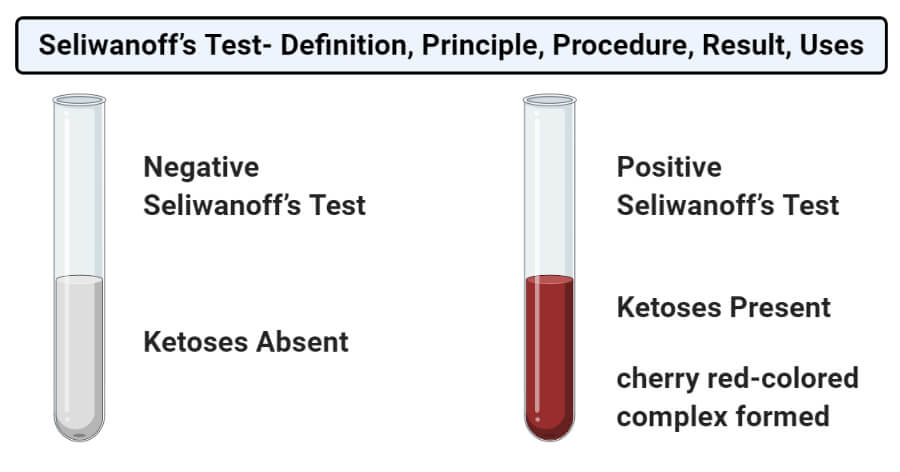
- The formation of the cherry red-colored complex indicates a positive result which means that the given sample contains ketoses.
- The absence of such color or the appearance of the color after a prolonged period of time indicates a negative result which means that the test sample doesn’t have ketoses.
Uses of Seliwanoff’s test
- Seliwanoff’s color reaction is used in the method for the colorimetric determination of fructose in fermentation media.
- A modified version of this test can be used for the determination of the concentration of ketoses in a given sample.
Limitations of Seliwanoff’s test
- The high concentration of glucose or other sugar may interfere by producing similar colored compounds with Seliwanoff’s reagent.
- Prolonged boiling can transform glucose to fructose by the catalytic action of acid and form cherry red-complex giving a false-positive result.
- This test is a generalized test and doesn’t distinguish between specific ketoses, and a separate test is required for the particular ketose sugar identification.
References and Sources
- Tiwari A. (2015). Practical Biochemistry. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
- Sánchez-Viesca, Francisco & Gómez, Reina. (2018). Reactivities Involved in the Seliwanoff Reaction. 10.11648/j.mc.20180601.11.
- 4% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seliwanoff%27s_test
- 3% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313745155_Practical_Biochemistry_A_Student_Companion
- 2% – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vOWoWxEdy0I
- 2% – https://diabetestalk.net/blood-sugar/chemical-test-to-distinguish-between-glucose-and-fructose
- 2% – https://biokamikazi.files.wordpress.com/2013/10/merged_document.pdf
- 1% – https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803100453548
- 1% – https://generalchemistrylab.blogspot.com/2011/12/seliwanoffs-test.html
- 1% – http://en.edubio.info/2017/02/seliwanoffs-test-for-ketose-sugars.html

It well briefed … thanks for your cooperating
Since concentrated HCl is 12 M, 33 mL into 100 mL will give 4 M HCl solution.
what is the conclusion for aldoses