RNA stands for Ribonucleic acid is a polymer of ribonucleotides. Transcription is the process in which DNA is transcribed into RNA with the help of the enzyme RNA polymerase. Transcription involves three steps; elongation, initiation, and termination. Rifamycins group of antibiotics inhibit RNA polymerase in RNA synthesis. Actinomycin D, an anticancer drug; a chemotherapeutic drug is also an RNA synthesis inhibitor.
Rifamycins: Antimicrobials having basket-like molecular structure belongs to the family ansamycin. Rifamycins were isolated from an actinomycete which was named Streptomyces mediterranei which was renamed and changed into Nocardia mediterranea. And later the actinomycete was reclassified as Amycolatopsis mediterranei. Rifamycins group of antibiotics shows better activity against Mycobacteria and is also effective against Gram-negative bacteria. Rifamycin group of antibiotics are lipid-soluble which are broad-spectrum bacteriostatic first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs.
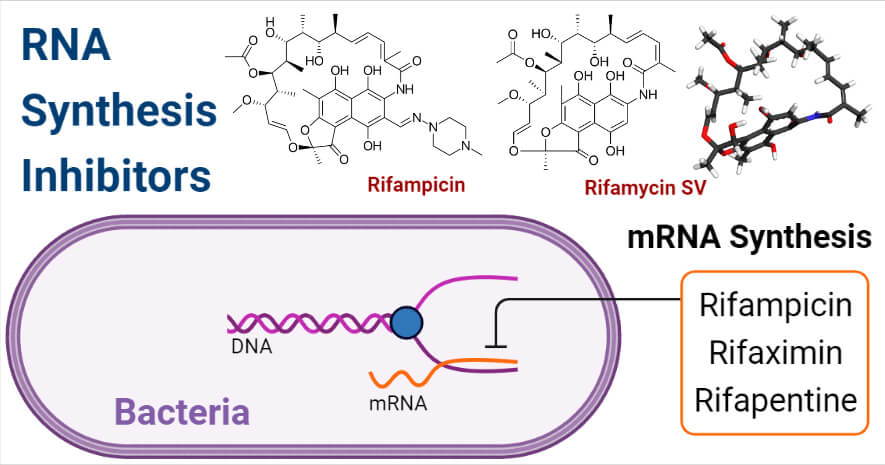
Rifamycin B was the parent compound of the Rifamycin group of antibiotics. It was originated in the presence of diethylbarburitic acid. Based on production, Rifamycin is classified into natural and semi-synthetic rifamycins. Rifampin and Rifaximin are semi-synthetic rifamycins and Rifamycin CV, Rifamycin SV is natural rifamycins. Rifamycins have several derivatives which include rifampin, Rifamycin CV, and Rifamycin SV which have different structures and properties. Since resistivity is growing rapidly rifamycins group of antibiotics are used in combination with other drugs to treat mycobacterial infections.
Interesting Science Videos
Mechanism of action of RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Rifamycin including other antimicrobials of this group is considered to treat Mycobacterium as well as other Gram-positive and negative. It inhibits RNA synthesis. Rifamycin’s mechanism of action shows the binding of antibacterial to the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by binding to their beta-subunits ( α1, β, β1, and Ϭ). Β-subunit is the binding site for rifampicin which is encoded by the gene rpoB. It blocks the initiation of mRNA transcription. Ribosomal and transfer RNA are also equally affected as mRNA. And further, it prevents the translation of polypeptides.
Examples of RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Rifampicin
Rifaximin
Rifapentine
Mechanisms of resistance of RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis is a serious issue. The resistivity in the rifamycin group is due to the mutation in the rpoB gene that decreases the efficacy to act on the infection. The mutation involved is a point mutation that results in the substitution of amino acid which either may be insertion or deletion. H406, S411, and D396 are the three amino acids that are mutated in resisted isolates are involved in oxygen and hydrogen interactions at the 8 and 21 positions. The other sites are susceptible to mutation. rpoB gene mutation results in lowering of affinity of enzyme which binds to the protein (wild-type). The lowering affinity between antimicrobials and target match up with the decreased sensitivity of the pathogens to inhibition by rifamycins.
References
- Baysarowich J, Koteva K, Hughes DW, Ejim L, Griffiths E, Zhang, K and Wright G D (2008). Rifamycin antibiotic resistance by ADP-ribosylation : Structure and diversity of Arr.
- Floss HG and Yu T (2005). Rifamycin s Mode of Action, Resistance, and Biosynthesis. 621–632.
- From, https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB11753
- Riva S and Silvestri, L C (1972). Rifamycins: a general view.

This content is awesome