Interesting Science Videos
Ctenophora Definition
Ctenophores are free-swimming, transparent, jelly-like, soft-bodied, marine animals having biradial symmetry, comb-like ciliary plates for locomotion, the lasso cells but nematocytes are wanting. They are also known as sea walnuts or comb jellies.
Phylum Ctenophora Characteristics
- They are free-swimming, marine, solitary, pelagic animals. No polymorphism and no attached stages were found.
- The body is transparent, gelatinous, pear-shaped, cylindrical, or flat or ribbon-shaped.
- They have a biradially symmetrical body along an oral-aboral axis.
- They have an external surface with comb-like 8 ciliary plates for locomotion. Hence name as comb jellies.
- They have a pair of long, solid, retractile tentacles.
- Their body organization is cell-tissue grade.
- Their body is acoelomate and “diploblastic” having ectoderm and endoderm. The body wall has outer epidermis, inner gastrodermis, middle jelly-like mesoglea with scattered cells, and muscle fibers. So, Ctenophora may also be considered as “triploblastic”.
- Their digestive system contains the mouth, stomodaeum, complex gastrovascular canals, and 2 aboral anal pores.
- They lack nematocysts.
- They have special adhesive and sensory cells i.e. colloblasts or lasso cells present in tentacles which helps in food captures.
- They lack skeletal, circulatory, respiratory, and excretory organs.
- Their nervous system is diffused types and the aboral end bears a sensory organ, called statocyst.
- They are monoecious (hermaphrodite); gonads are endodermal situated on walls of digestive canals.
- Their development direct with characteristic cydippid larva.
- They lack asexual reproduction and alternation of generation.
- Regeneration and paedogenesis are common in them.
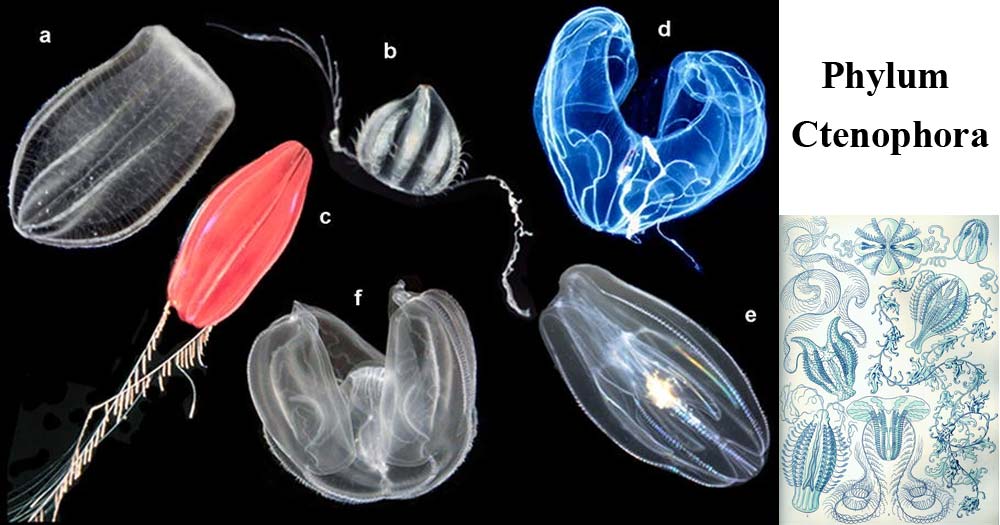
Figure: Pelagic ctenophores: (a) Beroe ovata, (b) Euplokamis sp., (c) Nepheloctena sp., (d) Bathocyroe fosteri, (e) Mnemiopsis leidyi, and (f) Ocyropsis sp. Image Source: Wikipedia.
Phylum Ctenophora Classification
Phylum Ctenophora contains about 100 know species and grouped in 2 classes
Class 1. Tentaculata
- Adults with 2 long aboral tentacles.
- In some larva has tentacles, while adults have oral lobes.
- Mouth narrow and pharynx small.
Order 1. Cydippida
- Body simple, round, and oval.
- Digestive canals terminate blindly; no anal pores.
- Tentacles are two long and branched.
- Tentacles are retractile into pouches or sheath.
- Examples: Mertensia, Pleurobrachia, Hormiphora
Order 2. Lobata
- Body oval, laterally compressed.
- Adults with 2 large oral lobes and 4 slender flap-like auricles around the mouth.
- Pouched or sheath tentacles in the larva.
- Tentacles reduced and without sheath in adults.
- Gastrovascular canals are connected by a ring at oral ends.
- Examples: Mnemiopsis, Bolinopsis
Order 3. Cestida
- Body elongated compressed/flat, ribbon-like.
- Two main tentacles in the sheath but reduced.
- Many small lateral tentacles along the oral edge.
- Combs plates in 4 rows but rudimentary.
- Examples: Cestum, Velamen
Order 4. Platyctenea
- Body greatly compressed/flat in the oral-aboral axis.
- 2 well- developed tentacles with sheath.
- Comb plates reduced in adults.
- Adapted for creeping.
- Examples: Ctenoplana, Coeloplana
Order 5. Thalassocalycida
- They are found surface waters down up to 2,765 Ms in Atlantic oceans and the Mediterranean Sea.
- The body is a bell of Medusa shaped and may be up to 15 cm in diameter.
- Mouth slit holds by a central cone-shaped peduncle.
- A pair of small tentacles hang from the side of the peduncle.
- Com jelly is with its transparent and colorless body. Usually different to see.
- They hold the bell wide opens to captures prey i.e. Zooplankton.
- Presumably hermaphroditic.
- This species has limited swimming ability compared to other comb jellies.
- Examples: Thalassocalyce inconstans.
Class 2. Nudu
- Body large, conical, and compressed laterally.
- Without tentacles and oral lobes.
- Wide mouth and large pharynx.
- Voracious feeder.
Order 1. Beroida
- No tentacles and oral lobes.
- Body large, conical, and laterally compressed.
- Mouth large.
- Voluminous Stomach.
- Examples: Beroe
References
- Kotpal RL. 2017. Modern Text Book of Zoology- Invertebrates. 11th Edition. Rastogi Publications.
- Jordan EL and Verma PS. 2018. Invertebrate Zoology. 14th Edition. S Chand Publishing.
