Extending the shelf life of food without disturbing its natural quality is a great concern in food technology. Ozone treatment is a possible alternative for food preservation as it has quick decomposition properties with little residual effect.
- Ozone is triatomic oxygen (O3) with strong oxidizing power and can inactivate microorganisms effectively.
- It is a very reactive form of oxygen.
- It is also termed as a “natural disinfectant”.
- U.S. FDA accepted it as a GRAS substance for water treatment in 1982 and food in 1997.
- Ozone use for water treatment is the best alternative to replace chemical treatment like chlorination.
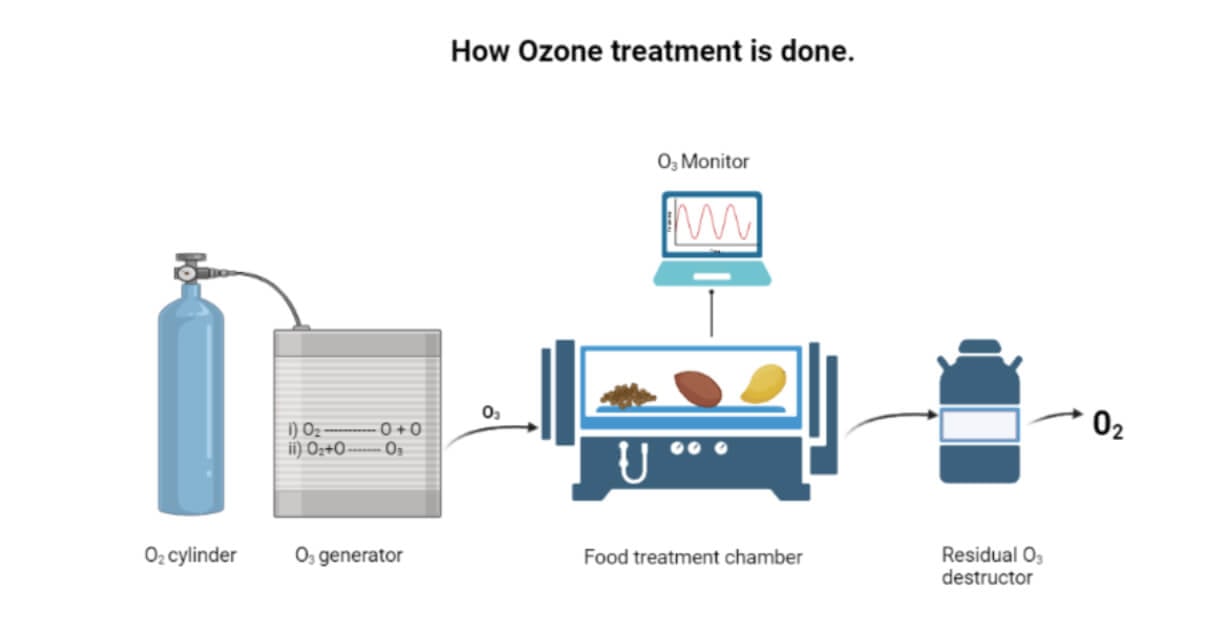
- Ozone generators are used to produce ozone at safe concentrations; for commercial production, it is generated by corona discharge.
- During ozone production, O2 breaks into highly reactive singlet oxygen, and this singlet oxygen interacts with additional O2 to form ozone (O3).
Interesting Science Videos
Forms of Ozone
- Gaseous ozone
- Ozone in gaseous form
- It is used for storage treatment
e.g., the use of Gaseous ozone to decontaminate the eggshell which reduces the risk of spoilage of egg, and use to preserve spices, grains, beans, etc
- Aqueous ozone
- Ozone that is incorporated into the water in bubble form
- It is used as a surface disinfectant
e.g., to reduce the microbial load of fish fillets
Properties of ozone
- Very reactive
- Gaseous ozone is soluble in water
- More stable at lower temperatures (4 – 120c)
- More stable at pH 5.0 and unstable at high pH
- The stability and effectiveness of ozone depend upon organic and inorganic materials present in food
Process of Formation of Ozone
Addition of a free radical of oxygen to molecular oxygen
- High voltage alternating current splits oxygen molecules into atoms
- Atoms of oxygen then combine with other oxygen molecules and form ozone (O3)
Mode of action of food treatment
- Destruct lipids, protein, nucleic acid, and other cellular components due to oxidative reactions
- Protein degradation and cellular structure modification
- Damage spore inner membrane due to oxidization
Application of Ozone Treatment
- To disinfect production areas, plant equipment, and surfaces from microorganisms
- Effective to kill spores of Bacillus and Clostridium species.
- Inhibit fungal growth in fruits and vegetables
- Gaseous ozone helps to decontaminate eggshell
- Reduce the level of natural microbiota in fish products
- Reduce microbial load in spices, grains, beans, etc.
Advantages of Ozone Treatment
- High antimicrobial activity as it is 3000 times faster than chlorine at killing microorganisms
- Fast decomposition to simple oxygen
- No waste generation
- Lower energy input as compared to other thermal and non-thermal techniques.
- Eco-friendly and economically feasible
Disadvantages of Ozone Treatment
- High ozone concentrations can be hazardous.
- Cause throat and nasal problems if inhaled by us.
- It decomposes quickly, so it cannot be stored.
- Ozone can react with proteins and fats in carcass treatment before inactivating microorganisms.
References
- Potter NP (1987), Food Science, CBS Pub, India.
- Rahman MS (1999), Handbook of Food Preservation, Marcel Dekker, Inc, NY.
- Desrosier EN (1963), The Technology of Food Preservation, AVI Publishing Company, New York.
- Sarron E, Gadonna-Widehem P, Aussenac T. Ozone Treatments for Preserving Fresh Vegetables Quality: A Critical Review. Foods. 2021 Mar 12;10(3):605. doi: 10.3390/foods10030605. PMID: 33809297; PMCID: PMC8000956.
- R. Pandiselvam, S. Subhashini, E.P. Banuu Priya, Anjineyulu Kothakota, S.V. Ramesh & S. Shahir (2019) Ozone based food preservation: a promising green technology for enhanced food safety, Ozone: Science & Engineering, 41:1, 17-34, DOI: 10.1080/01919512.2018.1490636.
