Interesting Science Videos
Mucic acid test definition
Mucic acid test is a test that is highly specific and is used for the detection of the presence of galactose and lactose. It is also termed galactaric acid that is named after the product of the reaction.
Objectives of Mucic acid test
- To detect the presence of galactose and lactose in a given sample.
- To distinguish between the galactose containing saccharides and other sugars.
Principle of Mucic acid test
- Monosaccharides upon treating with potent oxidizing agents like nitric acid yield saccharic acids (dicarboxylic acids).
- Nitric acid has the capacity to oxidize both aldehyde and primary alcoholic groups present at C1 and C6 respectively of galactose to yield an insoluble precipitate (rod-shaped crystals) of mucic acid under higher temperature.
- Lactose also yields a mucic acid, due to the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond between the glucose and galactose subunits of the carbohydrate.
- Other monosaccharides like glucose also have a similar structure; however, the resultant precipitate formed in glucose is water-soluble under room temperature.
Reaction
CH2OH-(CHOH)4-CHO + HNO3 → CH2OH-(CHOH)4-CHO-NO3 + H+
Requirements
1. Reagent
- Mucic acid reagent: concentrated nitric acid
- Test sample (1%)
- Distilled water
2. Materials required
- Test tubes
- Test tube stand
- Pipette
3. Equipment
- Water bath
Procedure of Mucic acid test
- Take 6 ml of each distilled water and test sugar solutions in four test tubes separately.
- Add 1 ml of Mucic acid reagent (concentrated nitric acid) to each tube.
- Heat the test tubes in the water bath for 1-1/2 hours until the volume of the solution is reduced to 2-3 ml.
- Let the test tube sit overnight before collecting the results.
Result and Interpretation of Mucic acid test
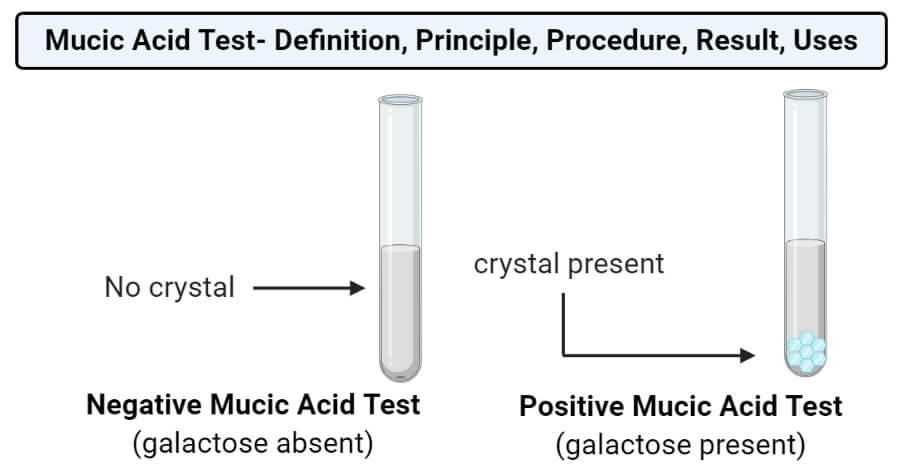
- The formation of crystal at the bottom of the tube indicates a positive result which means that the sample solution has galactose or its derivatives.
- The absence of such crystals indicates a negative result and represents that the sample doesn’t have galactose or its derivative. The solution might still have other carbohydrates.
Uses
- The most important use of the mucic acid test is to identify the presence of galactose or its derivatives in the food sample and in synthetics manufacture.
- This test can also be used to detect the presence of lactose or agar-agar.
Limitations
- This test cannot distinguish between monosaccharides and disaccharide derivations of galactose.
- In some cases, a false positive result might occur due to impurities with carbonyl groups at the terminal ends.
References and Sources
- Tiwari A. (2015). Practical Biochemistry. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
- Harisha S (2006). An introduction to Practical Biotechnology. Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd.
- 5% – https://biochemden.com/color-reactions-of-carbohydrates/
- 2% – https://www.thestudentroom.co.uk/showthread.php?t=1957903
- 2% – https://www.scribd.com/presentation/104408409/Experiment-5-Guide
- 1% – https://mynotesarchive.wordpress.com/2012/02/18/chem-lab-notes/
- 1% – https://msu.edu/course/lbs/145/luckie/Lab1.html
- 1% – https://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/Mucic+Acid
