Interesting Science Videos
Lead Sulfide Test Definition
Lead sulfide test (or Lead acetate test) is a biochemical test for the detection of amino acids like cysteine and cystine. The test is a specific test for the detection of amino acids containing sulfur, S-S group in cysteine, and S-H group in cystine. The test is also called a lead acetate test as the reagent for the test is lead acetate. Even though the test is specific for the detection of sulfur-containing amino acids, methionine doesn’t give a positive result in this test.
Objectives of Lead Sulfide Test
- To detect the presence of sulfur-containing amino acids in a sample.
- To detect protein-containing cysteine and cystine in a given sample.
- To distinguish between sulfur-containing and non-sulfur containing amino acids.
Principle of Lead Sulfide Test
The test is based on the principle of detection of sulfur in a solution by the degradation of the S-H or S-S group in amino acids under strongly alkaline conditions. Amino acids like cysteine and cystine release sulfur in the presence of strong alkaline conditions at a high temperature. The sulfur then combines with the alkali (NaOH) to form Na2 The Na2S thus formed reacts with lead acetate to form lead sulfide, which results in a black residue. For the reaction to take place, free sulfur ions should be present in the medium.
Reaction
Cysteine + 2NaOH → Serine + Na2S + H2O
Pb(CH3COO)2 + NaOH → Pb(OH)2 + 2CH3COONa
Pb(OH)2 + 2NaOH → Pb(ONa)2 + 2H2O
Na2S + Pb(ONa)2 + H2O → PbS (black precipitate) + 4NaOH
Requirements
Reagent
- 2% lead acetate solution in water
- 40% NaOH
- Sample
Material Required
- Test tubes
- Test tube stand
- Pipettes
Procedure of Lead Sulfide Test
- In a test tube, 2 ml of the amino acid solution is taken. To this, 2 ml of NaOH is added, and the solution is boiled for a minute.
- Once the test tube cools down, a few drops of lead acetate are added to the solution.
- The test tube is then observed for the formation of a precipitate.
Result and Interpretation of Lead Sulfide Test
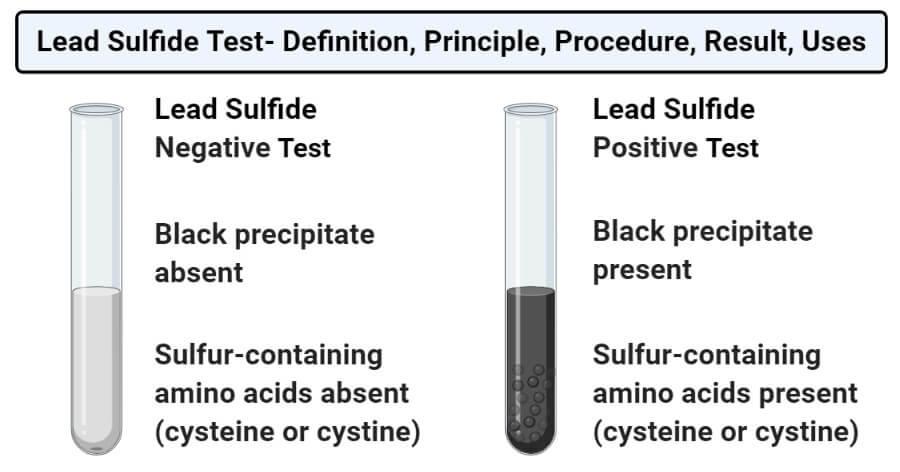
- Positive test: A positive test in the Lead sulfide test is represented by the formation of black precipitate at the bottom of the test tube. This indicates the presence of cysteine or cystine in the solution.
- Negative test: A negative result in the Lead sulfide test is represented by the absence of black residue in the test tube. This indicates the absence of cysteine or cystine.
Uses of Lead Sulfide Test
- The test is used to detect sulfur-containing amino acids like cysteine and cystine.
- It helps to distinguish between different groups of amino acids.
- The detection of cystine in urine is a pathological symptom of diseases like cystine stones in the kidneys and bladder.
Limitations
- Methionine doesn’t give a positive result in this test as the sulfur in the thioester bond in methionine is not released by the treatment with NaOH.
- The addition of excess lead acetate to the solution might result in white-colored precipitation.
References
- Tiwari, A. (2015). Practical Biochemistry. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
- Nigam S. C. and Omkar (2003). Experimental Animal Physiology and Biochemistry. New Age International Pvt. Limited. New Delhi.
- D (2012). Biochemistry. Fourteenth Edition. Academic Publishers. Kolkata.

Excellent and informative. Thanks
This article is well articulated thank you.
super. and thanks.