Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LPCB) Staining is a simple histological staining method used for the microscopic examination and identification of fungi.
Interesting Science Videos
Principle of Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LPCB) Staining
Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LPCB) Staining method works on the principle of aiding the identification of the fungal cell walls.
- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms with both macroscopic and microscopic characteristics.
- The fungal spore cell wall is made up of chitin of which the components of the Lactophenol Cotton Blue solution stains for identification.
- The lactophenol cotton blue solution acts as a mounting solution as well as a staining agent.
- The solution is clear and blue in color and it is made up of a combination of three main reagents:
- Phenol: It acts as a disinfectant by killing any living organisms
- Lactic acid: To preserve the fungal structures
- Cotton blue: To stain or give color to the chitin on the fungal cell wall and other fungal structures
- The stain will give the fungi a blue-colored appearance of the fungal spores and structures, such as hyphae.
Reagents of Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LPCB) Staining
A preparation of 50ml Lactophenol cotton Blue staining solution is made up of:
- Distilled water 50ml
- Cotton Blue (Aniline Blue) 0.125g
- Phenol Crystals (C6H5O4) 50g
- Glycerol 100ml
- Lactic acid (CH3CHOH COOH) 50ml
- 70% ethanol
Note: Lactophenol Cotton Blue solution is prepared at least 2 days before use.
Preparation of Lactophenol Cotton Blue solution
Lactophenol Cotton Blue solution is prepared for over two days leaving the reagents undisturbed to allow dissolving and maturation.
- Day 1: Dissolve the cotton blue in distilled water and leave to rest overnight. This eliminates insoluble dye.
- Day2: Using protective gloves, add phenol crystals to lactic acid in a glass beaker and stir using a magnetic stirrer until the crystals dissolve.
- Add glycerol
- Filter the Cotton blue and the distilled water into the phenol + glycerol +lactic acid solution and mix.
- Store at room temperature.
Procedure of Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LPCB) Staining
- On a clean microscopic glass slide, add a drop of 70% ethanol
- Add the fungal specimen to the drop of alcohol using a sterile mounter such as an inoculation loop (from solid medium), depending on the sample of use.
- Tease the fungal sample of the alcohol using a needle mounter, to ensure the sample mixes well with the alcohol.
- Using a dropper or pipette, add one or two drops of Lactophenol Cotton Blue Solution (prepared above) before the ethanol dries off.
- Carefully cover the stain with a clean sterile coverslip without making air bubbles to the stain.
- Examine the stain microscopically at 40X, to observe for fungal spores and other fungal structures.
Results and Interpretation
Fungal spores, hyphae, and fruiting structures stain blue while the background stains pale blue.
For example,
- Aspergillus niger stains the hyphae and fruiting structures a delicate blue with a pale blue background.
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes also stains the hyphae and fruiting structures a delicate blue with a pale blue background.
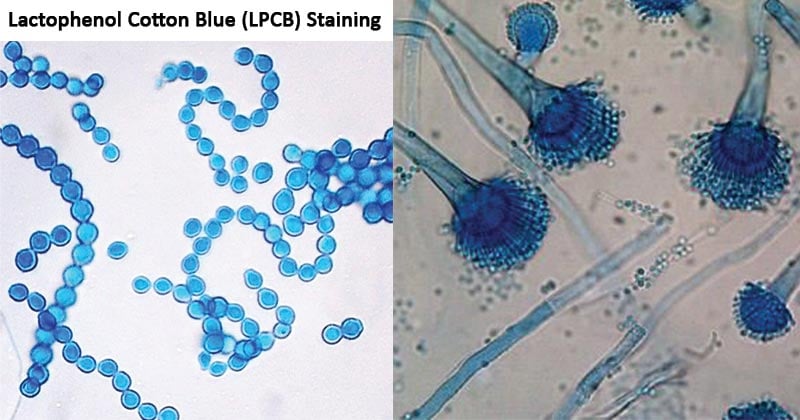
Figure: First: Scopulariopsis species on a lactophenol cotton blue stain. Image Source: stylish_streaking and Senthil Prabhu.
Limitations
- It can only be used as a presumptive identification method of fungi which should be followed up with other diagnostic tools such as biochemical and cultural examination.
- The components of the solution should be used before expiry, including the use of the solution before it expires.
- The solution may disrupt the original morphology of the fungi.
- The stain can only be used to identify mature fungi and its structures and not the young vegetative forms of fungi.
- The stain can not be stored for a long period of time.
Applications
- Used in the identification of suspected fungal samples.
- General identification of fungi and its structures.
References and Sources
- https://catalog.hardydiagnostics.com/cp_prod/Content/hugo/LactophenolCottonBlStn.htm
- http://www.himedialabs.com/TD/S016.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lactophenol_cotton_blue
- microbe online/lactophenolcottonblue
- https://laboratoryinfo.com/lactophenol-cotton-blue-lpcb/
- https://mycology.adelaide.edu.au/laboratory/lacto/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1706009/

Good work, and suggestions so how may become good scientist?how to write my paper presentation?
what can be done to prevent lactophenol blue solution to disrupt the morphology of fungi
Please, what is the essence of the 70% alcohol before staining?
useful & informative
Please for yeast cells such as Candida albicans, can this staining technique be used for its visualisation.
Helpful!
GOOD
Nice Notes