The saprophytic organisms which simulate the anthrax bacillus closely, both in their morphological and cultural characters within the group of Gram-positive aerobic sporing bacilli are termed as Anthracoid bacilli.
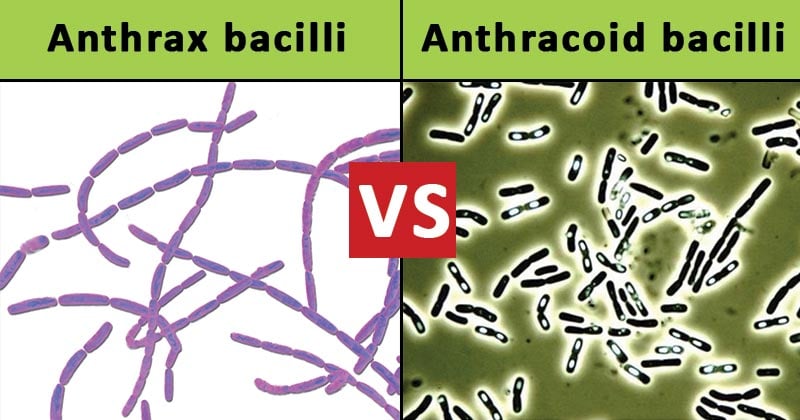
They have a general resemblance to anthrax bacilli such as producing dry wrinkled colonies and in the smear, appearing as chains of spore-bearing gram-positive bacilli.
Interesting Science Videos
However, they differ from anthrax bacilli in many ways as follows:
S.N. |
Character |
Anthrax bacilli |
Anthracoid bacilli |
| 1. | Known as | Bacillus anthracis | B. anthracis similis, B. pseudo-anthracis or “anthrax-like” bacilli and Pseudoanthrax. |
| 2. | Shape (Chain Length) | In long chains | In short chains |
| 3. | Position of spores | Central, do not bulge the bacilli. | Central, subterminal or terminal, may bulge the bacilli. |
| 4. | Capsule | Present | Absent |
| 5. | Motility | Non-motile | Motile |
| 6. | Under lower power microscope | Medusa head colony seen | Not seen |
| 7. | Oxygen requirement | Strict aerobe | Aerobic or facultative anaerobic |
| 8. | Growth at 45°C | No Growth | Growth usually seen |
| 9. | Blood Agar | No hemolysis (or weak) | Hemolytic colonies(usually well marked) |
| 10. | Turbidity | No Turbidity in broth | Turbidity seen usually |
| 11. | Solid medium with penicillin | String of pearls appearance | No growth |
| 12. | Gelatin stab agar | Inverted fir tree appearance | Absent |
| 13. | In nutrient broth | Fluffy Cotton wool without pellicle | Turbidity and pellicle formation but no fluffy Cotton wool |
| 14. | Salicin Fermentation | Negative | Usually Positive |
| 15. | Rate of gelatin liquefaction | Slow | Rapid |
| 16. | Lecithinase activity on egg yolk agar | — weak | + marked |
| 17. | Reduction of methylene blue in milk | Reduce methylene blue slowly | Rapidly reduce methylene blue |
| 18. | Chloral Hydrate | Growth inhibited by Chloral Hydrate | Not Inhibited |
| 19. | Susceptibility to Gamma Phage | Susceptible | Not susceptible |
| 20. | Penicillin sensitivity 10 unit disc | Susceptible | Resistant |
| 21. | Pathogens | Pathogenic | Except B. cereus, most of them are non-pathogenic or opportunistic pathogens with low virulence. |
| 22. | Diseases caused | ■ Cutaneous anthrax
■ Gastrointestinal anthrax ■ Inhalational anthrax ■ Anthrax meningitis. |
■ Bacillus cereus is the most important pathogen causing GI infection, ocular infections, and catheter-related infections.
■ Bacillus subtilis may act as an opportunistic pathogen, causing eye infections and septicemia. ■ Bacillus licheniformis has also been incriminated in patients with food poisoning. |
| 23. | Pathogenicity for mice or guinea pigs | Pathogenic (death in 24 – 48 hours) | No death |
| 24. | Contaminants | Not a common contaminant. | Common contaminants in laboratory cultures. |
| 25. | Organism(s) | Bacillus anthracis | B. cereus, B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. stearothermophilus etc. |
References
- http://ecoursesonline.iasri.res.in/mod/page/view.php?id=66763
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/difference-between-anthrax-bacilli-and-anthracoid-bacilli/
- http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/sites/default/files/medical_bacteriology_section_4_0.pdf
- Parija S.C. (2012). Textbook of Microbiology & Immunology.(2 ed.). India: Elsevier India.
- Sastry A.S. & Bhat S.K. (2016). Essentials of Medical Microbiology. New Delhi : Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers.
