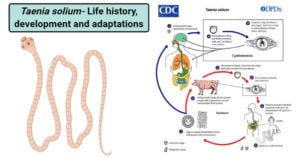
Reproductive System of Ascaris lumbricoides
Reproductive system of Ascaris lumbricoides Only sexual reproduction occurs in Ascaris. Sexes are separate i.e., dioecious in Ascaris and these roundworms also show distinct sexual dimorphism. Males are smaller than … Read more