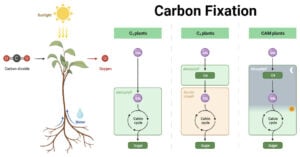
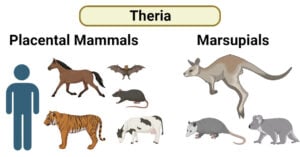
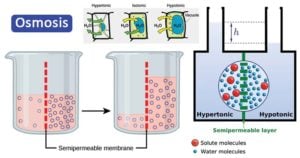
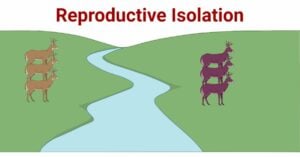
Carbon Fixation: Processes, Pathways, and Implications
Carbon fixation represents a biological phenomenon where photosynthesis transforms atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic substances. This process converts carbon atoms into various molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. It … Read more