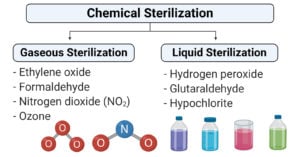
Chemical methods of sterilization- Gaseous and Liquid
What is Chemical Sterilization? Chemical Sterilization is the process of removal of microorganisms by the use of chemical bactericidal agents. Even if physical methods of sterilization are more appropriate for … Read more