Muscle Contraction: Definition, Proteins, Types, Steps
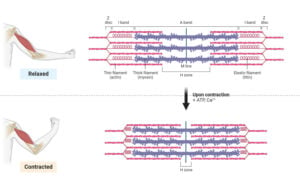
Muscle contraction is the stretching of the muscle fibers generating tension within the muscle cells/fibers. In some cases, tension can also be generated in muscle without muscle stretching. Hence, the … Read more