Beta (β) Lactamase Test is used to detect beta-lactamase enzymes produced by different bacteria.
- Beta-lactamase is a plasmid-encoded or chromosomal-encoded enzyme that hydrolyzes the beta-lactam ring of the beta-lactam class of antibiotics resulting inactivation of these drugs. In addition, the beta-lactam gene frequently resides on integron.
- The first beta-lactamase was described in 1940 as a “penicillinase” that is capable of hydrolyzing penicillin in E. coli.
- Beta-lactamase enzyme production may be constative or induced by exposure to antimicrobials.
- According to the Bush-Medeiros Classification System, beta-lactamase enzymes divide into 4 molecular classes (A-D) based on their amino acid structure.
- Beta-lactamase enzymes are detected by rapid beta-lactamase tests. This test gives results earlier than MIC or Disk diffusion test.
Interesting Science Videos
Objectives
To detect the enzyme beta-lactamase by chromogenic, iodometric, and acidometric tests, which confers beta-lactam resistance to various bacterial organisms.
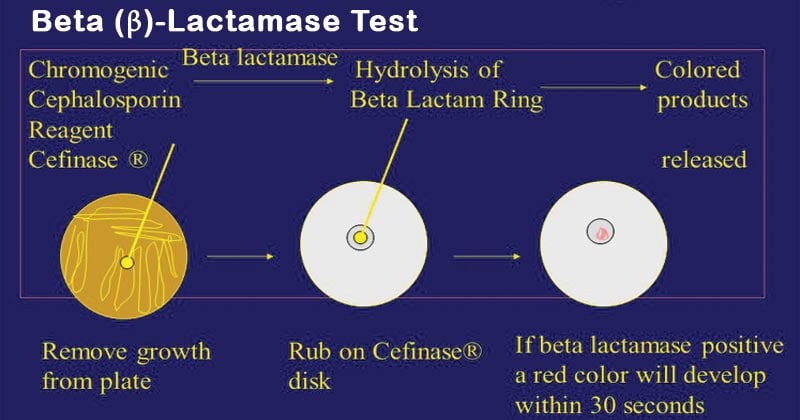
Chromogenic cephalosporin test (Nitrocefin test) of Beta (β) Lactamase Test
Principle of Nitrocefin test
Nitrocefin disks are impregnated with nitrocefin, a chromogenic cephalosporin. Bacteria produced a significant amount of β-lactamase enzyme resulting in hydrolyzed amide bond in a β- lactam ring. Color of the nitrocefin disk changed from yellow to red. The color change of the disk indicates a positive test, and the colors that remain the same indicate a negative test. These beta-lactamases are capable of inactivating “penicillinase-labile-penicillins” such as amoxicillin, ampicillin, penicillin, carbenicillin, mezlocillin, and piperacillin.
Requirement of Nitrocefin test
- Nitrocefin disk (commercially available, follow manufacture instructions) stored at 2-8 ℃.
- Sterile distilled water
- Glass slide or empty petri dish
- Sterile Pasteur pipette
- Sterile wooden stick and inoculating loop
- The test organism colony was grown overnight (18-24 hrs) on non-selective media.
Procedure of Nitrocefin test
- Using sterile forceps, dispense the required number of disks onto a clean microscope slide or an empty petri dish.
- Before inoculation, allow the nitrocefin disk to be brought to room temperature.
- Moisten each disk with 1 drop of sterile distilled water.
- With a sterile loop or applicator stick, smear several colonies onto the disk surface and also smear the positive control strain colony and negative control strain colony.
- Observe the disk for color change. Positive results usually appear within 15 s to 5 min. If no color change occurs within 5 min, the test is negative. However, positive reactions for some staphylococci may take up to 1 h.
Results and interpretation of the Nitrocefin test
Positive: yellow color changes to red when the culture inoculates.
Negative: no change in the color of the disk.
Positive and negative controls
Bacteria that give positive results: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 (Quality control)
Bacteria that give negative results: Haemophilus influenza ATCC 10211 (Quality control), S aureus ATCC 25923.
Applications of Nitrocefin test
- The chromogenic cephalosporins test (Nitrocefin) is a biochemical test that is a sensitive method for detecting beta-lactamase-producing strains of N. gonorrhoeae, H. influenza, Staphylococcus spp, Enterococcus spp, and Moraxella catarrhalis. It is the most reliable test for detecting beta-lactamase-producing Enterococcus spp.
- Easy to perform and gives results earlier than other methods.
- The chromogenic method is quicker and more convenient than the acidimetric and iodometric methods.
- The sensitivity and efficiency of the chromogenic method are high due to the detection of both penicillinase and cephalosporinase enzymes produced by isolates.
- Nitrocefin test is only reliable test for detecting β -lactamase production by Enterococcus spp.
- The chromogenic cephalosporin compound nitrocefin test was also used for detecting β-lactamase produced by Achromobacter.
- Nitrocefin has a wide susceptibility and sensitivity to the commercially available beta-lactam.
Limitations of the Nitrocefin test
- Moisten disk is critical to the development of the color, if the disk begins to dry out, it may be necessary to rehydrate the disk with a small amount of water.
- The indistinct and weak reaction was obtained for strains grown on blood agar plates.
- Beta-lactamase detection with the nitrocefin disk should not entirely replace conventional susceptibility test methods, as other factors also influence the results of such tests, and on occasion, intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antimicrobials has not been correlated with the production of beta-lactamase.
- Do not over-saturate the tip, as it could dilute the reagent.
- Detection of beta-lactamase activity in staphylococci may take up to one hour. Induction of the enzyme may also be required. This can be done by testing growth from the zone margin around an oxacillin disk.
- A negative result does not rule out resistance due to other mechanisms.
- Nitrocefin disk method cannot be used to test the members of Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas species, or other aerobic, gram-negative bacilli because the results may not be predictive of susceptibility to the beta-lactams most often used for therapy.
- The Nitrocefin disk cannot be used for organisms where penicillin resistance is not due to beta-lactamase production, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococci.
Acidimetric method of Beta (β) Lactamase Test
Principle of Acidimetric method
In acidimetric test, penicillin-phenol red substrate reacts with beta-lactamase enzyme resulting in penicilloic acid produced. The color of the disk or solution (in tube test) changes from violet or red to yellow due to the pH decreases. Color change into yellow indicates a positive test or no change in color indicates a negative test.
Requirement of Acidimetric method
For disk or strip test
- Acidimetric disk (commercially available, following manufacturer instruction) stored at 2-8 ℃.
- Sterile distilled water
- Glass slide or empty petri dish
- Sterile Pasteur pipettes
- Sterile wooden stick and inoculating loop
- The test organism colony was grown overnight (18-24 hrs) on non-selective media.
For tube test
- 0.5% Phenol red solution (add 0.5 g of phenol red to small amount of water, dissolved properly dissolved heat may be needed to dissolve dye and make up volume 100ml then store at 25°C. Shelf life is 6 months.)
- Crystalline potassium penicillin G (vial containing 20 million U). Store as indicated by the manufacturer.
- 1 N NaOH (add 4 g of NaOH crystals to 100 ml of water). Caution: This will cause heat production. Store at 25°C.
- Sterile 1- and 10-ml pipettes and pipette bulb
- Sterile polystyrene capped tubes (12 by 75 mm)
- Sterile wooden applicator sticks or inoculating loops.
Preparation of penicillin-phenol red substrate reagent
- Add 2 ml of the 5% phenol red solution to 16.6 ml of sterile distilled water.
- Add the phenol red-water solution (18.6 ml) to the vial of crystalline benzylpenicillin G.
- Remove the solution from the vial and place it in a sterile container.
- Add 1 N NaOH dropwise to this acidic solution until it develops a violet color (pH 8.5).
- Dispense in 0.1-ml aliquots into sterile tubes and freeze at – 20°C or lower in a non-frost-free freezer.
Procedures (for disk test) of Acidimetric method
- Using sterile forceps, dispense the required number of disks onto a clean microscope slide or an empty petri dish, and the remaining unused disk immediately place into the freezer.
- Before inoculation, allow the nitrocefin disk to be brought to room temperature.
- Moisten each disk with 1 drop of sterile distilled water.
- With a sterile loop or applicator stick, smear several colonies onto the disk surface and also smear the positive control strain colony and negative control strain colony.
- Observe the disk for color change. Positive results usually appear within 10 min. If no color change occurs within 10 min, the test is negative. However, positive reactions for some staphylococci may take up to 1 h. When dry, the color remains for up to 24 h.
Procedure for tube method of Acidimetric method
- Remove the desired number of reagent tubes from the freezer and allow them to thaw at room temperature (one tube per organism).
- With a sterile loop or applicator stick, add four or five colonies to the test solution to make an opaque, milky suspension.
- Observe for color change. A positive reaction will occur in less than 15 min. If no color change occurs within 15 min, the test is negative. A color change after 15 min usually indicates deterioration of the substrate not related to the presence of beta-lactamase and should not be considered positive. Since positive reactions for some staphylococci may take up to 1 h, results that turn positive after 15 min may not be reliable for these bacteria.
Results and interpretation of Acidimetric method
- Positive: Violet or red color changes to yellow.
- Negative: no change in color occurs.
Applications of Acidimetric method
- Acidometric method is more effective than iodometric method for detection of coagulase positive Staphylococcal β-lactamase.
- Rapid acidimetric method used for performing a beta-lactamase test on Haemophilus spp, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and staphylococcus spp.
- The test is easy to perform and interpret.
Limitations of Acidimetric method
- This test applies only to aerobic bacteria.
- Acidometric test don’t differentiate between acylase and β-lactamase activity.
- Only detect penicillinase, not cephalosporinase enzyme.
Iodometric method of Beta (β) Lactamase Test
Principle of Iodometric method
This method is based on the fact that β -lactamase can hydrolyze penicillin G and release a reducing product (penicilloic acid), which reduces iodine and prevent it from combining with starch. Discoloration of dark blue iodine starch complex indicates positive results.
Requirement of Iodometric method
- Penicillin: (6,000 µg/ml) dissolved in phosphate buffer (pH 6.0, 0.05 to 1 M) Store at 2 to 8°C. Shelf life is 24 h.
- Starch reagent: Add 1 g of soluble starch to 100 ml of distilled water and heat in a boiling water bath until starch dissolves. Store at 2 to 8°C. The shelf life is 1 week.
- Iodine reagents: Dissolve 2.03 g of iodine and 53.2 g of potassium iodide in a small volume of distilled water and make the final volume to 100 ml. Store at 2 to 8°C in a dark bottle; replace if precipitate is apparent. Shelf life is 2 months.
- Empty sterile microdilution tray or small test tube
- Sterile 1 ml pipettes and pipette bulb
- Sterile wooden applicator sticks or inoculating loops
Procedure of Iodometric method
- Dispense 0.1 ml of the penicillin solution into a well of a microdilution tray (or a small test tube).
- Add the test organism to make an opaque, milky suspension.
- Add 2 drops of the starch solution and mix. Let sit at room temperature (approximately 25°C) for 30 to 60 min. Add 1 drop of the iodine reagent. Shake or stir the mixture for 1 min.
- Observe for color change. Decolorization (to white) in less than 10 min indicates a positive reaction. If no color change occurs within 10 min, the test is negative. However, positive reactions for some staphylococci may take up to 1 h.
Results and Interpretation of Iodometric method
- Positive: fading of blue to colorless.
- Negative: blue or purple color.
Applications of Iodometric method
- Iodometric slide test results have been reported to be similar to the Nitrocefin disk test and thus, can be used in detecting Staphylococcal β-lactamase when chromogenic methods are not available.
- Iodometric method is more sensitive and accurate compared to acidometric method for the detection of beta-lactamase production by staphylococcus.
- Most reliable method for testing beta-lactamase production by N. gonorrhoeae.
Limitations of Iodometric method
- Iodometric test is specific to the β-lactamase test but is not a chromogenic method for the detection of enzymes from cephalosporinase activity.
- Acquisition of freshly prepared starch and iodine solution may hinder its routine use.
Reference
- Kuo, S. S., & Feng, T. Y. (1989). Iodometric method for detection of β-lactamase activity in yeast cells carrying ampicillin resistance gene in chimeric plasmids. Analytical biochemistry, 177(1), 165-167.
- Leber, A.L. (2016). Clinical Microbiology Procedure Handbook. Vol.1-3, American Society for Microbiology, ASM Press.
- Livermore, D. M. (1995). beta-Lactamases in laboratory and clinical resistance. Clinical microbiology reviews, 8(4), 557-584.
- Bidya, S., & Suman, R. S. (2014). Comparative study of three β lactamase test methods in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from two Nepalese hospitals. Open Journal of Clinical Diagnostics, 2014.
- Petersson, A. C., Eliasson, I., Kamme, C., & Miörner, H. (1989). Evaluation of four qualitative methods for detection of beta-lactamase production in Staphylococcus and Micrococcus species. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 8(11), 962-967.
- Levesque, R., Letarte, R., & Pechère, J. C. (1983). Comparative study of the beta-lactamase activity found in Achromobacter. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 29(7), 819-826.
