Interesting Science Videos
Barfoed’s Test Definition
Barfoed’s test is a chemical test used to detect the presence of monosaccharides which detects reducing monosaccharides in the presence of disaccharides. This reaction can be used for disaccharides, but the reaction would be very slow.
Objectives of Barfoed’s Test
- To detect reducing carbohydrates.
- To distinguish reducing monosaccharides from disaccharides.
Principle of Barfoed’s Test
The Barfoed reagent is made up of copper acetate in a dilute solution of acetic acid. Since acidic pH is unfavorable for reduction, monosaccharides, which are strong reducing agents, react in about 1-2 min. However, the reducing disaccharides take a longer time of about 7-8 minutes, having first to get hydrolyzed in the acidic solution and then react with the reagent. Once the reaction takes place, thin red precipitate forms at the bottom of the sides of the tube. The difference in the time of appearance of precipitate thus helps distinguish reducing monosaccharides from reducing disaccharides.
Reaction
(CH3COO)2Cu + 2H2O → 2CH3COOH + Cu(OH)2
Cu(OH)2 → CuO + H2O
D-glucose + 2CuO → D-gluconic acid + Cu2O
Requirements
1. Reagent
- Barfoed’s reagent: 0.33M solution of copper acetate is added to 1% acetic acid. The freshly prepared reagent should be used for the assay.
- Sample
2. Materials Required
- Test tubes
- Test tube stand
- Pipettes
3. Equipment
- Water bath
- Vortex
Procedure of Barfoed’s Test
- Take 1 ml of a given sample in a clean, dry test tube. The concentration of disaccharides sample (if used) should not exceed 1% (w/v).
- Take control of 1 ml of distilled water in another tube.
- Add about 2-3 drops of Barfoed’s reagent to both the tubes and mix them in a vortex.
- Keep the test tubes in the water bath for 1-2 minutes. The boiling should not be done for more than 2 minutes as the disaccharides might hydrolyze into monosaccharides and give a positive result.
- Observe the appearance of color in the test tubes.
- Noted own the time taken for the appearance of color in the tubes.
Result and Interpretation of Barfoed’s Test
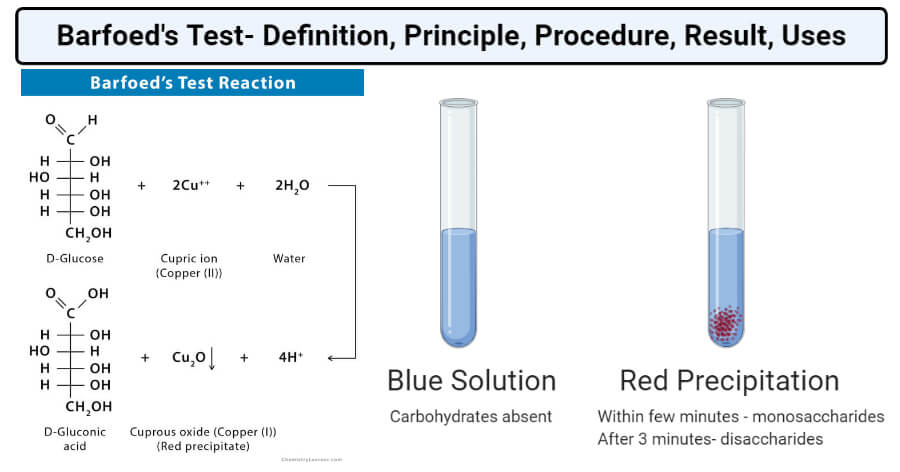
Image Reaction Source: Chemistry Learner, Created with BioRender.com.
- The presence of red precipitate detects the presence of reducing monosaccharides in the sample.
- If the color appears within the first few minutes, the sample contains reducing monosaccharides.
- However, if the color appears later than the first 3 minutes, the sample is of reducing disaccharides.
Uses of Barfoed’s Test
- This test is used to identify reducing monosaccharides and distinguish the reducing disaccharides from reducing monosaccharides.
Limitation of Barfoed’s Test
- This test cannot be used to detect sugar in urine as urine contains Cl– ions, which might interfere with the reaction.
- If a higher concentration of disaccharides is present in a sample, it might give a positive result.
References and Sources
- Tiwari A. (2015). Practical Biochemistry. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing.
- 3% – https://www.coursehero.com/file/70797005/Lab-Report-3-Carbohydratedocx/
- 2% – https://www.coursehero.com/file/p6hnhh1n/2-Barfoeds-Test-Barfoeds-test-is-used-to-distinguish-between-reducing-mono-and/
- 2% – https://generalchemistrylab.blogspot.com/2011/12/barfoeds-test-for-monosaccharides.html
- 1% – https://www.coursehero.com/file/pml2bh/6-Place-the-test-tubes-in-a-boiling-water-bath-for-10-minutes-to-develop-the/
- 1% – https://medicalstudyzone.com/barfoeds-test/
- 1% – https://allmedicalstuff.com/benedicts-test/

How Cl- ions interfere the reaction(which ought to be happened with sugars)
Great results