Interesting Science Videos
What is Immunology?
Immunology is the study of how the body responds to foreign substances and fights off infection and other disease. Immunologists study the molecules, cells, and organs of the human body that participate in this response.
Immunity
Immunity is a condition of being able to resist a particular disease especially through preventing the development of pathogenic microorganism or by counteracting the effects of its products.
Innate immunity is something already present in the body and non-specific. Innate immunity is our first defense against invaders.
Adaptive immunity is created in response to exposure to a foreign substance and specific. The adaptive immune response is mediated by immune cells known as lymphocytes.
Immune System
The immune system is a network of cells and organs that work together to protect the body from infectious organisms. Many different types of organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites are capable of entering the human body and causing disease. It is the immune system’s job to recognize these agents as foreign and destroy them.
Antibodies and Antigens
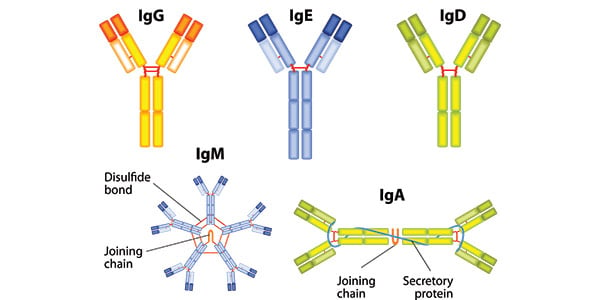
Antibodies, or Y-shaped immunoglobulins, are proteins found in the blood that help to fight against foreign substances called antigens. Antigens, which are usually proteins or polysaccharides, stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies. There are five different antibody types, each one having a different Y-shaped configuration and function. They are the Ig G, A, M, D, and E antibodies.
B-Cells (B lymphocytes)
B lymphocytes, the cells that produce antibodies, arise and maturation occur in the bone marrow. Thus, B lymphocytes now refer to bone marrow–derived lymphocytes.
T-Cells (T lymphocytes)
T lymphocytes, the mediators of cellular immunity, arise in the bone marrow, and migrate to and mature in the thymus; T lymphocytes refer to thymus-derived lymphocytes.
Hypersensitivity
However, in some instances the immune response can be the cause of disease, both as an undesirable effect of an immune response directed against an exogenous antigen, or as a consequence of an autoimmune reaction. These undesirable immune responses known as hypersensitivity, is an abnormal state of immune reactivity that has deleterious effects on the host.
Autoimmunity
Failure of the immune system to “tolerate” self antigens may result in the development of pathological processes known as autoimmune diseases. At the clinical level, autoimmunity is apparently involved in a variety of apparently unrelated diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), myasthenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and hemolytic anemia.

Wow