Interesting Science Videos
Stratified cuboidal epithelium definition
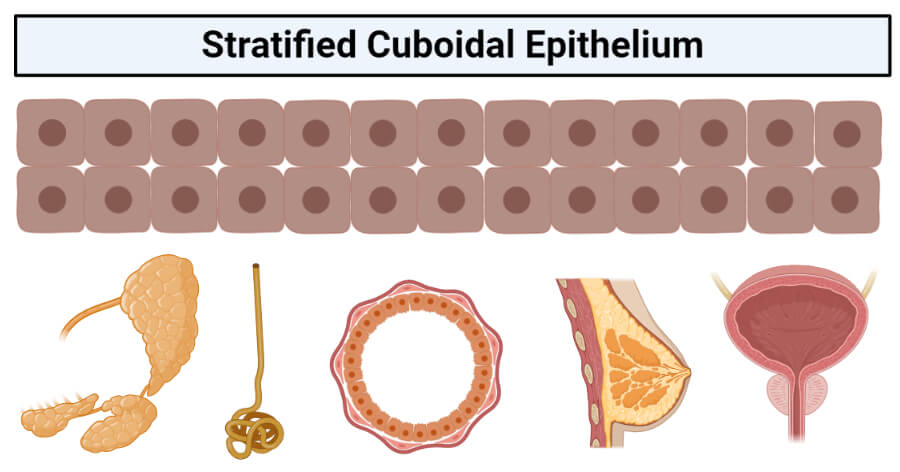
Stratified cuboidal epithelium has multiple layers of cells in which the apical layer is made up of cuboidal cells while the deeper layer can be either cuboidal or columnar. As in the case of stratified squamous epithelium, the cells in the deeper layers might be different than the layer on the top. The modification of the cells on the apical surface is based on the location and function of the epithelial tissue. This epithelium is fairly rare and is only found in some areas throughout the body.
Structure of stratified cuboidal epithelium
- The stratified cuboidal epithelium consists of many layers of cells, of which the cells on the outmost layer are cube-shaped.
- The lower, deeper layers can be both cuboidal or columnar in shape.
- The cells are tightly packed to ensure no gap is present in two cells.
- The basal layer of the epithelium is attached to the basement membrane while the rest of the layers are connected to one another to maintain structural integrity.
- The cells are bound to each other via tight junctions like desmosomes or gap junctions except the apical surface of the outmost layer, which is exposed towards the lumen of the organ.
- As the cells in the basal layer divide, new layers of cells are formed on top. These cells might modify better to suit the function of the epithelium in that region.
- At the apical layer, after dead cells lose cell junctions, they are sloughed off, but they are continuously replaced as new cells emerge from basal cells.
- The epithelium is avascular; that is, there is no direct supply. The epithelium acquires the necessary nutrients, water, and oxygen via diffusion.
- However, the epithelium does have its own nerve supply.
Functions of the stratified cuboidal epithelium
As the epithelium is limited to just a few organs throughout the body, the functions of this epithelium are also based on the organs.
Protection
- The primary function of stratified epithelium is protection.
- As the epithelium has multiple layers, it protects the underlying tissues and internal organs against several physical and microbial damages.
- The gap junctions and desmosomes present on the cells create an impermeable layer preventing the entry of foreign particles.
- At the same time, this epithelium also acts as gatekeepers, filtering out the unwanted particles while allowing the entry of nutrients and water into the cells.
- Because the cells are continuously replaced and repaired, they act as the first line of defense for the protection of the body.
Absorption and secretion
- The stratified cuboidal epithelium also has the function of limited absorption and secretion.
- The epithelium present around the ducts of certain glands secretes some amount of fluid, among other things into the duct.
- Similarly, the stratified cuboidal epithelium in the urethra absorbs water and some ions from the urine.
Location and examples
- In the exocrine system, the stratified cuboidal epithelium is found as the lining of the ducts of the salivary glands, sweat glands, and mammary glands.
- In the same way, it is found in parts of the male urethra in the urinary system.
References and Sources
- Mescher AL (2016). Basic Histology. Fourteenth Edition. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Tortora GJ and Derrickson B (2017). Principles of Physiology and Anatomy. Fifteenth Edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Waugh A and Grant A. (2004) Anatomy and Physiology. Ninth Edition. Churchill Livingstone.
- 4% – https://quizlet.com/118694985/tissue-level-of-organization-ch-4-flash-cards/
- 2% – https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-simple-stratified-and-pseudostratified-epithelial-tissue/
- 1% – https://www.toppr.com/guides/biology/tissues/epithelial-tissue/
- 1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/integumentary-system-373580
- 1% – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3175552/
- 1% – https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/stratified-epithelium
- 1% – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1600-0420.2006.00840.x
- 1% – https://bodytomy.com/functions-of-epithelial-cells
- 1% – https://biologydictionary.net/simple-cuboidal-epithelium/
- <1% – https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/epithelial-tissue/

In the endocrine system, the stratified cuboidal epithelium is found as the lining of the ducts of the salivary glands, sweat glands, and the mammary glands.
correction –
sweat gland and mammary gland = exocrine
Thanks, it has been corrected to exocrine system. 🙂