Interesting Science Videos
Storage Granules Definition
- Storage granules are membrane-bounded vesicles containing condensed materials.
- They are also known as zymogen granules or condensing vacuoles.
- Storage granules are an important component of metabolism in many organisms spanning the bacterial, eukaryotes and archaeal domains.
- These granules are the parts of the cell that store the cell’s energy reserves as well as other important metabolites.
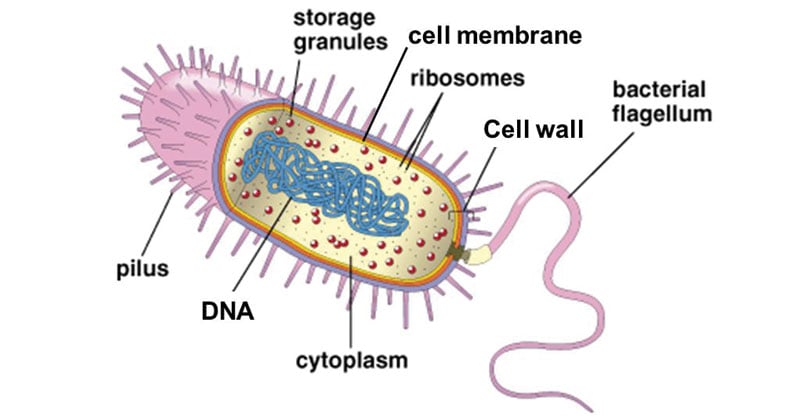
Figure: Diagram of Storage Granules. Image Source: Slide Player
Structure of Storage Granules
- Storage granules are simple small organelles, bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane. On the inside of the membrane, it contains the stored material.
- Different materials may be stored for different purposes by storage granules depending upon the location where they are found. For example, mast‐cell storage granules contain histamine, while those of pancreatic B cells contain insulin.
- Generally, storage granules are polyphosphate bodies that contain a large amount of phosphorous and oxygen. They also have increased levels of iron and magnesium.
- Primary lysosomes which are also called storage granules are newly formed organelles bounded by a single membrane and typically having a diameter of 100 nm. They contain the degradative enzymes which have not participated in any digestive process.
Functions of Storage Granules
- Granules found in plastids or in the cytoplasm, assumed to be food reserves, often of glycogen or other carbohydrate polymers.
- In prokaryotes, nutrients and reserves may be stored in the cytoplasm in the form of glycogen, lipids, polyphosphate, or in some cases, sulfur or nitrogen.
- Sulfur granules are especially common in bacteria that use hydrogen sulfide as an electron source.
- The lysosomes of plant cells are membrane-bounded storage granules containing hydrolytic digestive enzymes, e.g., large vacuoles of parenchymatous cells of corn seedlings, protein or aleurone bodies and starch granules of cereal and other seeds.
References
- Verma, P. S., & Agrawal, V. K. (2006). Cell Biology, Genetics, Molecular Biology, Evolution & Ecology (1 ed.). S .Chand and company Ltd.
- Alberts, B. (2004). Essential cell biology. New York, NY: Garland Science Pub.
- https://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Storage_granule
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jemt.1070320209
- https://www.cellsalive.com/cells/bactcell.htm
- Toso, D. B., Henstra, A. M., Gunsalus, R. P., & Zhou, Z. H. (2011). Structural, mass and elemental analyses of storage granules in methanogenic archaeal cells. Environmental microbiology, 13(9), 2587-99.
- http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803100535190
- https://bio.libretexts.org/TextMaps/Microbiology/Book%3A_Microbiology_(Boundless)/4%3A_Cell_Structure_of_Bacteria%2C_Archaea%2C_and_Eukaryotes/4.6%3A_Specialized_Internal_Structures_of_Prokaryotes/4.6B%3A_Cell_Inclusions_and_Storage_Granules
- https://www.reference.com/science/storage-granules-important-cell-97c6939fc28e88f1

Chemical nature of storage granules of bacteria is?
I feel that is one of the so much vital info for me. And i’m satisfied studying your article.
But want to observation on few common things, The website taste is great, the articles is truly great :
D. Excellent job, cheers