- Earthworms have well-developed sense organs or receptor organs.
- Simple in structures.
- Reacts to a number of stimuli with the help of 3 types of sense organs: epidermal receptor, buccal receptor, and photoreceptor.
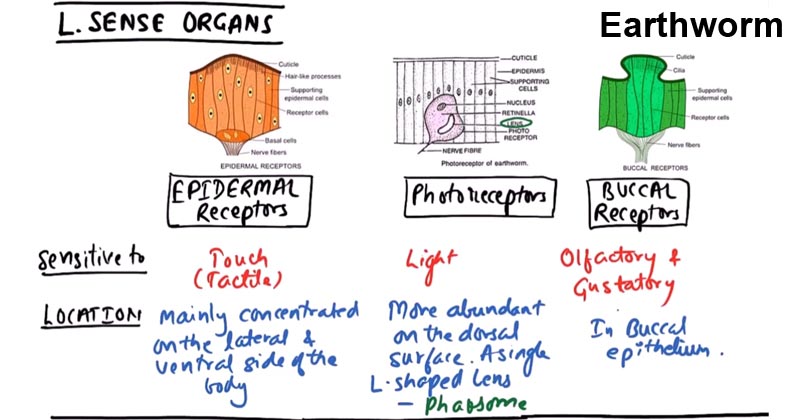
Figure: Sense organs of Earthworm. Image Source: Studio Biology.
Interesting Science Videos
Epidermal receptors
- Distributed all over the epidermis but more abundant on lateral sides and ventral surface of the body.
- They consist of an ovoid tall, slender receptor cell in the epidermis which causes an elevation of the cuticle.
- These cells are separated from each other by space.
- Each cell has a nucleus at different levels and posses internally a few basal cells.
- The receptor cells bear a small hair-like process at their outer ends which penetrate the cuticle and project beyond it.
- And connected nerve fibers at the inner ends.
- They are tactile (relating to touch) in function. i.e., tangoreceptors.
- According to some, they also respond to chemical and thermal stimuli and change in temperature.
- Hence, earthworms are very sensitive to touch and vibrations transmitted through solid objects, though they cannot hear at all.
Buccal receptors
- Found in the epithelium of the buccal cavity in large numbers.
- Similar to epidermal receptors they consist of a group of tall cells which project beyond the epithelial cells except
- They possess broader outer ends.
- They have better sensory hair-like processes.
- Their nuclei lie below the middle parts of the cells.
- These receptors serve to smell i.e., olfactorecptors and taste food i.e.,
- These cells can distinguish between the tastes of different vegetable foods but
- Their sense of smell is poorly developed.
- Also, respond to chemical stimuli.
Photoreceptors
- It is a single ovoid cell in the inner parts of the epidermis.
- Has a nucleus and cytoplasm with a network of neurofibrillae and small transparent L-shaped lens or optic cell or Phaosome
- These cells are curved and made up of hyaline substances.
- One or two nerve fibers enter this optic cell.
- The lens focuses light rays from all directions on neurofibrils.
- Neurofibrils converge to an afferent nerve fiber which leaves the cell at its base to join the central nervous system.
- Restricted only to the dorsal surface and are more numerous on prostomium and peristomium and gradually decrease in number towards the posterior end of the body.
- Totally absent in clitellum.
- These receptors are sensitive to light and also called little eyes or
- The network of photoreceptors is formed by branching and rebranching of the nerve fibers entering into it and characteristically called
- Photoreceptors enable the worm to judge the intensity and duration of light.
- The earthworm shows a negative response to even low light.
- Hence, they retreat into their burrow at daytime and come out at night i.e., nocturnal in habitat.
Video Lecture: Sense Organs in Earthworm By Studio Biology.

References and Sources
- Kotpal RL. 2017. Modern Text Book of Zoology- Invertebrates. 11th Edition. Rastogi Publications.
- Jordan EL and Verma PS. 2018. Invertebrate Zoology. 14th Edition. S Chand Publishing.
- 7% – https://www.biologydiscussion.com/invertebrate-zoology/earthworms/pheretima-habit-and-habitat-and-external-features/29340
- 2% – https://www.shareyouressays.com/knowledge/biology-question-bank-144-mcqs-on-animal-kingdom-answered/114611
- 1% – https://www.answers.com/Q/Why_do_earthworms_come_out_at_night
- 1% – https://askabiologist.asu.edu/smell-taste
