The sandwich ELISA quantify antigens between two layers of antibodies (i.e. capture and detection antibody). Sandwich ELISA is named so as antigen is sandwiched between two antibodies. The sandwich assay uses two different antibodies that are reactive with different epitopes on the antigen with a concentration that needs to be determined.
The antigen to be measured must contain at least two antigenic epitope capable of binding to antibody, since at least two antibodies act in the sandwich. Either monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies can be used as the capture and detection antibodies in Sandwich ELISA systems. Monoclonal antibodies recognize a single epitope that allows fine detection and quantification of small differences in antigen. A polyclonal is often used as the capture antibody to pull down as much of the antigen as possible.
A fixed quantity of one antibody is attached to a series of replicate solid supports, such as plastic microtiter multi-well plate. Test solutions containing antigen at an unknown concentration are added to the wells and allowed to bind. Unbound antigen is removed by washing, and a second antibody which is linked to an enzyme is allowed to bind. This second antibody-enzyme complex constitutes the indicator system of the test. The antigen serves as bridge, so the more antigen in the test solution, the more enzyme-linked antibody will bind. The test solution is used in parallel with a series of standard solutions with known concentrations of antigen that serve as control and reference. The results obtained from the standard solutions are used to construct a binding curve of the second antibody as a function of antigen concentration. The concentration of antigens can be inferred from absorbance readings of standard solutions.
Interesting Science Videos
Sandwich ELISA
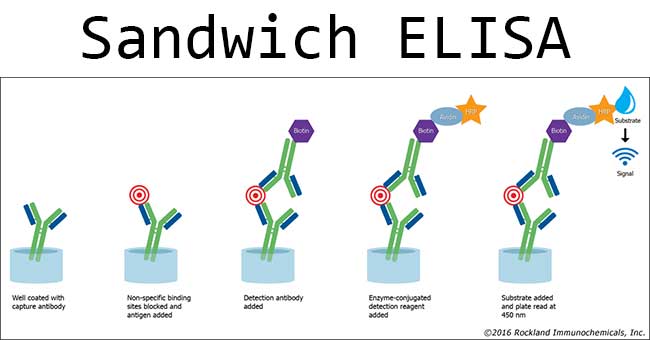
Sandwich ELISA is used for the detection of antigen. In this test, the known antibody is coated and immobilized onto the wells of microtiter plates. The test sample containing the suspected antigen is added to the wells and is allowed to react with the antibodies in the wells. After the step of washing the well, a second enzyme-conjugated antibody specific for a different epitope of the antigen is added and allowed to incubate. After removing any free secondary antibody by rewashing, the specific substrate is added, and the ensuing chromogenic reaction is measured. The chromogenic reaction is then compared with a standard curve to determine the exact amount of the antigen present in the test sample. In a positive test, an enzyme acts on the substrate to produce a color, and its intensity can be measured by spectrophotometer or ELISA reader. The change of color can also be observed by the naked eye.
Steps/ Method of Sandwich ELISA
The steps are as follows:
- Prepare a surface to which a known quantity of capture antibody is bound.
- Block any nonspecific binding sites on the surface.
- Add antigen-containing sample to the plate.
- Wash the plate, so that unbound antigen is removed.
- A specific antibody is added, and binds to antigen (hence the ‘sandwich’: the Ag is stuck between two antibodies);
- Add enzyme-linked secondary antibodies as detection antibodies that also bind specifically to the antibody’s Fc region (non-specific).
- Wash the plate, so that the unbound antibody-enzyme conjugates are removed.
- Add substrate that is converted by the enzyme into a color or fluorescent or electrochemical signal.
- Measure the absorbeance or fluorescence or electrochemical signal (e.g., current) of the plate wells to determine the presence and quantity of antigen.
Sandwich ELISA Advantages:
- It has high specificity since two antibodies are used and antigen/analyte is specifically captured and detected.
- It is suitable for complex samples as antigen does not require purification prior to measurement.
- Has good flexibility and sensitivity, since both direct and indirect detection methods can be used.

Very Nice article,understandtable with easy language.keep posting sir
I clear my confusion from here nand I need these pdf
Iwnont thise resarch pdf please