The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) which consists of ribosomes on its surface is known as the rough endoplasmic reticulum. So it is also called the granular endoplasmic reticulum.
- Translocon is the binding site of the ribosome on the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- These ribosomes look like studs and they can distinguish the organelle from the smooth sections of the ER.
- Proteins are synthesized from amino acids. It is with the aid ribosome.
- Ribosomes consist of four RNA molecules.
- The attachment of ribosomes over the surface of RER through two types of glycoproteins. They are:
- Riboprotein I (6500 daltons) and Riboprotein II (6400 daltons).
- RER consists of more cisternae and fewer tubules and vesicles.
- Near the nucleus, it is more abundant where it is connected with its outer membrane.
- RER is basophilic.
- So, it is also called ergastoplasm by Garnier, 1897.
- RER is present in the cells which are involved in the active transport of protein as well as in the synthesis of enzymes. It includes:
- Acinar cells of the pancreas
- Plasma cells
- Goblet cells
- Cells of endocrine glands
- In conjunction with the Golgi complex, RER helps in the formation of primary lysosomes.
- It involves the synthesis, folding, and modification of proteins.
- It includes those cells which need to be transported to different cellular organelles in the cell.
- It is involved in the response of the cell to unfolded protein.
- It plays a role in the induction of apoptosis.
- It is due to the close interaction with mitochondria.
- Polysomes are strings of ribosomes that synthesize the proteins.
- Morphology also aids in the identification. Its structure is often convoluted and flattened which seems like the sac.
- It originates in proximity to the nucleus.
- RER has the membrane in association with the outer nuclear membrane.
- It forms large membrane sheets which are double.
- It is best studied within the secretory cells specialized in these functions.
Interesting Science Videos
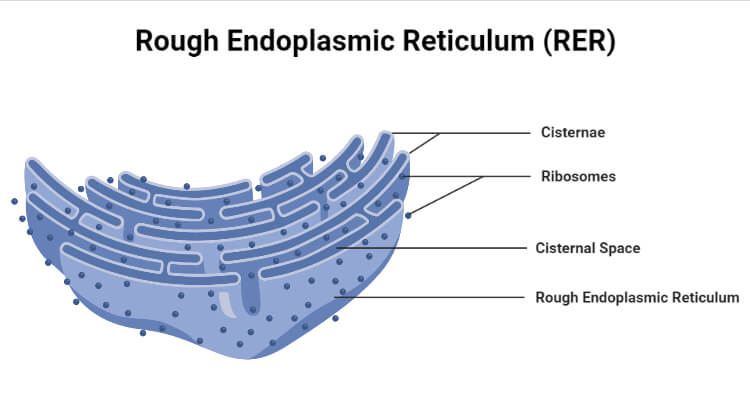
Structure of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
It consists of three structures. They are:
Cisternae
- Its diameter is 40 to 50 µm.
- They are long, flattened, sac-like, and unbranched tubules.
- In the bundles, they are aligned parallel.
- RER usually is present as cisternae, They are found in cells like the pancreas, brain, and notochord where the synthesis usually takes place.
Vesicles
- The diameter of the vesicle is 25 to 500 µm.
- They are oval-shaped.
- They seem like the vacuole which is bound by the membrane.
- They are usually found in the cytoplasm in isolated form.
- It is found in most cells. As compared to SER they are less abundant.
Tubules
- They are branched structures.
- It forms the reticular system.
- They are usually present in all cells.
- Its diameter is 50 to 190 µm.
- These structures are usually found in SER.
Functions of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
- It is the site for the synthesis of protein.
- Polypeptides are synthesized.
- Ribosomes synthesize proteins and enzymes.
- It then enters through the RER’s channel which is used both for intracellular use and extracellular transport.
- Some proteins are to be secreted from the cell or they need to be exported.
- Some proteins are essential in the synthesis of cellular membranes.
- Such proteins are assumed to be synthesized by the RER.
- In the nascent protein at the side of COOH, about 40 amino acids are present. They are protected inside the tunnel of free or bound ribosomes.
- Similarly, it is found that the lumen of the RER is involved in the protection of the rest of the chain at the NH2 end.
- During the translation, nascent polypeptide chai pass to the cisternae of ER.
- When the growing polypeptide chain, reaches the cisternae, it gets trapped in it by folding it into the secondary and tertiary structure.
- It provides the surface area for the association of many things.
- It includes metabolically active enzymes, amino acids, and ribosomes.
- It protects the secretory proteins from the protease enzymes which are present in the cytoplasm.
- So they pass in the cisternae of RER instead of passing into the cytoplasm
- By losing the ribosomes, it forms the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
- For holding the ribosomes, it consists of ribophorins.
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes the zymogens of lysosome enzymes.
- The RER provides enzyme precursors for the formation of lysosomes with the help of the Golgi complex.
Protein glycosylation
- It is the process of the addition of sugar in secretory proteins.
- During this process, oligosaccharides get transported in the proteins.
- This oligosaccharide is always transferred to the NH2 group on the side chain of an asparagines residue of the protein.
- So, this oligosaccharide is said as asparagines-linked or the N-linked.
- This transfer is aided by the enzyme glycosyltransferase. It is a membrane-bound enzyme. On the luminal surface of the ER membrane, its active site is exposed.
- In the Endoplasmic membrane, the precursor oligosaccharide is held by dolicol.
- Dolicol is the carrier which is a special lipid molecule.
Comparison of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) with Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Ribosomes: Present in rough ER and absent in smooth ER.
Composition: Rough ER is made up of more cisternae and few tubules. Smooth ER is made up of more tubules and vesicles.
Presence: Rough ER is present in protein and enzyme-forming cells like Pancreatic cells, new cells, etc. Smooth ER is found mainly in lipid forming cells: adipocytes, interstitial cells, adrenal cortical cells, etc.
Ribophorins: Present in rough ER and absent in smooth ER.
Formation: Rough ER is believed to be formed from the outer nuclear membrane. Smooth ER is developed from rough ER by loss of ribosomes.
Function: Rough ER helps information and transportation of proteins and enzymes. Smooth ER helps in the formation of lipid, glycogen, and steroids.
References
- Shakya, M., Mehata, K.R., Gautam, M.K., Pokhrel, K.R., and Khanal, K. (2020 ) “ Principles of Biology”, Asmita Books Publisher and Distributors Ltd, Bhotahity, Nepal
- Verma, P. S., and Agrawal, V. K. (2006). Cell Biology, Genetics, Molecular Biology, Evolution & Ecology (1 ed.). S.Chand and Company Ltd.
- https://biologydictionary.net/rough-endoplasmic-reticulum/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/cell-biology/The-endoplasmic-reticulum#ref313734
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endoplasmic_reticulum

Good am too much interested to read this