- The second major blood grouping system is the Rhesus (Rh) system.
- Philip Levine, in 1939, discovered that the sera of most women who gave birth to infants with hemolytic disease contained an antibody that reacted with the red cells of the infant and with the red cells of 85% of Caucasians.
- In 1940, Landsteiner and Wiener injected blood from the monkey Macacus rhesus into rabbits and guinea pigs, and discovered the resulting antibody agglutinated rhesus (Rh) red cells, which appeared to have the same specificity as the neonatal antibody.
- The donors whose cells were agglutinated by the antibody to Rh red cells were termed Rh positive; those whose cells were not agglutinated were termed Rh negative.
- It is now known that the antibody obtained by Landsteiner and Wiener reacts with an antigen (LW) is different but is closely related to the one that is recognized in human hemolytic disease, but nevertheless the Rh nomenclature is still retained.
- Like the ABO blood types, the Rh factor is an inherited blood protein, or antigen, on red blood cells.
Interesting Science Videos
Rh Blood Group Antigens
- The term Rh blood group system refers to the five main Rh antigens (C, c, D, E, and e) as well as many other less frequent Rh antigens.
- The terms Rh factor and Rh antigen are similar, and both refer to the RhD antigen only.
- Of all the Rh antigens, antigen D (RhD) is most important.
D-antigen
- Individuals either have or do not have the RhD antigen on the surface of their red blood cells.
- This is usually indicated by “RhD positive” (does have the RhD antigen) or “RhD negative” (does not have the antigen) suffix to the ABO blood type.
- This suffix is often shortened to “D pos”/“D neg,” “RhD pos”/“RhD neg,” or +/-.
- The latter symbol is generally not preferred in research or medical situations, because it can be altered or obscured accidentally.
- There are several alloantigenic determinants within the Rh system.
- Clinically, the D antigen has a lot of medical importance. This is because RhD negative individuals who receive RhD positive erythrocytes by transfusion can develop alloantibodies that may lead to severe reactions with further transfusions of RhD-positive blood.
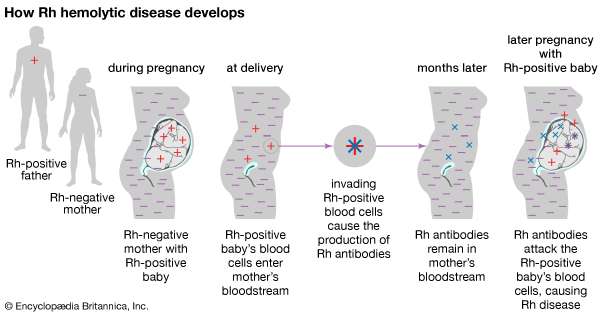
- The D antigen also poses a problem in RhD-negative mothers who bear a child with RhD-positive red cells inherited from the father. The entry of fetal erythrocytes into the maternal circulation at parturition or trauma during the pregnancy (such as in amniocentesis) can lead to alloimmunization against the RhD antigen. This may cause hemolytic disease of the newborn in subsequent pregnancies. This can now be prevented by the administration of Rh (D) immunoglobulin to these women within 72 hours of parturition.
- Unlike the ABO system, there are no natural antibodies against Rh antigens.
- Antibodies against Rh antigens develop only in certain situations, such as in Rh incompatible pregnancy or transfusion.
- Most of these antibodies are IgG antibodies and few IgM antibodies.
- These are incomplete antibodies and can be detected in newborn blood by direct Coombs’ test and in mother blood by indirect Coombs’ test.

Please when a 3 months pregnant Rh negative woman losses the pregnancy due to miscarriage or abortion on her first pregnancy, is she
1. sensitized?
2. Did the foetus blood mix with her own?
3. If No please at what stage of pregnancy is the foetus blood said to mix with the mother’s.
4. If Yes please what’s the solution to protect future pregnancy.
Thanks for your concern and this are very important knowledge.
Nice thanks i am Very to this knowledge
effective for learning
Very informative Article.