- Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique in which organisms may be differentiated by analysis of patterns derived from cleavage of their DNA.
- It is a technique that exploits variations in homologous DNA sequences.
- A restriction fragment length polymorphism is defined by the existence of alternative alleles associated with restriction fragments that differ in size from each other. Simply, the variations in the restriction DNA fragments length between individuals of a species is called RFLP.
- The basic technique of identifying such restriction fragment length polymorphisms involve fragmenting a sample of DNA by a restriction enzyme, which can recognize and cut DNA wherever a specific short sequence occurs, in a process known as a restriction digest.
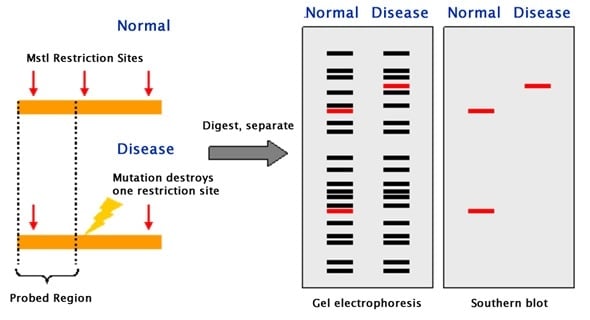
- The resulting DNA fragments are then separated by length through a process known as agarose gel electrophoresis, and transferred to a membrane via the Southern blot procedure. Hybridization of the membrane to a labeled DNA probe then determines the length of the fragments which are complementary to the probe.
- An RFLP occurs when the length of a detected fragment varies between individuals.
- Although now largely obsolete due to the rise of inexpensive DNA sequencing technologies, RFLP analysis was the first DNA profiling technique inexpensive enough to seek widespread application.
Interesting Science Videos
Principle of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
If two organisms differ in the distance between sites of cleavage of a particular restriction endonuclease, the length of the fragments produced will differ when the DNA is digested with a restriction enzyme. The similarity and differences of the patterns thus generated can be used to differentiate species (and even strains) from one another.
Steps Involved in Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
- The first step in this process is to isolate the DNA from the target.
- Once the the DNA is isolated from the sample it is subjected to restriction digestion using restriction enzymes.
- The digested DNA sample is then subjected to gel electrophoresis, in which the DNA is separated based on its size. Many DNA fragments with slight differences in length are produced.
- The gel is then exposed to a chemical to denature double-stranded DNA to become single- stranded.
- This is followed by southern blotting where DNA is transferred from gel to nylon membrane.
- The nylon membrane is then exposed to solution with radioactive complementary nucleotide probes that hybridize to specifically chosen DNA sequences on nylon membrane.
- The membrane is then placed against X- ray film, where hybridized radioactive probes cause exposure of X-ray film, producing an autoradiogram.
- RFLP analysis is carried out to detect differences in pattern to confirm polymorphisms.
Applications of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
RFLP analysis was formerly an important tool in genome mapping, localization of genes for genetic disorders, determination of risk for disease, and paternity testing.
RFLP can be used in many different settings to accomplish different objectives:
- In paternity cases or criminal cases to determine the source of a DNA sample. (i.e. it has forensic applications).
- Determining the disease status of an individual. (e.g. it can be used in the detection of mutations)
- To measure recombination rates which can lead to a genetic map with the distance between RFLP loci.
- In the characterization of genetic diversity or breeding patterns in animal populations.
- RFLP has been developed for chromosomes mapping of humans, mice, maize, tomato, rice, etc.
Advantages of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
- The main advantage of RFLP analysis over PCR-based protocols is that no prior sequence information, nor oligonucleotide synthesis, is required.
- Results are based on reliable genotypic characteristics’ rather than on phenotypes.
- RFLP based Genetic Marker
- RFLP is the co dominant marker thus can estimate heterozygosity.
- RFLP & is very useful study in Genomic DNA Sequence.
- Highly robust methodology with good transferability between laboratories.
Limitations of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
- Slow
- Cumbersome
- Requires a large amount of sample DNA.
- Automation not possible
- Low levels of polymorphism in some species
- Few loci detected per assay
- Need a suitable probe library
- Needing the combined process of probe labeling, DNA fragmentation, electrophoresis, blotting, hybridization, washing, and autoradiography.
References
- https://www.slideshare.net/ferisaber/rflp-55298956
- https://www.slideshare.net/orampo/restriction-fragment-length-polymorphism-29253376
- http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/staff/dave/roanoke/genetics980211.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Restriction_fragment_length_polymorphism
- https://www.princeton.edu/~lsilver/book/MG8.html
- https://www.slideshare.net/ArunimaSur/rflp-rapd
- https://cropgenebank.sgrp.cgiar.org/images/file/learning_space/molecular_markers/volume1/RFLPs.pdf

Useful basic information about RFLP
Thank you so much I appreciate it a lot
The “Steps involved in ….” pic doesnt match the text. Southern blot isnt shown. Pic shows a simple demo technique sometimes used in skool, but that isnt real RFLP.
Yes, the picture doesn’t match the steps, its the simple demo only, Thanks 🙂
Very useful for Post graduate students