Interesting Science Videos
What is Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)?
Papanicolaou stain is also known as the pap stain and the procedure of the stain is known as a pap smear.
- It is a polychromatic stain that uses multiple dyes to differentially stain various components of the cells.
- It is a histological and cytopathological staining technique used to differentiate cells in a smear preparation.
- It is the most common screening method for cervical cancer.
- Several specimens can be used to prepare the pap smear depending on the screening infection, including sputum, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, abdominal fluid, tumor biopsies, synovial fluid, fine needle aspirates, pleural fluids.
- The technique was developed by George Papanicolaou in 1942.
Objectives of Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)
- To define the cell nuclear to aid in the identification of nuclear abnormalities of cancer cells.
- To stain the cytoplasm and make it transparent for visualization
- To differentiate and identify certain cell types such as acidophils and basophils.
Principle of Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)
The stain uses both basic and acidic dyes such that the basic dye stains acidic components of the cell while the acidic dyes stain the basic components of the cells. This is based on the ionic charges of the components of the cell with the principle of attraction and repulsion of the ions and the dyes. Five dyes are used in three solutions as the main reagents used in the stain.
- Hematoxylin: This is a natural dye that stains the cell nuclear blue. The dye attaches to the sulfate groups of DNA because it has a high affinity for nuclear chromatins. The most common hematoxylin dyes used are Harris’ hematoxylin, Gills’ H is the commonest cytologically although Gills’ hematoxylin and Hematoxylin S.
- Orange Green 6: It is an acidic counterstain that stains the cytoplasm of mature keratinized cells. The components of the target stain orange in varying intensities of the dye.
- Eosin Azure: It is the second counterstain, a combination of eosin Y, light green SF, and Bismarck brown. Eosin Y stains the cytoplasm of mature squamous cells, nucleoli, Red blood cells, and cilia pink. The eosin dyes commonly used are EA 31 and EA 50, while EA 65. Light green SF stains the cytoplasm of active cells such as columnar cells, parabasal squamous cells, and intermediate squamous cells, blue. Bismarck brown Y stains nothing and sometimes it is often omitted.
Composition of the Reagents of Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)
Harris’ hematoxylin
- Hematoxylin = 2.5g
- Ethanol = 25ml
- Potassium alum = 50g
- Distilled water (50°C) = 500ml
- Mercuric oxide = 1-3g
- Glacial acetic acid = 20ml
Orange G 6
- Orange G (10% aqueous) = 25ml
- Alcohol = 475ml
- Phosphotungstic acid = 0-8g
EA 50
- 0.04 M light green SF = 5ml
- 0.3M eosin Y = 10ml
- Phosphotungstic acid = 1g
- Alcohol = 365ml
- Methanol = 125ml
- Glacial acetic acid = 10ml
Other reagents include 95% ethanol, 100% ethanol, tap water, Scott’s tap water, xylene
Basic Procedure for Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)
- Fix the smear with 95% Ethanol 15 minutes
- Rinse in tap water
- Add the Harris Hematoxylin dye for 1-3 minutes
- Rinse in tap water or Scott’s tap water
- Dip the preparation in 95% Ethanol 10 dips
- Add orange G-6 stain for 1.5 minutes.
- Dip in 95% Ethanol 10 dips
- Add Eosin dye; EA-50, or Modified EA-50, or EA-65 stain for 2.5 minutes.
- Dip in 95% ethanol 10 dips, 2 changes
- Add 100% Ethanol for 1 minute
- Clear in 2 changes of xylene, 2 minutes each
- Mount with permanent mounting medium
Results and Interpretation of Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)
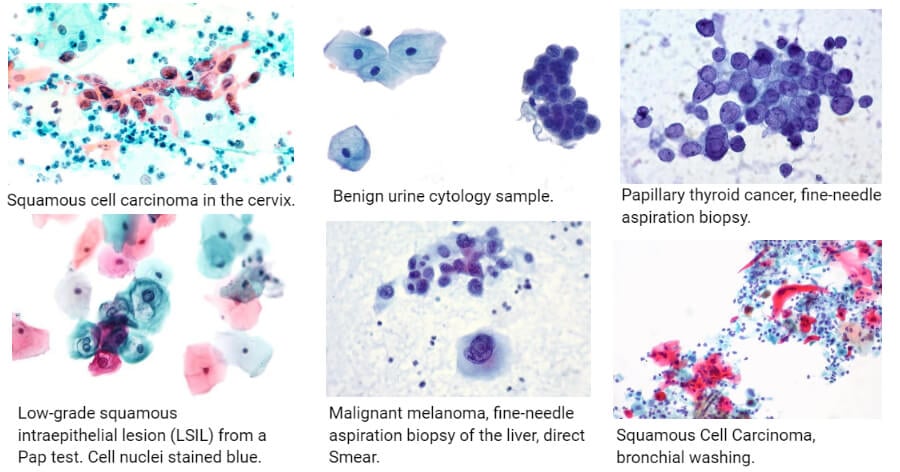
Image Source: Wikipedia.
Staining dyes will stain different components of the cell with different colors and intensities as follows:
- Nuclei: Blue
- Acidophilic cells: Red
- Basophilic cells: Blue Green
- Erythrocytes: Orange-red to dark pink
- Keratin: Orange-red
- Superficial cells: Pink
- Intermediate and Parabasal Cells: Blue-Green
- Eosinophil: Orange Red
- Metaplastic cells: May contain both blue/green and pink
- Candida: Red
- Trichomonas: Grey-green
Applications of Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)
- Used in the Pap smear (or Pap test).
- Screening for cervical cancer.
- Examination of myeloma cancer cells of the liver.
- Screening for thyroid cancer.
- Screening for cell carcinomas.
- Examination and characterization of benign tumors.
- Identification of Candida species.
- Identification of Chlamydia trachomatis.
Limitations of Papanicolaou Staining (Pap stain)
- It is only a screening test that must be followed up with more specialized diagnostic tests.
- It has low sensitivity with limited accuracy.
References and Sources
- 12% – https://laboratoryinfo.com/papanicolaou-pap-staining-principle-procedure-interpretation/
- 3% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341038479_New_screening_method_for_cervical_cancer_-_polar_prob_TruScreen/fulltext/5eaa3675a6fdcc70509b06db/New-screening-method-for-cervical-cancer-polar-prob-TruScreen.pdf
- 3% – http://ihcworld.com/_protocols/special_stains/papanicolaou_stain.htm
- 1% – https://wikimili.com/en/H&E_stain
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pap_stain

The information was helpful, and thanks for work well done.
Am medical Laboratory Technology live in uganda Am looking for scholaship so that finish my couse.If you can help ,help.