Interesting Science Videos
Objective of Microdase (Modified Oxidase) Test
This test is used to differentiate gram-positive, catalase-positive cocci (micrococci from staphylococci).
Principle of Microdase (Modified Oxidase) Test
The microdase test, also known as modified oxidase test is a rapid test to differentiate Staphylococcus from Micrococcus which are Gram positive cocci possessing catalase enzyme. The differentiation is based on the detection of oxidase enzyme. For the detection of oxidase enzyme a filter paper circular disks impregnated with tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (oxidase reagent) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) are used. The modified oxidase reagent is prepared as 1% (w/v) tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine in certified grade dimethyl sulfoxide. DMSO aids in the permeability of cells to the reagent. In the presence of atmospheric oxygen, the oxidase enzyme reacts with the oxidase reagent and cytochrome C to form the colored compound, indophenol indicated as blue or purplish blue coloration on the disc after the introduction of bacterial colony on the disc.
Media Used in Microdase (Modified Oxidase) Test
Oxidase Disc
Filter paper disks impregnated with tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (oxidase reagent) in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Procedure of Microdase (Modified Oxidase) Test
- Using sterile forceps transfer a Microdase disk from the stock bottle to a petri dish.
- Using a wooden applicator stick, rub a small amount of several colonies of an 18-24 hour pure culture grown on blood agar onto the top of microdase disk.
- Incubate at room temperate for 2 minutes
- Observe for the colour development
Result Interpretation of Microdase (Modified Oxidase) Test
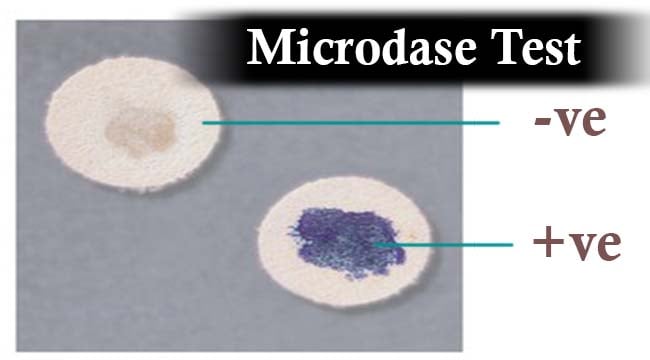
Positive test: development of blue or purple blue on the disc within 2 minutes
Negative test: no color change
Limitations
- Staphylococci should yield a negative color change, except for S. sciuri, S. lentus, and S. vitulus.
Quality Control
Positive: Micrococcus luteus (ATCC10240)
Negative: Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC25923)
References
- Tille P.M (2014). Bailey and Scott’s diagnostic microbiology.Thirteen edition. Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 3251 Riverport Lane, St. Louis, Missouri 63043
- Faller A, Schleifer KH. Modified oxidase and benzidine tests for separation of staphylococci from micrococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jun;13(6):1031–1035.
- Tarrand JJ, Gröschel DH. Rapid, modified oxidase test for oxidase-variable bacterial isolates. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 1982;16(4):772-774.
