Masson’s Trichrome Staining definition
Masson’s Trichrome Staining is a histological staining method used for selectively stain collagen, collagen fibers, fibrin, muscles, and erythrocytes. It uses three stains for staining hence the term Trichrome. These are Weigert’s Hematoxylin, Biebrich scarlet-acid fuschin solution, and Aniline blue.
Interesting Science Videos
Objectives of Masson’s Trichrome staining
- To stain the collage fibers.
- To stain collagen.
- To stain keratin.
- To stain fibrin.
- To stain muscle fibers.
Principle of the Masson’s Trichrome Staining
By use of the three stains, Masson’s Trichrome staining technique is used for the detection of collagen fibers in tissues such as the skin, heart, muscles. The samples are formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections, or frozen sections. Weigert’s Hematoxylin, an iron hematoxylin dye is used to stain the nuclei. This dye is resistant to decolorization by acidic staining solutions. Biebrich scarlet-acid fuschin solution stains all the acidic tissues such as the cytoplasm, muscle, and collagen. Phosphomolybdic or phosphotungstic acid is used as a decolorizing agent, making the Biebrich Scarlet-acid fuschin to diffuse out of the collagen fibers. this leaves the muscle cells staining red. Aniline blue stains the collagen along which 1% acetic acid is added to show a difference in the tissue sections. The collagen fibers stain blue and the nuclei stains black, with a red background.
Read Also: Wheatley Trichrome Staining
Reagents and Reagent preparation
Bouin’s Solution (It improves the quality of Masson Trichrome Stain)
- Saturated Picric acid 75 ml
- 40% Formaldehyde 25 ml
- Glacial acetic acid 5 ml
Weigert’s Iron Hematoxylin Solution
- Stock Solution A
- Hematoxylin 1g
- 95% alcohol 100ml
- Stock solution B
- 29% Ferric chloride in water 4ml
- Distilled water 95ml
- Concentrated Hydrochloric acid 1ml
- Equal parts of stock solution A and B are mixed for use. The mixture is only stable for not more than 3 months.
Biebrich Scarlet-Acid Fuschin Solution
- 1% aqueous Biebrich Scarlet 90ml
- 1% aqueous Acid fuschin 10 ml
- Glacial acetic acid 1 ml
Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Solution
- 5% Phosphomlybdic acid 25ml
- 5% Phosphotungstic acid 25ml
Aniline Blue Solution
- Aniline blue 2.5g
- Glacial acetic acid 2ml
- Distilled water 100ml
1% Acetic Acid Solution
- Glacial acetic acid 1ml
- Distilled water 99ml
Procedure of Masson’s Trichrome Staining
- Deparaffinize and rehydrate using 100% alcohol, 95% alcohol, and 70% alcohol sequentially.
- Wash in distilled water.
- For tissues fixed with Formalin, re-fix in Bouin Solution for 1 hour at 56C. This improves the quality of the stain.
- Rinse with running tap water for 5-10 minutes to remove yellow color.
- Stain with Weigert’s iron hematoxylin solution for 10 minutes.
- Rinse the stain with running tap water for 10 minutes.
- Wash in distilled water.
- Stain with the Beibrich-Scarlet Acid Fuschin solution for 10-15 minutes.
- Wash in distilled water.
- Differentiate in the phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid solution for 10-15 minutes or until the collagen loses its red color.
- Transfer the stained section to aniline blue solution and stain for 5-10 minutes.
- Rinse the stained section briefly in distilled water and differentiate with 1% acetic acid solution for 2-5 minutes.
- Wash in distilled water.
- Quickly dehydrate through 95% ethyl alcohol.
- Clear in xylene.
- Mount with a mounting medium.
Results and Interpretation of Masson’s Trichrome Staining
- Collagen fiber stains blue.
- The nuclei stains black.
- The muscles, cytoplasm, and keratin stain red.
- The background stains red.
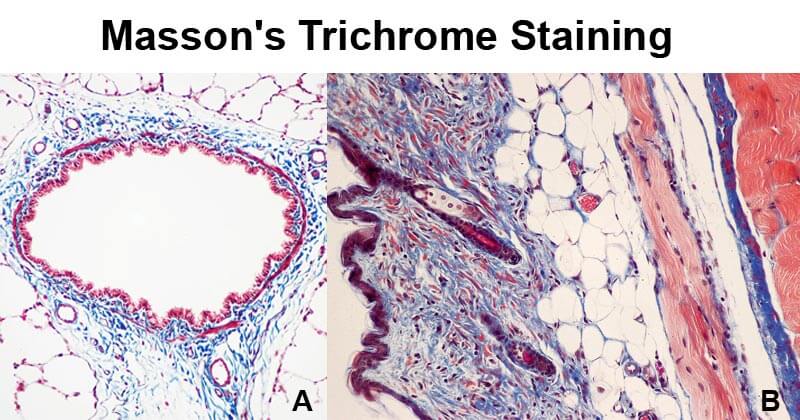
Figure A- Masson’s trichrome stain of rat airway. Connective tissue is stained blue, nuclei are stained dark red/purple, and cytoplasm is stained red/pink. Figure B- Mouse skin stained with Masson’s trichrome stain. Image Source: Wikipedia.
Applications
- To study muscular dystrophy and other muscular pathologies
- To study cardiac infections and other cardiac pathologies
- To study hepatic pathologies such as cirrhosis
- to study kidney pathologies such as glomerular fibrosis
- To detect and analyze tumors on hepatic and kidney biopsies.
Advantages
- It can be used to measure and differentiate the collagen deposition as compared to the Hematoxylin-Eosin Y Staining method.
- It produces clear images of the collagen fiber as compared to other stains.
- It is more accurate than most staining techniques.
Limitations
- The stock solutions must be used within 24 hours of preparation.
- The stain must be performed with caution and while wearing protective clothing to avoid exposure to the corrosiveness of the reagents used.
References and Sources
- https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=MY2016000018
- https://webpath.med.utah.edu/HISTHTML/MANUALS/MASSONS.PDF
- https://www.labce.com/spg531613_massons_trichrome_staining___chemistry.aspx
- http://www.ihcworld.com/_protocols/special_stains/masson_trichrome.htm
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/massons-trichrome-stain
- https://treat-nmd.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/cmd-MDC1A_M.1.2.003-67.pdf
- https://www.polysciences.com/default/catalog-products/life-sciences/histology-microscopy/staining-histology-cytology/dyes-and-stains-for-histology/massons-trichrome-stain-kit/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Masson%27s_trichrome_stain

Your presentation was very detailed!!! I love it!! I am currently studying for my HT, and this helps me to understand a lot more.
Thank you!!