Interesting Science Videos
Gelatin Hydrolysis Test Definition
Gelatin hydrolysis test is a biochemical test performed as a presumptive test for the identification of Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, and other Gram-positive bacilli.
- Gelatin hydrolysis test is also termed as the Gelatin Liquefaction test as it involves the liquefaction of gelatin in the presence of the gelatinase enzyme.
- Gelatinase is an important enzyme in various pathogenic organisms as it is produced extracellularly, which hydrolyses gelatin which is derived from the collagen found in the connective tissues of vertebrates.
- These enzymes might work as a virulence factor that dissolves the connective tissues of the host’s cells which aids in the invasive infections.
- Gelatin is a protein that liquefies in the presence of gelatinase enzyme as the enzyme breaks down the complex structure of gelatin into monomeric amino acids.
- The test has been used for years as a presumptive test for the identification of a wide variety of organisms like Serratia, Pseudomonas, Flavobacterium, and Clostridium.
Objectives of Gelatin Hydrolysis Test
- To test an organism’s ability to liquefy gelatin by the production of gelatinase enzyme.
- To differentiate organisms into different groups based on their ability to hydrolyze gelatin.
Principle of Gelatin Hydrolysis Test
- Gelatin is a protein derived from animal connective tissue, collagen, which forms a solid structure at lower temperatures.
- The protein is metabolized or degraded by a group of enzymes called gelatinase.
- Gelatinases are proteolytic enzymes that hydrolyze gelatin into polypeptides and individual amino acids.
- The degradation of gelatin, like most proteins, occurs in two steps; the first step involves the degradation of gelatin into polypeptides, followed by the conversion of polypeptides into amino acids.
- Gelatinase is important in most bacteria as the gelatin is a large polymer and thus cannot be transported into the cell.
- The enzyme, thus, breaks down gelatin into smaller units, which can be transported into the cell and utilized by the bacteria.
- In the hydrolysis test, media with gelatin is used, and its hydrolysis is observed either by the liquefaction of the media or by flooding with mercuric chloride.
- The mercuric chloride added to the medium precipitates gelatin while the areas where the gelatin is hydrolyzed appear clear.
Microorganisms Tested
- Gram-negative rods that require gelatin for identification, especially for the separation of the fluorescent Pseudomonas: Pseudomonas putida (negative) from Pseudomonas fluorescens (positive).
- Gram-positive rods as needed for identification to the species level.
Media, Reagent, and Supplies Used
Media Used
- Nutrient Gelatin Media is used for the demonstration of gelatin hydrolysis either by adding mercuric chloride or by the liquefaction of gelatin.
- The composition of the Nutrient Gelatin Media is given below:
| S.N | Ingredients | Gram/liter |
| 1. | Tryptose | 20.0 |
| 2. | Beef extract | 3.0 |
| 3. | Gelatin | 10.0 |
| 4. | Manganese sulfate | 0.01 |
| 5. | Agar | 15.0 |
| Final pH at 25°C: 6.8 ±0.2 | ||
Reagent Used
- Mercuric chloride (HgCl2)
Supplies Used
- Inoculating needle
- Incubator at 37°C
- Pipettes
Procedure of Gelatin Hydrolysis Test
A. Preparation of the media
- About 128 grams of the dehydrated medium is taken in a beaker with 1000 milliliters of warm (50°C) distilled water.
- The solution is then heated with agitation to bring it to boiling in order to dissolve the medium completely.
- The medium is dispensed into several test tubes and autoclaved at 15 lbs pressure (121°C) for 15 minutes. In the case of the agar plate method, the medium is autoclaved in the beaker.
- The tubed medium is cooled to 45-50°C in an upright position.
B. Gelatin Hydrolysis
Gelatin hydrolysis can be observed whether via nutrient gelatin stab method or by flooding the agar plates with mercuric chloride.
1. Stab method
- The gelatin medium in the tube is inoculated with 4-5 drops of a 24-hour broth medium.
- The inoculated tubes are incubated at 37°C in air for 24-48 hours. If the organisms grow well at 25°C, the incubation has to be done at 25°C.
- After the first incubation, the tubes are to be placed at 4°C for another 24 hours.
2. Plate method
- Heavy inoculum of an 18-24 hour culture is taken with an inoculating loop and inoculated on nutrient gelatin medium.
- The plates are then incubated at 37°C for 24-48 hours.
Result Interpretation of Gelatin Hydrolysis Test
Tube test
- Partial or total liquefaction of gelatin in the test tubes indicates a positive result.
- Complete solidification of gelatin at 4°C represents a negative result.

Figure: Gelatin hydrolysis. Positive; liquefaction at top of the tube. Image Source: Bailey and Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology. Elsevier.
Plate Method
- A clear zone around the colonies after the addition of mercuric chloride (HgCl2) indicates a positive result on agar plates.
- No clear zones around the colonies after the addition of mercuric chloride are representative of a negative result.
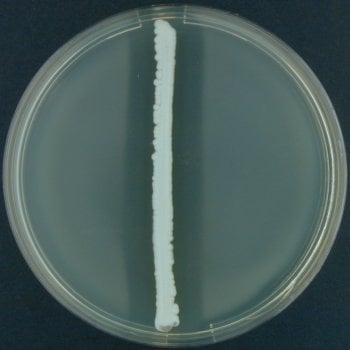
Figure: Gelatin hydrolysis positive reaction. Image Source: Department of Veterinary Disease Biology, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen.
Denmark.
Control organisms
- Positive result: Bacillus subtilis.
- Negative result: Escherichia coli.
Uses of Gelatin Hydrolysis Test
- Gelatin hydrolysis test is used to test the ability of an organism to produce gelatinases.
- Gelatin hydrolysis test helps in the identification of Serratia, Pseudomonas, Flavobacterium, and Clostridium.
- The test distinguishes the gelatinase-positive, pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus from the gelatinase-negative, nonpathogenic Staphylococcus epidermidis.
- The test can be used to differentiate genera of gelatinase-producing bacteria such as Serratia and Proteus from other members of the family Enterobacteriaceae.
Limitations of Gelatin Hydrolysis Test
- Gelatinase mostly acts at the surface of the tube medium. Shaking the tube while it is warm might result in a false-negative result.
- Gelatin may vary in its gelling ability; therefore, an uninoculated control should be inoculated with the test. The control must be refrigerated along with the test, prior to reading.
- False-positive results may occur with the tube method in some media or saline on prolonged incubation, i.e. greater than 4 hours. This can be detected in the uninoculated control tube.
- The plate method is not recommended for the determination of gelatin liquefaction by fastidious species and obligate anaerobes.
- If the tubes are incubated at temperatures greater than 20°C the tubes must be chilled below 20°C before reactions can be carried out.
References and Sources
- Nutrient Gelatin. M060. HiMedia Laboratories.
- Biochemical Tests for the Identification of Aerobic Bacteria. (2016). Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook, 3.17.1.1–3.17.48.3.
- Thomas Edison E. dela Cruz, Jeremy Martin O. Torres. 2012. Gelatin hydrolysis test protocol.
- Joseph J. McDade, R. H. Weaver. RAPID METHODS FOR THE DETECTION OF GELATIN HYDROLYSIS. Journal of Bacteriology. Jan 1959, 77 (1) 60-64.
- 4% – https://microbeonline.com/gelatin-hydrolysis-test-principle-procedure-expected-results/
- 3% – http://www.himedialabs.com/TD/M060.pdf
- 2% – https://www.thomassci.com/Laboratory-Supplies/Microbiological-Media/_/Nutrient-Gelatin1
- 2% – https://sfamjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/jam.12840
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/gelatin
- 1% – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3426542/
- 1% – https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/collagen
- 1% – https://microbiologynotes.com/gelatin-hydrolysis-test-principle-uses-media-procedure-and-result/
- 1% – https://microbenotes.com/gelatin-hydrolysis-test-principle-procedure-and-result-interpretation/
- 1% – http://www.uwyo.edu/molb2210_lab/info/biochemical_tests.htm
- <1% – https://quizlet.com/134986028/microbiology-lab-exam-3-flash-cards/
- <1% – https://jb.asm.org/content/jb/8/4/297.full.pdf
- <1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microbiological_culture

This information is resourceful