Image Source: Freepik Company S.L.
Interesting Science Videos
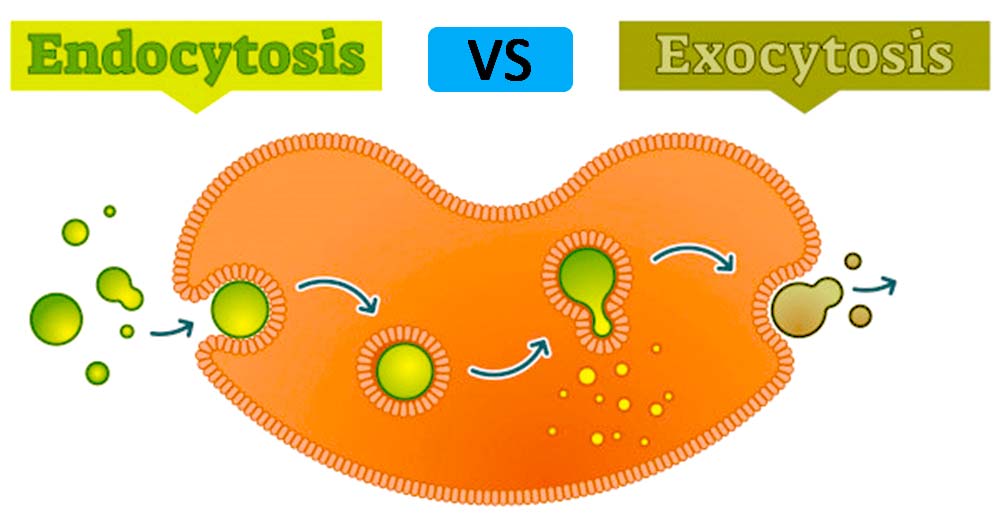
Similarities of Endocytosis and Exocytosis
- Endocytosis and exocytosis mechanisms are forms of Active Transport, both using energy to transport particles in and out of the cell.
- They both have different types similar in that they both transport materials across the cell membrane by forming vesicle pores.
Differences between Endocytosis and Exocytosis
| Characteristic | Endocytosis | Exocytosis |
Definition | Endocytosis is a cellular mechanism where a cell internalizes substances from the external environment. These substances undergo certain processes of breaking down to smaller elements either for use by the cell or for elimination purposes. | Exocytosis is a process that is used to transport materials from inside the cell to the external part of the cell by the use of energy. The mechanism uses special vesicles fille with the particles of interest to transport Generally, in this mechanism of exocytosis, a special vesicle bound to the cell membrane, containing the cellular particles will expel the cell content to the external part of the cell. |
Types | There are three types based on the mechanisms of particle. They include:
| There are also 3 types depending on the sequence of processes involved in transporting particles out of the cell. They include:
|
Energy | Being a form of active transport, they use some energy (ATP) during particle transportation. | It is a type of active transport, using a lot of energy (ATP) for transporting particles out of the cell. |
Functions | Endocytic mechanisms are used to:
| Exocytosis is known for its functions in:
|
References and Sources
- https://microbenotes.com/endocytosis-definition-process-and-types-with-examples/
- https://microbenotes.com/exocytosis-definition-process-and-types-with-examples/
- https://socratic.org/biology/movement-in-and-out-of-cells/transport-across-the-cell-membranes
- https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-exocytosis-4114427
- https://quizlet.com/333668107/active-transport-flash-cards/
- https://pediaa.com/difference-between-endocytosis-and-exocytosis/
