Interesting Science Videos
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are Gram-positive and the two most common pathogenic cocci of medical importance.
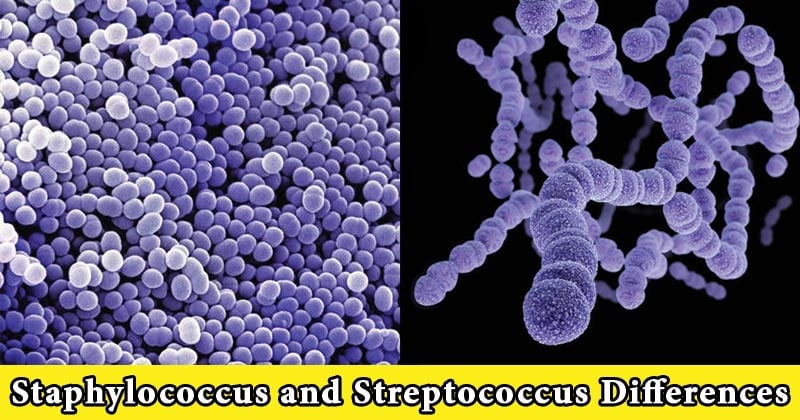
They are both non-motile, non-sporing, and facultative anaerobes which can be differentiated on the following grounds:
|
S.N. |
Character | Staphylococcus |
Streptococcus |
| 1. | Cellular Arrangement | Spherical cells in clusters (grape like clusters). | Spherical or ovoid cells in chains or pairs. |
| 2. | Fission/Division | Irregular division in all three planes. | Division in one linear direction. |
| 3. | Catalase Test | Positive (Presence of catalase enzyme) | Negative |
| 4. | Halotolerance | Halotolerant. Can tolerate upto 8% salt concentration. | Inhibited by high concentration of salt. |
| 5. | Capnophile | No | Yes |
| 6. | Common Culture Media Used | Mannitol Salt Agar
Nutrient Agar |
Blood Agar |
| 7. | Growth on Ordinary Culture Media | Possible | Not possible |
| 8. | Nutritional requirement | Simple | Complex (fastidious organism) |
| 9. | Colony morphology | 2-3 mm in diameter, circular, opaque golden yellow colonies (Staphylococcus aureus) | b-haemolysis ,1 mm, circular, tiny needle tip colonies (Streptococcus pyogenes) |
| 10. | Hemolysis | No hemolysis or beta hemolysis. | Either alpha,or beta or gamma hemolysis. |
| 11. | Species Number | About 40 staphylococcal species have been identified so far. | About 50 Streptococcal species have been identified so far. |
| 12. | Differentiation into groups | By means of coagulase test. | By means of hemolysis pattern in Blood Agar and group specific cell wall polysaccharide (Lancefield grouping). |
| 13. | Species Differentiation | – Coagulase test
– Novobiocin sensitivity test – Biochemical tests |
– Type of hemolysis
– Cell wall carbohydrate group (A, B, C, etc) – Bile Solubility Test – CAMPT Test – Optochin Sensitivity Test |
| 14. | Normal Flora | Staphylococci are found mostly on the skin as commensals. | Mucosal membrane of human and animals. Mostly found in the oral cavity and respiratory tract. |
| 15. | Pathogens | Most of the Staphylococcal species are non-pathogens. | Streptococcus cause many diseases. |
| 16. | Pathogenic Species | Staphylococcus aureus,
Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, etc. |
Streptococcus pyogenes,
Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus bovis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, etc. |
| 17. | Virulence Factors | Polysaccharide capsule, slime layer, teicholic acid, lipoteicholic acid, adhesive proteins, clumping factor, protein A, exoenzymes ( DNase, hyalurinidase, phosphatase, lipase, exocoagulase, fibrinolysin), enterotoxin, exfoliative toxin, cytotoxins(a-haemolysin b- haemolysin d- haemolysin g-haemolysin, Leukocidin) | Lipoteicholic acid, F-protein, capsule, exotoxin, streptolysin S and O (haemolysin), Exoenzymes (hyaluronidase ,DNase, streptokinase) |
| 18. | Diseases caused | Food poisoning, bacterial conjunctivitis, skin diseases, community-acquired meningitis, Pneumonia, Surgical Site Infection, Wound infection, impetigo, cellulitis, toxic shock syndrome, osteomyelitis and endocarditis. | Strep throat, Scarlet fever, Impetigo, Toxic shock syndrome,
Cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis (flesh-eating disease), sinusitis, blood infections, pneumonia and meningitis in newborns. |
| 19. | Types of Symptoms
|
The symptoms of the Staphylococcal infections can include fever, chills, low blood pressure and red, swollen, tender pimple-like bumps. | The symptoms of a Streptococcal infection can include fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, rash, red and weeping skin sores, confusion, and dizziness. |
| 20. | Treatment options | Antibiotics like penicillin or methicillin if resistant. Vancomycin if MRSA. | Penicillin / penicillin V amoxicillin |
References
- Brooks, G. F., Jawetz, E., Melnick, J. L., & Adelberg, E. A. (2010). Jawetz, Melnick, & Adelberg’s medical microbiology. New York: McGraw Hill Medical.
- Parija S.C. (2012). Textbook of Microbiology & Immunology.(2 ed.). India: Elsevier India.
- Sastry A.S. & Bhat S.K. (2016). Essentials of Medical Microbiology. New Delhi : Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers.
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/differences-between-staphylococcus-and-streptococcus/
- http://www.fidanoski.ca/medicine/staphylococcus-streptococcus.htm http://pediaa.com/difference-between-streptococcus-and-staphylococcus/
- http://semmelweis.hu/mikrobiologia/files/2014/10/FGM_06.pdf
- http://www.uwyo.edu/virtual_edge/lab16/staphstrep_background.htm

If possible please also the complete test like Coagulase Test, CAMPT Test etc. for the same. In my opinion that will enrich your article more.
Thanks, all the biochemical test are there in my website. You can find from: https://microbenotes.com/category/biochemical-test/