Interesting Science Videos
Differences between Exotoxins and Endotoxins
Toxins are small molecules, peptides, or proteins produced by living cells that are capable of causing diseases or structural damage when they come in contact or are absorbed by tissues. Toxins and enzymes play an important role in the pathogenicity of pathogenic bacteria. Toxins may aid in invasiveness, damage cells, inhibit cellular processes, or trigger immune response and damage.
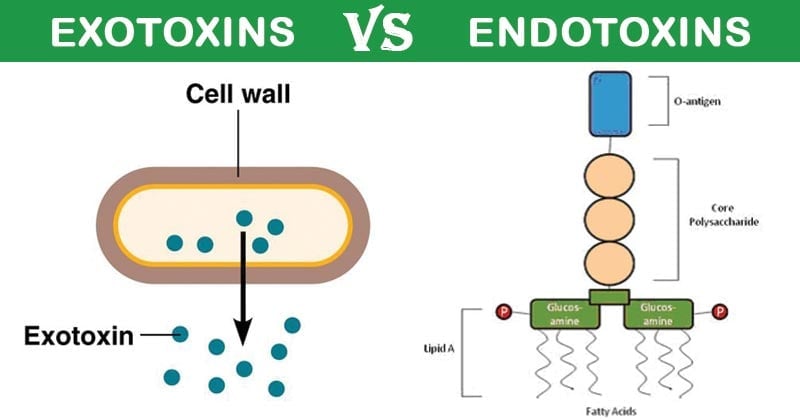
Toxins are of two types: Exotoxins and Endotoxins.
|
S.N. |
Character | Exotoxins |
Endotoxins |
| 1. | Definition | Proteins produced inside pathogenic bacteria as a part of their growth and metabolism. | Lipid portions of lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) that are the part of outer membrane of bacteria. |
| 2. | Produced by | Mostly Gram positive bacteria and also Gram negative bacteria. | Gram negative bacteria. |
| 3. | Chemical Nature | Protein (polypeptide) complexes | Lipopolysaccharide-protein complexes |
| 4. | Molecular weight | 10KDa. | 50-1000KDa. |
| 5. | Components | Usually composed of two subunits A and B. The A subunit is seen to have catalytic activity, whereas the B subunit is required for binding with an appropriate cell receptor. |
Composed of three basic components:
1. O-antigen 2. Core oligosaccharide 3. Lipid A |
| 6. | Enzymes present | Hyaluronidase, Collagenase, certain protease, Nuclease, Neuraminidase, Certain protease, Phospholipase A | Catalase, Fibrolysin, IgA / IgG proteases |
| 7. | Chromosomal Location | Located on extrachromosomal genes (e.g. plasmids). | Located on chromosomal genes. |
| 8. | Secreted by | Secreted by organisms ; living cell | Integral part of cell wall ; lysed cell |
| 9. | Secretion | Secreted out of the cell. | Generally not released outside the cell until death of cell. |
| 10. | Cell Lysis | Not required | Required |
| 11. | Stability to heat | Heat labile (60-80°C) | Heat stable (250°C) |
| 12. | Filtration | Filterable | Not Filterable |
| 13. | Boiling | Denatured on boiling | Not denatured on boiling. |
| 14. | Enzyme Activity | Mostly has enzymatic activity. | Enzymatic activity absent or limited. |
| 15. | Specificity | Exotoxins are enzymes; this makes them highly specific in their mechanism and for their host cells. | Endotoxins are comparatively not very specific in nature. |
| 16. | Specific receptors | Usually binds to specific receptors. | Specific receptors not found. |
| 17. | Specificity to bacterial strain | Specific to certain bacterial strain. | Not specific to any bacterial strain. |
| 18. | Immunogenicity | Highly immunogenic. | Weakly immunogenic. |
| 19. | Fever Induction | No | Fever by induction of interleukin 1 (IL-1) production. |
| 20. | Toxicity | Highly toxic, fatal in µg quantities. | Moderately toxic, fatal in mg quantities. |
| 21. | Mode of action | Various modes (Mostly by enzyme-like mechanisms). | Includes TNF and Interlukin-1 |
| 22. | Potency | High: A single toxin molecule can act on a large number of host cells. | Low: A large amount of toxin is needed to cause a disease. |
| 23. | Effects | Either cytotoxin, enterotoxin or neurotoxin with defined action on cells or tissues. | General symptoms such as fever, diarrhea, vomiting etc. |
| 24. | Neutralization by Antibodies | Can be neutralized. | Cannot be neutralized. |
| 25. | Detection | Detected by many tests (neutralization, precipitation, etc) | Detected by Limulus lysate assay. |
| 26. | Conversion to Toxoids | Possible (On treatment with formalin). eg. For the prevention of diphtheria, botulism, and tetanus. | Not possible |
| 27. | Availability of vaccines | Effective vaccines available. | No effective vaccines available. |
| 28. | Diseases caused | Tetanus, diphtheria, botulism etc. | Meningococcemia, sepsis by gram negative rods etc. |
| 29. | Examples | Toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Bacillus anthracis | Toxins produced by E.coli, Salmonella Typhi, Shigella, Vibrio cholera |
References
- Murray, Patrick R. (2016). Medical Microbiology.Eighth edition. India: Elsevier Inc.
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/differences-between-exotoxins-and-endotoxins/
- http://medimoon.com/2013/04/difference-between-endotoxin-and-exotoxin/
- https://biologywise.com/endotoxins-vs-exotoxins
- http://www.differencebetween.net/science/difference-between-endotoxins-and-exotoxins/
- http://www.easybiologyclass.com/difference-between-bacterial-endotoxin-and-exotoxin-comparison-table/
- Microbiology and Immunology. Kaplan Medical.
