Interesting Science Videos
Differences between B Cells and T Cells
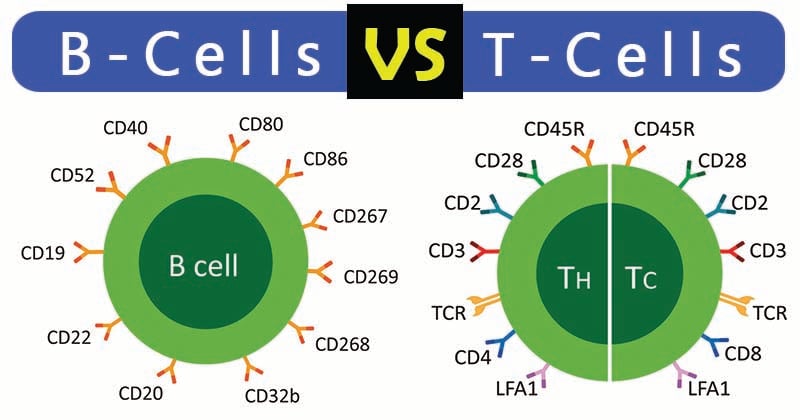
The major differences between them are:
| S.N. | Characteristics | B lymphocytes (B cells) | T lymphocytes (T cells) |
| 1. | Site of Maturation | B lymphocytes both originate and mature in the bone marrow. | T lymphocytes mature in the thymus after its origination in the bone marrow. |
| 2. | Position | Mature B cells occur mostly outside the lymph node. | Mature T cells occur mostly inside the lymph node. |
| 3. | Distribution | Germinal centers of lymph nodes, spleen, gut, respiratory tract; also subcapsular and medullary cords of lymph nodes. | Parafollicular areas of cortex in lymph nodes, periarteriolar in the spleen. |
| .4. | Receptors | The B-cell receptors (BCRs) constitute of membrane antibodies known as immunoglobulin surface receptors. | Surface receptors are called T-cell receptors (TCRs) and differ from membrane antibodies. |
| 5. | Binds with | Extracellular antigens such as bacteria, free viruses and other circulating free foreign material. | The foreign antigen in association with self-antigen only such as a virus-infected cell. |
| 6. | The need of Antigen Processing | Antigen processing is not necessary. | Antigen processing is necessary. |
| 7. | Connection | They bind directly with the antigens on the surface of the invading virus or bacteria. | They can only bind to antigens on the outside of infected cells and not directly. |
| 8. | C3 complement receptor | Receptors for C3 complement present. | Receptors for the C3 complement are absent. |
| 9. | Cell Surface Marker | CD19 is the cell surface markers of B cells. | CD3 is the cell surface markers of T cells. |
| 10. | Microvilli on the cell surface | Present | Absent |
| 11. | Types of Active Cells | They differentiate into plasma cells and memory cells. | They differentiate into many subsets of T cells such as Cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells), Helper T cells (CD4+ T cells) and suppressors cells along with memory cells. |
| 12. | Abundance | It constitutes about 20% of lymphocytes in the blood. | It constitutes about 80% of lymphocytes in the blood. |
| 13. | Secretory Product | Antibodies are the chief secretory product of B cells. | Cytokines (lymphokines) are the chief secretory product of T cells. |
| 14. | Type of Immunity | Involved in humoral (antibody-mediated) immunity. | Involved in cell-mediated immunity. |
| 15. | Life Span | They have comparatively a shorter life span. | They have a comparatively longer life span. |
| 16. | Relationship | Since B cells are also Antigen Presenting cells, they present antigens to T-cells. | They help to activate B cells and aid in antibody production against antigens which are T-dependent. |
| 17. | Functions | Help eliminate free foreign invaders by enhancing immune responses against them; provide immunity against most foreign antigens and bacteria. | Help lyse virus-infected cells and tumor cells; provide immunity against most viruses and intracellular bacterial pathogens; help B cells in antibody production. |
References
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/differences-between-b-cells-and-t-cells/
- http://education.seattlepi.com/functional-difference-between-t-cells-b-cells-4573.html
- http://pediaa.com/difference-between-t-cells-and-b-cells/
- Lydyard, P.M., Whelan,A.,& Fanger,M.W. (2005).Immunology (2 ed.).London: BIOS Scientific Publishers.
