Interesting Science Videos
Structure of Coltivirus
- Coltivirusparticles are 60–80 nm in diameter having two concentric capsid shells with a core that is about 50 nm in diameter.
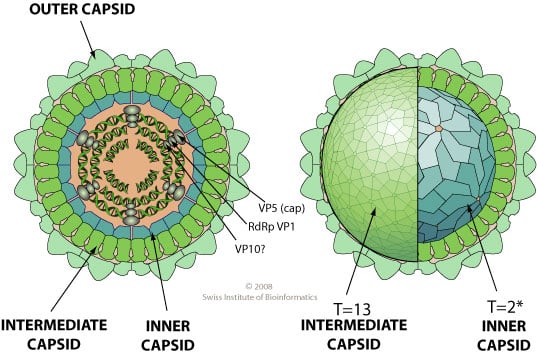
- They have a relatively smooth surface capsomeric structure and icosahedral symmetry.
- Non enveloped, icosahedral virion with a triple capsid structure, about 60-80 nm in diameter.
- Each virion contains a full‐length copy of 12 segments of linear, double‐stranded, positive‐sense RNA.
- The buoyant density of the virus in CsCl is 1.38 g cm−3.
Genome of Coltivirus
- The genome consists of 12 dsRNA segments coding for 13 proteins that are numbered in order of decreasing size.
- The genome comprises approximately 29,000 bp, with segment lengths that range between 675 and 4350 bp.
- The terminal 5′- and 3′-sequences of the coltivirusgenome are conserved.
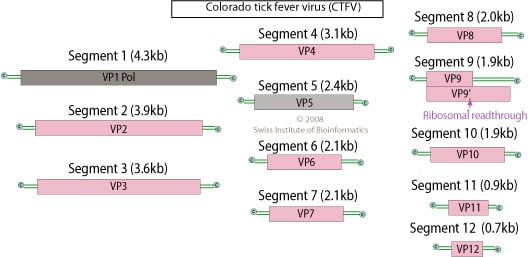
- The 12 segments are VP1(Pol)- RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, VP2-Methyltransferase, cell-receptor recognition site, VP3- RNA replication factors, VP4, VP5-Guanylyltransferase, VP6-Nucleotide binding, NTPase, VP7-RNA replication factors, VP8, VP9-Kinase, helicase, VP10, VP11, VP12-RNA replication factors.
Epidemiology of Coltivirus
- The virus that causes Colorado tick fever is the second most common Arbovirus in the United States, and several hundred cases are reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) annually.
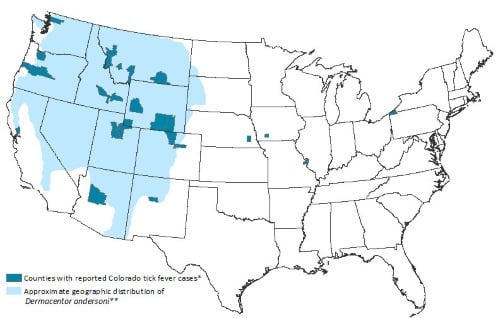
- It has been found in California, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, South Dakota, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming, as well as the Canadian provinces of British Columbia and Alberta.
- CTFV is caused by a Coltivirus, and is a member of the Reoviridae. It is found in the mountain regions of western USA and Canada, especially in the Rocky Mountain area in Colorado.
Replication of Coltivirus
- Attachment to host receptors and mediates endocytosis of virus into host cell.
- Particles are partially uncoated in endolysosomes, but not entirely, and penetrate in the cytoplasm.
- Early transcription of the dsRNA genome by viral polymerase occurs inside the sub-viral particle (naked core), so that dsRNA is never exposed to the cytoplasm.
- Full-length plus-strand transcripts from each of the dsRNA segments are synthesized. These plus-strand transcripts are used as templates for translation.
- Viral proteins and genomic RNAs aggregates in cytoplasmic viral factories.
- (+)RNAs are encapsidated in a sub-viral particle, in which they are transcribed to give RNA (-) molecules with which they become base-paired to produce dsRNA genomes.
- The capsid is assembled on the sub-viral particle.
- Mature virions are released presumably following cell death and associated breakdown of host plasma membrane.
Pathogenesis of Coltivirus
- Colorado tick fever is a viral infection transmitted by the bite of the wood tick Dermacentor andersoni.
- The virus circulates between ticks and rodents, with humans being the secondary hosts.
- The tick’s saliva then contains the virus, and it becomes infectious for life.
- The adult tick then transmits the virus to humans through a bite, where it infects bone marrow cells.
- The virus replicates in those bone marrow cells, which disrupts the development and replication of leukocytes(white blood cells), eosinophils, and basophils.
- Because of this, thrombocytopeniacould also a potential result.
- Erythrocytes, which are enucleated red blood cells, seem to be infected while they are erythroblasts, their nucleated precursor stage.
- The virus stays in these red blood cells without harming it for up to four months.
- Here, it is protected from the immune system’s attacks.
- Antibody to the virus is found only about two weeks after symptoms begin to show, but the virus can still be found in blood cells for about six weeks.
Clinical manifestations of Coltivirus
- Clinical illness consists of headache, fever, myalgia, arthralgia, retro-orbital pain, photophobia and neck stiffness, accompanied by a macular, maculopapular or petechial rash in about 10% of cases and leukopenia are the cardinal features
- It is biphasic in about half the patients, characterized by 2–3 days of illness, then 2 days of remission, followed by 2–3 days’ more illness.
- The acute illness lasts 5–10 days.
- Children may develop CNS infection encephalitis or hemorrhagic fever may occur.
- Prolonged convalescence characterized by weakness and fatigue is common in adults.
Lab Diagnosis of Coltivirus
- Culture and RT-PCR during first 2 weeks of illness.
- Serologic assays (e.g., IgM-capture EIA, indirect fluorescent antibody, and plaque-reduction neutralization) on convalescent samples.
- Conventional blood tests are also generally not helpful, although leukopenia is a common finding in many patients.
- However, it is likely that many cases of Colorado tick fever are attributed to other viral infections and never correctly diagnosed.
Treatment of Coltivirus
- No specific antiviral treatment is available.
- Patients with suspected CTF are given supportive care as appropriate.
Prevention and control of Coltivirus
- No vaccine to prevent CTF.
- Use of insect repellent
- Wearing long sleeves and pants
- Avoidance of wooded and bushy areas with high grass
- Performing thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors

Helpful