- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms means they have true nucleus which are enclosed in membranes.
- They are non-vascular organisms. They do not have vascular system. Xylem and Phloem are absent.
- Fungi have cell walls (plants also have cell walls, but animals have no cell walls).
- There is no embryonic stage for fungi.

- They reproduce by means of spores. There are sexual and asexual spores. Sexual spores are Oospores, Zygospores, Ascospores, Basidiospores, etc. and Asexual spores are Sporangiospores, Aplanospores, Zoospores, Conidia, etc.
- Depending on the species and conditions both sexual and asexual spores may be produced.
- They are typically non-motile.
- Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alteration of generation. They have both haploid and diploid stage.
- Fungi are achlorophyllous, which means they lack the chlorophyll pigments present in the chloroplasts in plant cells and which are necessary for photosynthesis.
- The vegetative body of the fungi may be unicellular or composed of microscopic threads called hyphae.
- Hyphae can grow and form a network called a mycelium.
- Yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not produce hyphae.
- The structure of cell wall is similar to plants but chemically the fungi cell wall are composed of chitin (C8H13O5N)n.
 Figure: Structure of Chitin
Figure: Structure of Chitin - The cell membrane of a fungus has a unique sterol and ergosterol.
- Fungi are heterotrophic organisms. They obtains its food and energy from organic substances, plant and animal matters.
- Fungi grow best in acidic environment (tolerate acidic pH).
- Fungi digest the food first and then ingest the food, to accomplish this the fungi produce exoenzymes like Hydrolases, Lyases, Oxidoreductase, Transferase, etc.
- Fungi store their food as starch.
- Biosynthesis of chitin occurs in fungi.
- Many of the fungi have a small nuclei with repetitive DNA.
- During mitosis the nuclear envelope is not dissolved.
- Nutrition in fungi – they are saprophytes (gets energy from dead and decaying matters), or parasites (lives in a host, attack and kill) or symbionts (mutually beneficial).
- Optimum temperature of growth for most saprophytic fungi is 20-30°C while (30-37)°C for parasitic fungi.
- Growth rate of fungi is slower than that of bacteria.
- Reproduction in fungi is both by sexual and asexual means.
- Sexual state is referred to as teleomorph (fruiting body), asexual state is referred to as anamorph (mold like).
- Reproduction occurs by both asexual (Axamorph) and sexual (Teliomorph) mode:Asexual methods: fragmentation, fsomatic budding, fission, asexual spore formation
Sexual methods: gametic copulation, gamate-gametangium opulation, gametangium copulation, somatic copulation and Spermatization. - Pheromone is a chemical substance produced by fungi, which leads to the sexual reproduction between male and female fungi cells.
- Some fungi are macroscopic and can be seen by naked eyes. Mold or mushrooms are examples of macroscopic form of fungi.
- In 1991, a landmark paper estimated that there are 1.5 million fungi on the Earth.
- Only about 300 species of fungi are infectious to human.
- Examples: Candida albicans, Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus neoformans, Histoplasma, Pneumocystis jirovecii, etc.
Characteristics of Fungi
About Author

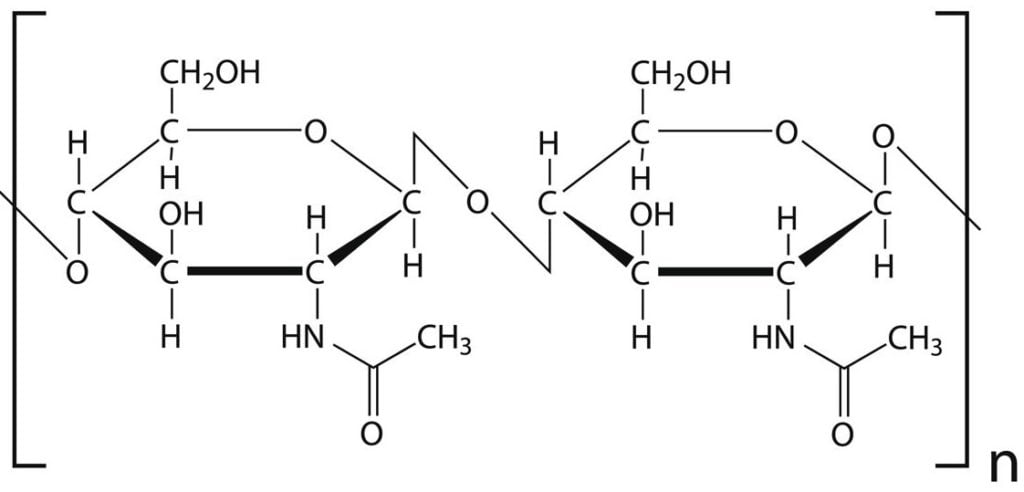 Figure: Structure of Chitin
Figure: Structure of Chitin
THis is so nice
wow Mashaa Allah its so helpful
Thanks
Thanks 👍
Thank you the information is very helpful
Very nice thank you so much
Thank you so much 🙂
Very helpful can send some summaries about the kingdom animalia
yes its very very helpfull.
Very nice very helpful thank you 🙃
Send me notes for, the details structure of the cell membrane