Interesting Science Videos
Celsius Scale Definition
Celsius scale, or centigrade scale, is a temperature scale that is based on the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point of water at 100°C.
- The scale was introduced by and also named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742 A.D. This scale uses the symbol °C.
- Initially, the Celsius scale used 0°C for the boiling point of water and 100°C for the melting point of ice, but the scale was later reinverted in the form that is used today.
- In this scale, the lower fixed point is considered 0°C, and the upper fixed point is considered 100°C.
- The region between these two temperatures is divided into 100 equal parts so that each part equals to one degree Celsius (1°C).
- Thus, in the inverted form of the Celsius scale, the freezing point of water is 0°C, and the boiling point of water is 100°C.
- However, a modern Celsius scale has been adopted that is based on the triple point of Vienna Standard Mean ocean water and has improved with the concept of absolute zero.
- According to this, the modern concept of the Celsius scale is not based on the freezing point and boiling point of water, but on the triple point of water.
- After May 2019, the absolute zero, the lowest temperature possible is denoted by 0K or -273.15°C. Before that, however, the temperature of the triple point of water was defined exactly at 273.16 K or 0.01 °C.
- The average human body temperature is 37°C on the Celsius scale.
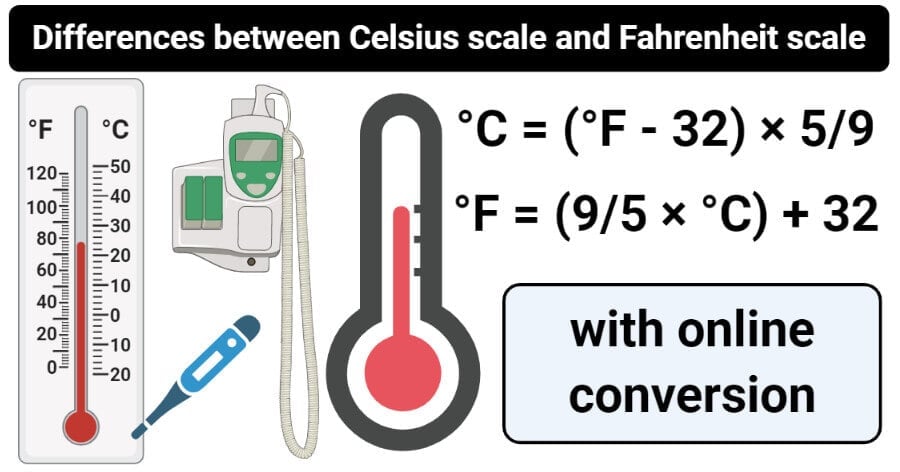
- The formula for the conversion of Celsius scale into the Fahrenheit scale is given by:
°F = (9/5 × °C) + 32
- Celsius scale is commonly used in areas that use metric system units and thus is used for all scientific purposes.
Fahrenheit Scale Definition
Fahrenheit scale is a temperature scale that is based on the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point of water at 212°F.
- The scale was introduced by and also named after the physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1720 A.D. This scale uses the symbol °F.
- The lowest defining point in the Fahrenheit scale is the temperature of a solution of brine with an equal amount of ice, water, and salt (ammonium chloride).
- The temperature of the average human body was first established at 96°F, which was later adjusted to 98.6°F.
- In this scale, the lower fixed point is considered 32°F, and the upper fixed point is considered 212°F.
- The region between these two temperatures is divided into 180 equal parts so that each part equals to one Fahrenheit degree (1°F).
- Thus, the freezing point of water is 32°F, and the boiling point of water is 212°F on the Fahrenheit scale.
- The formula for the conversion of degree Fahrenheit to degree Celsius is given by:
°C = (°F – 32) × 5/9
- The absolute zero value in the Fahrenheit scale is -459.67° F.
- Fahrenheit scale is the first standardized temperature scale to be used in the world. It was prevalent in most English-speaking nations until the 1960s.
- The Celsius scale then replaced this scale after 1960 in most countries except the United States.
Celsius Scale vs. Fahrenheit Scale
| Basis for Comparison | Celsius Scale | Fahrenheit Scale |
| Definition | Celsius scale, or centigrade scale, is a temperature scale that is based on the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point of water at 100°C. | Fahrenheit scale is a temperature scale that is based on the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point of water at 212°F. |
| Denoted by | Celsius scale or simply Celsius is abbreviated as Degree C (°C). | Fahrenheit is abbreviated as Degree F (°F). |
| Introduced by or Named after | It is named after the astronomer ‘Andres Celsius’. | It is named after the physicist ‘Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit’. |
| The freezing point of water | The freezing point of water or the melting point of ice in the Celsius scale is 0°C. It is the lower fixed point of the scale. | The freezing point of water or the melting point of ice in the Fahrenheit scale is 32°F. It is the lower fixed point of the scale. |
| The boiling point of water | The boiling point of water, as described in the Celsius scale, is 100°C. It is the upper fixed point of the scale. | On the Fahrenheit scale, the boiling point of water is 212°F. It is the upper fixed point of the scale. |
| Average human body temperature | The average human body temperature, as measured in the Celsius scale, is 37°C. | The average human body temperature in the Fahrenheit scale is 98.6°F. |
| Absolute zero value | On the Celsius scale, the absolute zero value is set at -273.15°C. | The absolute zero value in the Fahrenheit scale is -459.67°F. |
| Divisions | The melting and boiling point of water in the Celsius scale is divided into 100 equal divisions, each division representing 1°C. | The melting and boiling point of water in the Fahrenheit scale is divided into 180 equal intervals, each division denoting 1°F. |
| Used | The Celsius scale is widely used in almost every part of the globe. | Fahrenheit scale is mostly used in the United States and some of its territories. |
| Conversion | It can be converted into Fahrenheit by the formula; °F = (9/5 × °C) + 32 | Degree Fahrenheit is easily convertible into Celsius by the formula; °C = (°F – 32) × 5/9 |
Online temperature converter calculator
Celsius to Fahrenheit Converter
Enter a temperature in Celsius:
Fahrenheit to Celsius Converter
Enter a temperature in Fahrenheit:
Celsius and Fahrenheit temperature table from -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F)
| Celsius | Fahrenheit |
| -40°C | -40°F |
| -39°C | -38.2°F |
| -38°C | -36.4°F |
| -37°C | -34.6°F |
| -36°C | -32.8°F |
| -35°C | -31°F |
| -34°C | -29.2°F |
| -33°C | -27.4°F |
| -32°C | -25.6°F |
| -31°C | -23.8°F |
| -30°C | -22°F |
| -29°C | -20.2°F |
| -28°C | -18.4°F |
| -27°C | -16.6°F |
| -26°C | -14.8°F |
| -25°C | -13°F |
| -24°C | -11.2°F |
| -23°C | -9.4°F |
| -22°C | -7.6°F |
| -21°C | -5.8°F |
| -20°C | -4°F |
| -19°C | -2.2°F |
| -18°C | -0.4°F |
| -17°C | 1.4°F |
| -16°C | 3.2°F |
| -15°C | 5°F |
| -14°C | 6.8°F |
| -13°C | 8.6°F |
| -12°C | 10.4°F |
| -11°C | 12.2°F |
| -10°C | 14°F |
| -9°C | 15.8°F |
| -8°C | 17.6°F |
| -7°C | 19.4°F |
| -6°C | 21.2°F |
| -5°C | 23°F |
| -4°C | 24.8°F |
| -3°C | 26.6°F |
| -2°C | 28.4°F |
| -1°C | 30.2°F |
| 0°C | 32°F |
| 1°C | 33.8°F |
| 2°C | 35.6°F |
| 3°C | 37.4°F |
| 4°C | 39.2°F |
| 5°C | 41°F |
| 6°C | 42.8°F |
| 7°C | 44.6°F |
| 8°C | 46.4°F |
| 9°C | 48.2°F |
| 10°C | 50°F |
| 11°C | 51.8°F |
| 12°C | 53.6°F |
| 13°C | 55.4°F |
| 14°C | 57.2°F |
| 15°C | 59°F |
| 16°C | 60.8°F |
| 17°C | 62.6°F |
| 18°C | 64.4°F |
| 19°C | 66.2°F |
| 20°C | 68°F |
| 21°C | 69.8°F |
| 22°C | 71.6°F |
| 23°C | 73.4°F |
| 24°C | 75.2°F |
| 25°C | 77°F |
| 26°C | 78.8°F |
| 27°C | 80.6°F |
| 28°C | 82.4°F |
| 29°C | 84.2°F |
| 30°C | 86°F |
| 31°C | 87.8°F |
| 32°C | 89.6°F |
| 33°C | 91.4°F |
| 34°C | 93.2°F |
| 35°C | 95°F |
| 36°C | 96.8°F |
| 37°C | 98.6°F |
| 38°C | 100.4°F |
| 39°C | 102.2°F |
| 40°C | 104°F |
| 41°C | 105.8°F |
| 42°C | 107.6°F |
| 43°C | 109.4°F |
| 44°C | 111.2°F |
| 45°C | 113°F |
| 46°C | 114.8°F |
| 47°C | 116.6°F |
| 48°C | 118.4°F |
| 49°C | 120.2°F |
| 50°C | 122°F |
| 51°C | 123.8°F |
| 52°C | 125.6°F |
| 53°C | 127.4°F |
| 54°C | 129.2°F |
| 55°C | 131°F |
| 56°C | 132.8°F |
| 57°C | 134.6°F |
| 58°C | 136.4°F |
| 59°C | 138.2°F |
| 60°C | 140°F |
| 61°C | 141.8°F |
| 62°C | 143.6°F |
| 63°C | 145.4°F |
| 64°C | 147.2°F |
| 65°C | 149°F |
| 66°C | 150.8°F |
| 67°C | 152.6°F |
| 68°C | 154.4°F |
| 69°C | 156.2°F |
| 70°C | 158°F |
| 71°C | 159.8°F |
| 72°C | 161.6°F |
| 73°C | 163.4°F |
| 74°C | 165.2°F |
| 75°C | 167°F |
| 76°C | 168.8°F |
| 77°C | 170.6°F |
| 78°C | 172.4°F |
| 79°C | 174.2°F |
| 80°C | 176°F |
| 81°C | 177.8°F |
| 82°C | 179.6°F |
| 83°C | 181.4°F |
| 84°C | 183.2°F |
| 85°C | 185°F |
| 86°C | 186.8°F |
| 87°C | 188.6°F |
| 88°C | 190.4°F |
| 89°C | 192.2°F |
| 90°C | 194°F |
| 91°C | 195.8°F |
| 92°C | 197.6°F |
| 93°C | 199.4°F |
| 94°C | 201.2°F |
| 95°C | 203°F |
| 96°C | 204.8°F |
| 97°C | 206.6°F |
| 98°C | 208.4°F |
| 99°C | 210.2°F |
| 100°C | 212°F |
References and Sources
- 3% – https://www.lenntech.com/calculators/temperature/temperature.htm
- 3% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Celsius
- 3% – https://biodifferences.com/difference-between-celsius-and-fahrenheit.html
- 2% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scale_of_temperature
- 2% – http://www.jspayne.com/php/SummaryGet.php?FindGo=Fahrenheit
- 1% – https://www.nextgurukul.in/wiki/concept/icse/class-7/physics/heat/temperature-and-its-measurement/3959265
- 1% – https://www.britannica.com/technology/Celsius-temperature-scale
- 1% – https://www.britannica.com/science/Fahrenheit-temperature-scale
- 1% – https://www.answers.com/Q/What_is_used_in_the_U.S_Celsius_or_Fahrenheit
- 1% – https://www.answers.com/Q/On_which_temperature_scale_is_100_degrees_the_boiling_point_of_water
- 1% – https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-centigrade-definition-conversion.html
- 1% – https://kids.britannica.com/students/article/heat/274809
- 1% – https://didyouknow.org/celsius/
- 1% – http://www.saburchill.com/physics/chapters/0097.html
- 1% – http://abyss.uoregon.edu/~js/glossary/temperature_scale.html
- <1% – https://www.scribd.com/document/381249252/general-science-pdf
- <1% – https://hypertextbook.com/facts/1997/LenaWong.shtml
