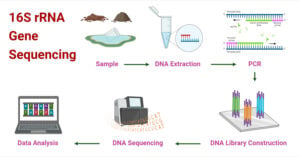
Methylation Sequencing: Principle, Methods, Steps, Uses, Diagram
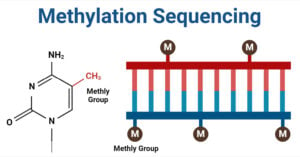
Methylation sequencing is a method of sequencing used to study DNA methylation patterns across the genome which is an important biological process that adds methyl group (CH3) to the cytosine … Read more