Punnett Square- Definition, Types, Application, Examples, Limitations
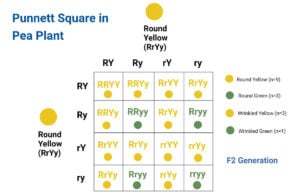
Punnett Square Definition The Punnett square is a table or checkboard grid that is used to determine all possible genotypes from a particular cross. Punnett square is a simple square … Read more