Homozygous vs. Heterozygous: 10 Differences, Examples
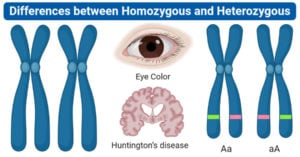
Homozygous Definition Homozygous is a genetic condition where an individual inherits the same alleles of a gene from both the parents. Heterozygous Definition Heterozygous is a genetic condition where an … Read more