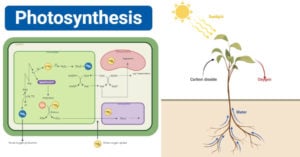
Photosynthesis Process: Steps, Equation & Diagram
Photosynthesis is defined as the process, utilized by green plants and photosynthetic bacteria, where electromagnetic radiation is converted into chemical energy and uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and … Read more