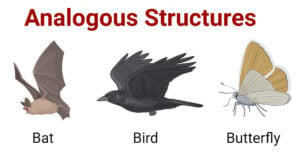
Analogous Structures: Definition & Evolutionary Examples
Evolution is the driving process of nature through which new species arise from their ancestral forms. The concept of evolution is essential for understanding how life on Earth has developed … Read more