- Ti plasmid (Tumor-inducing plasmid) is an extrachromosomal genetic material found in Agrobacterium tumefaciens which causes crown ball disease in certain dicot plant species.
- Ti plasmid was developed in the 1980s from various observations.
- Ti plasmid can be transferred to plant chromosomes.
- It also has the ability to transfer other foreign DNA sequences into the plant chromosome.
- It is around 200 kb large.
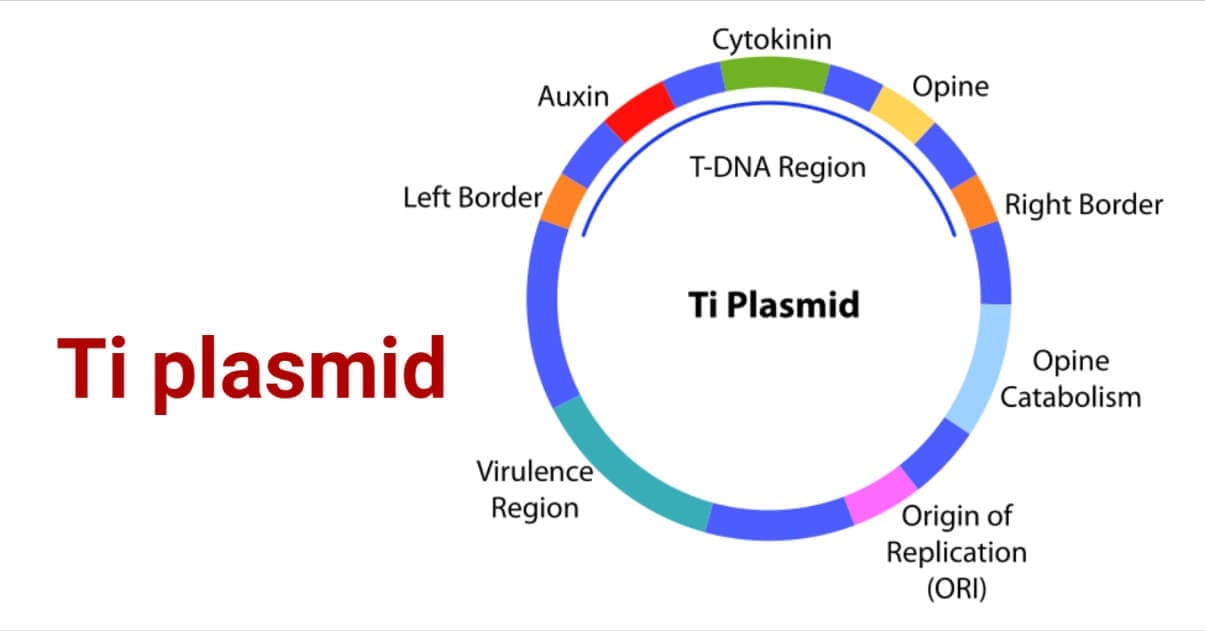
- Ti plasmid has three important regions.
Interesting Science Videos
Structure of Ti plasmid
T-DNA region – this region carries genes responsible for inducing tumors in plants. Other foreign genes of interest can be inserted in this region.
For inducing a tumor, only the T- DNA is transferred from one cell to another.
Vir region – this region consists of virulence genes. It is responsible for the excision, integration, and transfer of T-DNA into the plant chromosome.
Opine catabolism region – this region catabolizes opines, which are specialized amino acids. It is responsible for catabolizing opines produced by the T-DNA region. Opines often act as a source of Nitrogen in the bacteria.
- Other regions include the origin of replication, T-DNA border sequence, plant hormone synthesis region, and conjugation region.
Plant hormone synthesis region – this region is responsible for the synthesis of essential plant hormones like auxins and cytokinin.
Ti plasmid Conjugation region – process involving Ti plasmid includes the transfer of whole Ti plasmid from one cell to another.
- The T-DNA border sequence is 24bp with direct repeats. It marks the border of the T-DNA and is important for the transfer of plant chromosomes.
Types of Ti plasmid
Based on the differences in the T DNA region, there are two types of Ti plasmids:
1. Nopaline
- It has a continuous region of T-DNA, which is approximately 25 kb in length.
- It produces an opine known as Nopaline (C11H20N4O6).
2. Octopine
- It is subdivided into two regions which are 13 kb and 8 kb long.
- It produces an opine known as Octopine (C9H18N4O4).
- It was first isolated from Octopus octopodia in 1927.
Applications of Ti plasmid
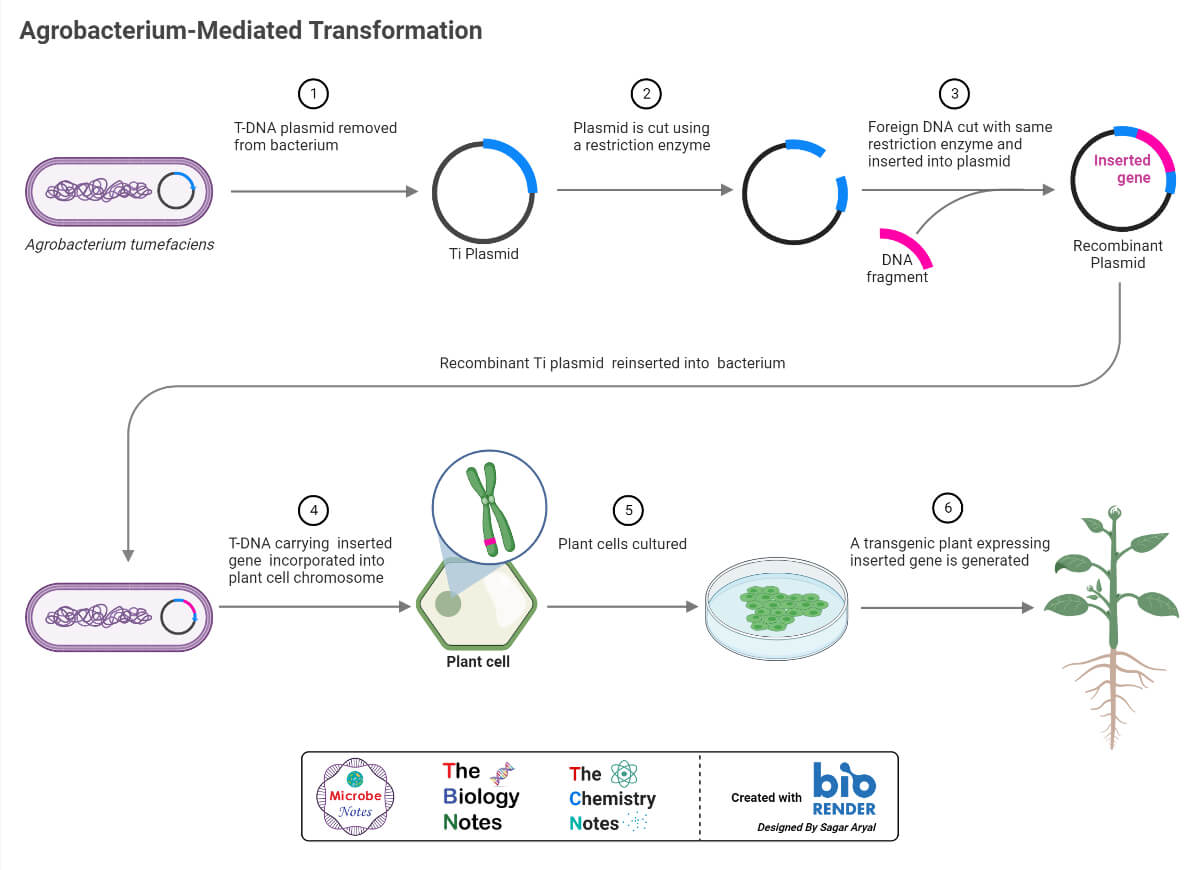
- Ti plasmid can be used as a vector for transformation involving Agrobacterium tumefaciens and is used for producing transgenic plants.
- With the use of restriction enzymes, a particular gene of interest can be inserted into the plasmid and transformed.
- It is used for the development of stress-tolerant plant varieties.
- Ti plasmids are also responsible for inducing amino acids and sugar-phosphate derivatives known as opines.
Limitations of Ti plasmid
- Ti plasmid is relatively a larger plasmid, and smaller plasmid vectors may be preferred in some cases.
- Ti plasmid usually works only in plants that can be infected by Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
- It cannot be used for monocot plants.
References
- Gordon, J. E., & Christie, P. J. (2014). The Agrobacterium Ti Plasmids. Microbiology spectrum, 2(6), 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0010-2013. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0010-2013
- Todd R Steck, Ti plasmid type affects T-DNA processing in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, FEMS Microbiology Letters, Volume 147, Issue 1, February 1997, Pages 121–125, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1997.tb10230.x
- Schell, J., & Van Montagu, M. (1977). The Ti-plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, a natural vector for the introduction of nif genes in plants?. Basic life sciences, 9, 159–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-0880-5_12
- An G. (1995). Binary Ti plasmid vectors. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 44, 47–58. https://doi.org/10.1385/0-89603-302-3:47
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2022). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 108172, Octopine. Retrieved July 6, 2022 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Octopine.
