- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious respiratory tract infection caused by SARS-CoV-2.
- The mode of transmission for this disease is through close physical contact and small droplets that develop during coughing, sneezing, and even talking.
- Even though these droplets might be inhaled during breathing, this disease is not considered air-borne according to WHO.
- The incubation period, the duration from the exposure to the virus to the onset of symptoms ranges from 1-14 days with an average of 5 days.
- The virus is most contagious for the first three days after the appearance of symptoms.
Interesting Science Videos
Signs and Symptoms of COVID-19
- The complete clinical manifestation is not yet clear as the symptoms that have been reported range from mild to severe, with some cases even resulting in death.
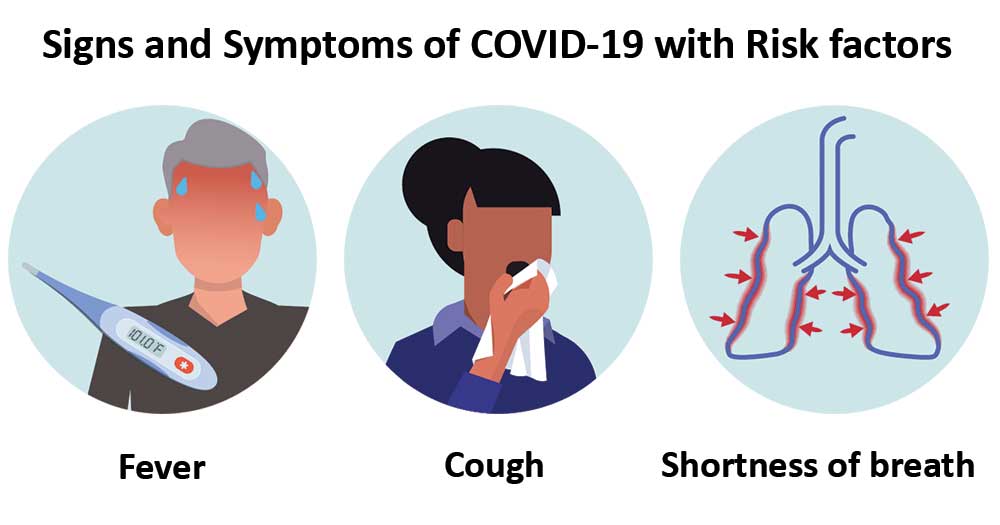
Image Source: CDC
The most commonly reported symptoms include:
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Myalgia or fatigue
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- Respiratory issues
The less common symptoms include:
- Headache
- Aches and pains
- Sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Hemoptysis
- Runny nose
- Phlegm-producing cough
- Patients with mild symptoms usually recover after one week, while severe cases might experience progressive respiratory infection due to alveolar damage from the virus, which may lead to death.
- Cases leading to death are primarily seen in middle-aged and elderly patients with pre-existing diseases (cancer surgery, cirrhosis, hypertension, heart diseases, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease).
- In patients with some underlying disease, the infection tends to develop rapidly into acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, metabolic acidosis, which are hard to correct and coagulation dysfunction, ultimately leading to death.
- However, patients with no pre-existing conditions are also found to be suffering from severe symptoms and even death.
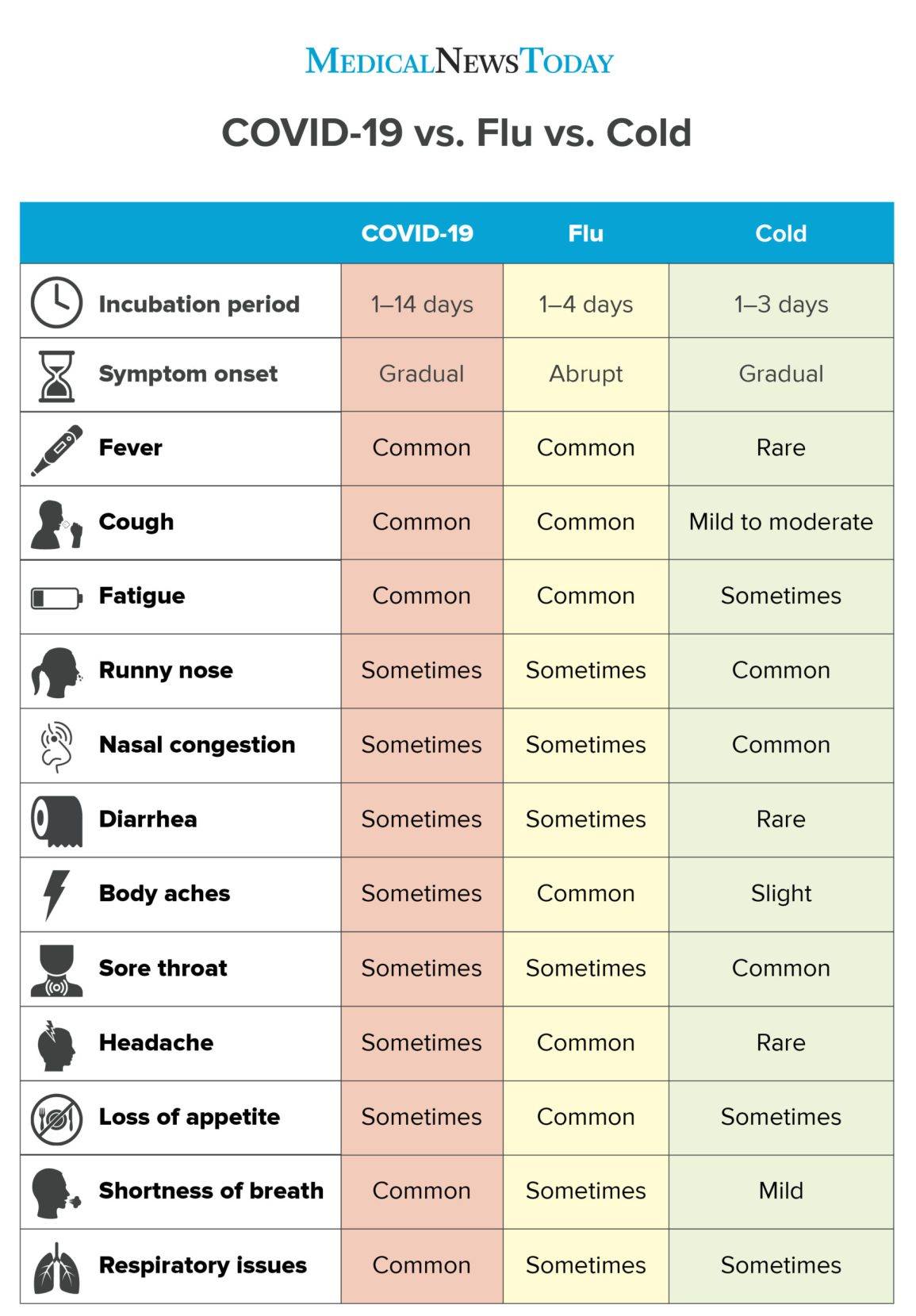
Figure: Comparing the symptoms of COVID-19, the flu, and a cold. Source: Medical News Today
Risk factors of COVID-19
- The primary risk factor associated with coronavirus is age.
- Most of the severe cases and death have been observed in patients above the age of 65.
- A case fatality rate of 0.32% is seen in those aged below 60 years and 6.4% in those aged ≥60 years. The rate is as high as 13.4% in those aged more than 80 years.
- The disease tends to progress faster in older adults, with the duration from the occurrence of the first symptoms to death shorter among people aged 65 years or more.
- The elderly male with comorbidities and ARDS usually show a higher death risk.
- Besides, people with underlying disorders (i.e., hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, cardiovascular disease), are found to be at more risk of developing severe symptoms.
- However, the risk of infection is the same for people of all ages.
- The risk mainly depends on the condition of a particular area. The people in areas heavily contaminated with the virus, more specifically in areas where there is a COVID-19 outbreak unfolding, are at a higher risk than others.
- Medical officials and people taking care of the patients are also at a higher risk.
References
- Guo Y, Cae Q, Hong Z, et al. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak – an update on the status. Millitary Medical Reasearch. (2020) 7:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
- Adhikari et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infectious Diseases of Poverty. (2020) 9:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-020-00646-x
- Verity R et al.(2020) Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7
- Liu W et al. Detection of Covid-19 in children in early January 2020 in Wuhan, China. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 12. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2003717
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_3
- https://www.bbc.com/news/health-51674743
- https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html
- https://www.google.com/covid19/
- https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
Sources
- 3% – https://mmrjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
- 3% – https://idpjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40249-020-00646-x
- 1% – https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1931524413001412
- 1% – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27022033
- 1% – https://www.gov.nu.ca/sites/default/files/files/4_%20Modes%20of%20Transmission%20-%20march%205%20-%20low%20res.pdf
- 1% – https://www.bundesgesundheitsministerium.de/en/press/2020/coronavirus.html

I’d like to thank you for the brief and clear information on Covid-19.
Also I have a question regarding the disease of Covid-19.
1) WHO said Covid-19 is not an air-borne disease. How it could be? Since it is transmited by droplets and it may stay in air approximately 3hrs…why not air-borne disease.
2)Is there any research based answers of drinking tea, Luke water, lemon juice and garlic has prevention of covid-19?
Thanx