As the Broth dilution method are time-consuming, many laboratories in the United States adopted disc diffusion tests in the early 1950s. Kirby Bauer tests also known as the Disc diffusion test is used for antibiotic susceptibility testing. Lack of standardization creates a problem in the 1960s and later Kirby and Bauer reviewed the description. In 1961, WHO standardized the procedure. Currently, CLSI updates and modifies the original procedure which ensures uniformity worldwide. This test is mainly performed to determine the sensitivity or resistivity of aerobes or facultatively anaerobes against different classes of antibiotics.
Aim/ Objectives
- This technique aids physicians to assist in selecting treatment options.
- The growth of organisms determines the ability of antibiotics to inhibit the organisms.
Interesting Science Videos
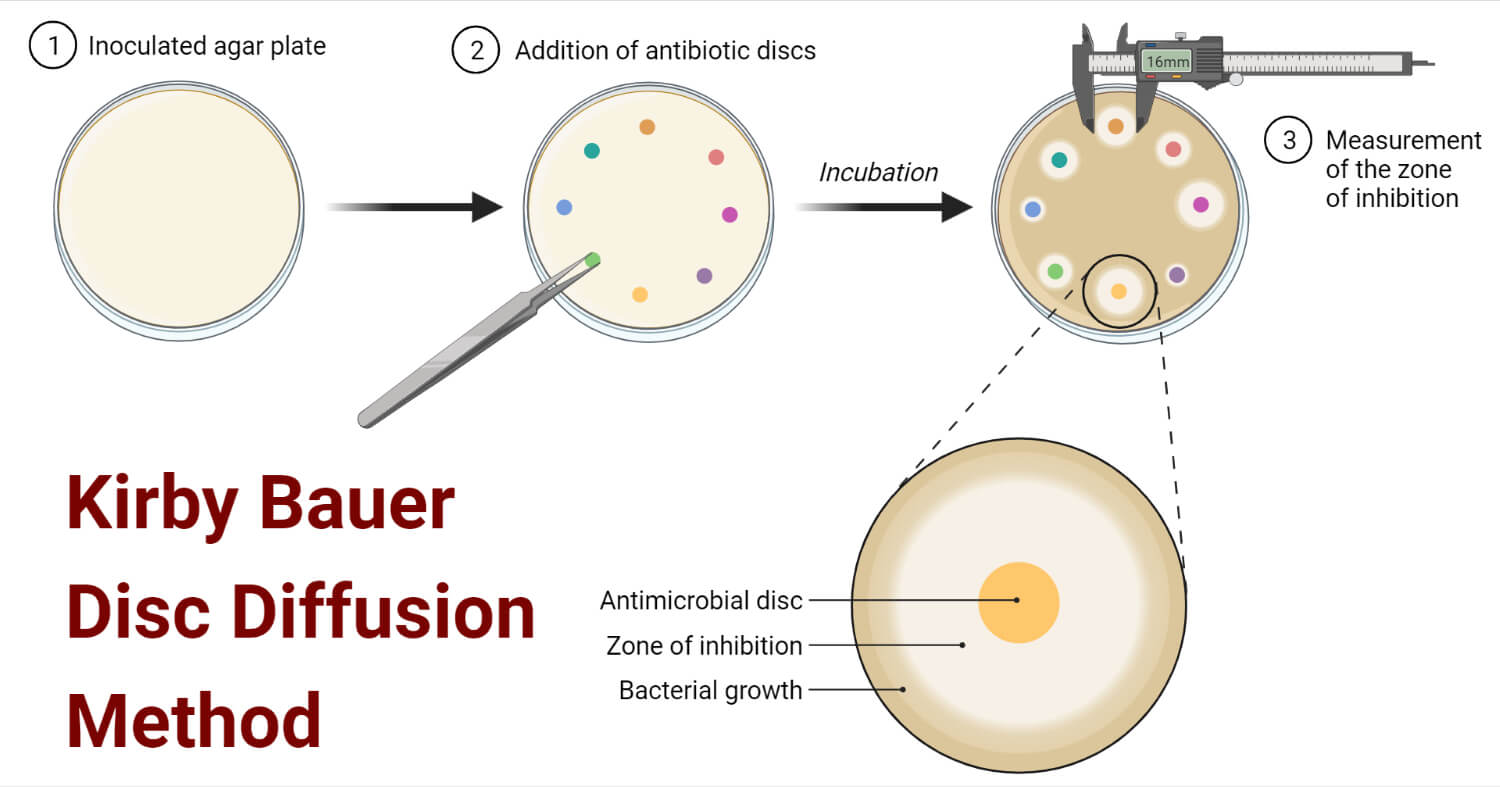
Principle of Kirby Bauer Disc Diffusion Method
The organism to be tested must be incubated overnight in broth and must be compared with the 0.5 McFarland Turbidity standard. Mueller- Hinton agar must be used as it does not inhibit sulphonamides and ensures reproducibility and with composition and PH of the medium. The agar when poured on Petri dishes should be 4mm.
Materials Required
- Mueller- Hinton agar
- Antibiotic discs
- Cotton swabs
- Petri dishes
- 0.5 McFarland Turbidity standard
- Inoculum
- Forceps
- Metric ruler or caliper
Procedure of Kirby Bauer Disc Diffusion Method
- Sterilize the area with disinfectant and open burner before performing the test.
- A sterile cotton swab is dipped into the inoculum and remove excess medium by pressing the swab onto the wall of the tube.
- Swab the surface area of the plate completely by rotating the plate. This technique is called lawn culture or carpet culture.
- Allow the plates to dry for 5 minutes so that the medium absorbs the inoculum properly.
- Firstly sterilize the forceps with alcohol before picking up antibiotic discs.
- Discs should be placed at a distance of 24mm.
- Lightly touch each disc with forceps to ensure that it is in good contact to avoid misplacement.
- Incubate the plate upside down for 24 hours at 37ºC.
Result and Interpretation of Kirby Bauer Disc Diffusion Method
- After 24 hours of incubation, use a metric ruler to measure the zone of inhibition and include the diameter of the disc in the measurement.
- Compare the result with CLSI guidelines to report the result.
- The results are reported as Susceptible (S), Intermediate (I), or Resistant (R).
Uses of Kirby Bauer Disc Diffusion Method
- Antibiotic susceptibility testing is a very important step to monitor antimicrobial resistance.
- It guides the clinician to select the best antimicrobial agent.
- To acquire information on microorganisms of public health importance.
Advantages
- This test is used in determining the antibiotics of choice to treat an infection.
- It can be useful in monitoring antimicrobials and for the selection of proper antibacterial agents.
- It doesn’t require special equipment to perform and can be interpreted by all medical personnel.
- It costs less to perform this test.
Limitations
- Not all slow or fastidious organisms can be tested accurately.
- It is not considered a gold standard test as it is only for screening the susceptibility pattern of the organisms according to the CLSI guideline.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antibiotic_sensitivity_testing – 5%
- https://www.asmscience.org/content/education/protocol/protocol.3189 – 2%
- https://asm.org/getattachment/2594ce26-bd44-47f6-8287-0657aa9185ad/Kirby-Bauer-Disk-Diffusion-Susceptibility-Test-Protocol-pdf.pdf – 1%
- https://www.pharmadekho.com/swab-testing-of-various-surfaces-for-bioburden-determination/ – 1%
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279912715_Current_Methods_for_the_Identification_of_Carbapenemases – 1%

very useful
Good notes for a concerned student
Nice information source asit gives appreciatable answers though.