DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is a double-stranded molecule that contains the genetic information of an organism.
- It is a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides joined by a phosphodiester bond.
- It is found in chromosome, nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast.
- The DNA closed covalently at its two ends is called circular DNA, which is not covered by histone protein; it is found in nucleotides of bacteria and viruses.
- Ends are free in linear DNA covered by histone protein; it is found in eukaryotes.
Interesting Science Videos
History of DNA
- DNA was discovered in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher, a Swiss researcher.
- The demonstration that DNA contained genetic information was first made in 1944 by Avery, McCarty, and MacLeod.
- In the 1880s, Fisher discovered the presence of purine and pyrimidine bases in nucleic acids.
- Chargaff identified that the content of purine and pyrimidine in the DNA was the same.
- In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick developed the double helix model of DNA, for which they were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1962 with Willikins.
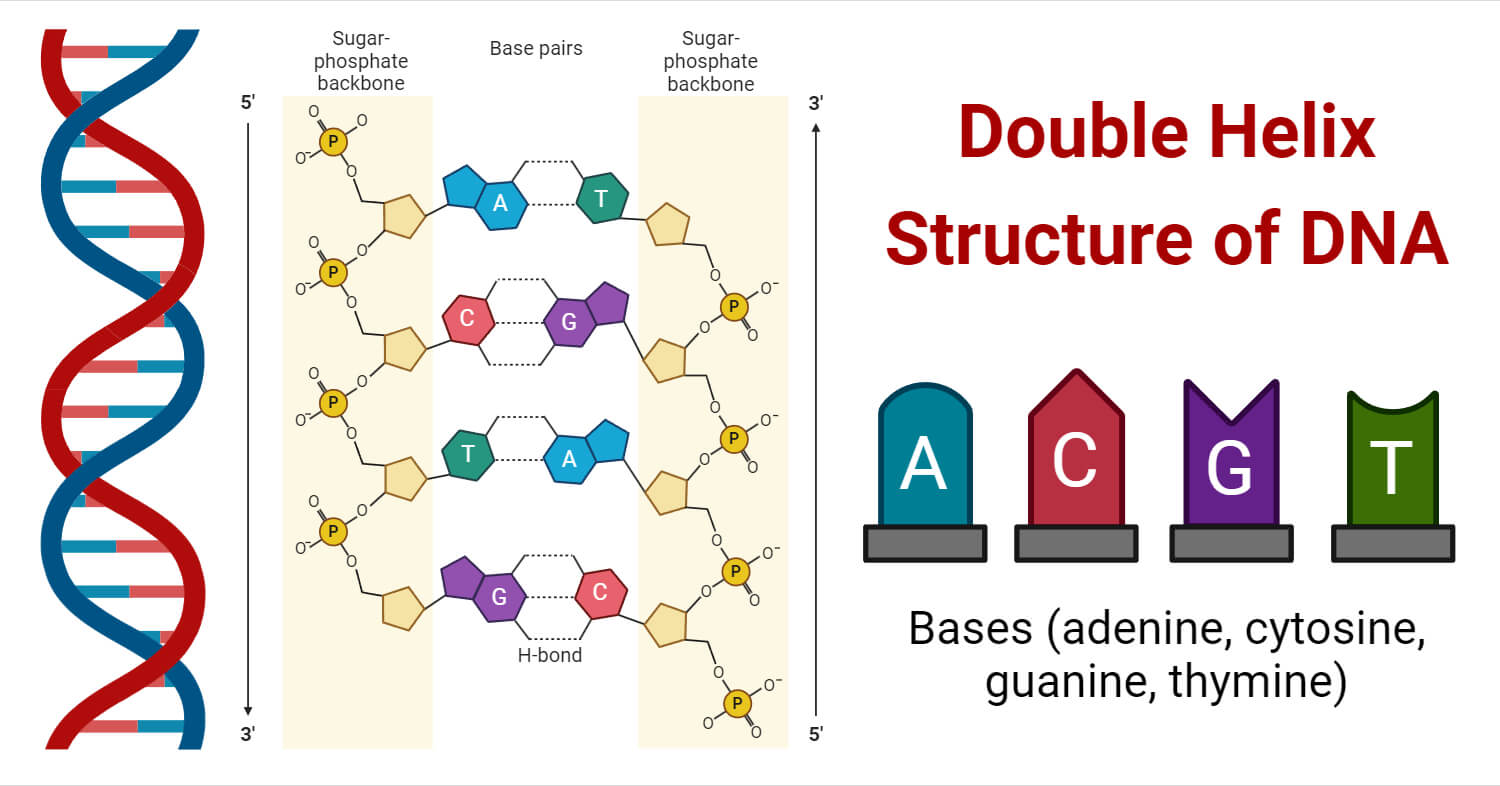
Double Helix Structure of DNA
Watson and Crick (1953) proposed the double helical model of DNA possesses following features:
- It is a polymer of about 1010 deoxyribonucleotides.
- It is a macromolecule made up of helically twisted two antiparallel strands i.e., one strands run in the 5’ to 3’ direction (5’→3’) while the other in 3’to 5’direction (3’→5’). It lies in opposite orientation with respect to each other with 3’-hydroxyl terminus of one strand opposite the 5’-phosphate terminus of the 2nd strand.
- These two strands of DNA together are called DNA duplex which is spirally coiled around central axis in right handed manner.
- The distance of one complete spiral turn is 34 A° (3.4 nm) and has about 10 pairs of nitrogen bases on a complete turn. The distance between two pairs of nitrogen bases is 3.4 A°.
- The diameter (or width) between two strands of a double helix is 20 A°.
- Each deoxyribonucleotide is made up of an outer phosphoric acid, middle deoxyribose sugar and central nitrogenous base (A, T, C and G).
- Purine and pyrimidines are two types of Nitrogen bases.
- Adenine and Guanine falls under purine base while Cytosine and Thymine are pyrimidine base.
- The A – T pair has 2 Hydrogen bonds while G – C pair has 3 Hydrogen bonds. The GC is stronger than AT.
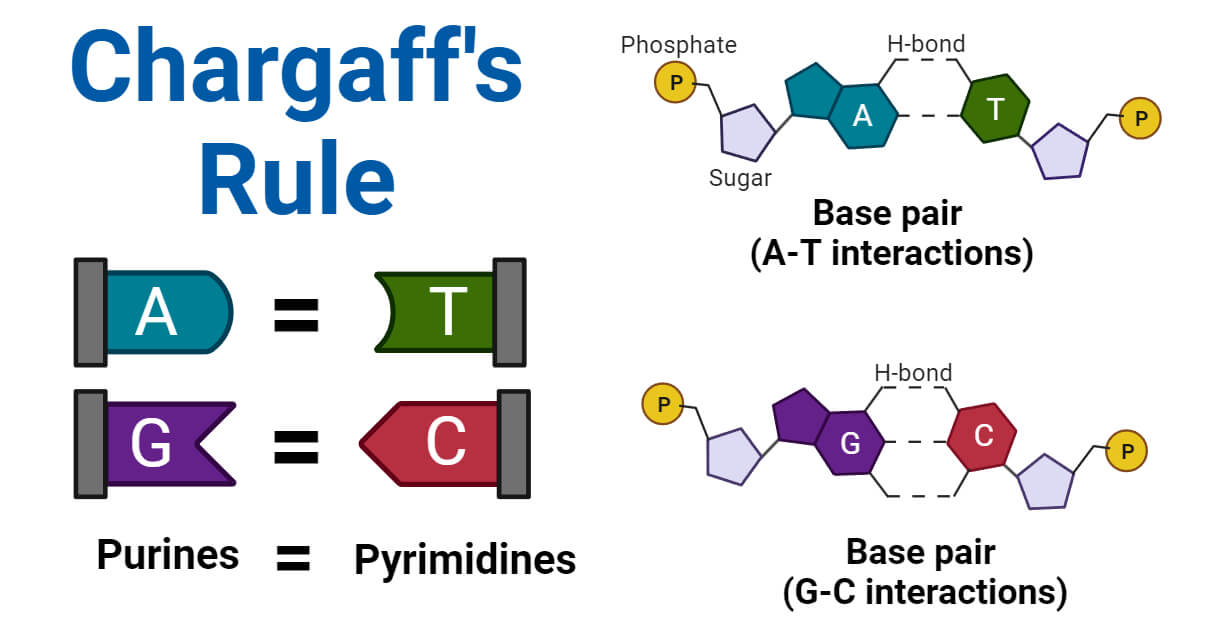
- The complementary base pairing in DNA helix proves Chargaff’s rule.
- Chargaff’s rule (1950): It includes:
- Total amount of purine is equal to the total amount of pyrimidines (i.e. G + A = T + C)
- Amount of Adenine (A) is equal to the amount of Thymine (T) and the amount of Guanine (G) is equal to the amount of cytosine (C) (i.e. A = T, G = C)
- The ratio of (A + T) / (G + C) is constant for a species (human being 1.55, pea 1.62, Euglena 0.88, E. coli 0.93, etc.). This ratio (A + T) / (G + C) is not equal to one.
- Sugar deoxyribose and phosphate occurs in equimolar proportion.
- The nucleotide in the helix are joined together by phosphodiester bonds. Sugar and phosphate molecules from the backbone of the DNA strand.
- The sugar and phosphate backbone do not conceal the bases inside. There are two groove along the surface of the DNA molecule. One is wide and deep is called minor groove and other is narrow and shallow is called minor groove.
Types of DNA
The double helix model of DNA proposed by Watson and Crick is B-DNA which is right handed spiral and has 10 base pairs in one turn of helix.
On the basis of number of base pairs in a turn, DNAs are of following forms:
- A-DNA: This type of DNA has 11 base pairs in a turn and right handed duplex. Its major grooves are very deep and minor grooves are very shallow.
- B-DNA: This type of DNA has 10 base pairs in a turn and right handed duplex. Watson and Crick proposed this model of DNA. It is metabolically stable form of DNA.
- C-DNA: This type of DNA has 9 base pairs in a turn and right handed duplex. The axis lies close to the minor groove.
- D-DNA: This type of DNA has 8 base pairs in a turn and right handed duplex.
- Z-DNA: This type of DNA has 12 base pairs in a turn and left handed duplex. It has zig-zag sugar phosphate backbone in antiparallel organization.
Functions of DNA
- DNA is a genetic material which carries all the hereditary information from one generation to other.
- DNA controls all the biological activities of cells as it synthesizes proteins, enzymes and biochemical.
- DNA synthesize RNA through the process transcription.
- DNA guides the process of protein synthesis in the cell.
- DNA helps in recombination during meiosis by crossing over.
References
- Keshari AK and Adhikari KK (2012), A Textbook of Higher Secondary Biology (Class XII), Vidyarthi Pustak Bhandar, Kathmandu, pp 597-601.
- Shakya M, Mehta KR, Gautam M, Pokharel KR and Khanal K (2022), Principles of Biology Grade XII, Asmita Books Publisher and Distributors, Kathmandu, pp 160-162.
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/1-The-double-helix-structure-of-DNA-It-is-constructed-of-four-different-building_fig1_40533831
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26821/
- https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Double-Helix
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/discovery-of-dna-structure-and-function-watson-397/
- https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/dna-as-the-genetic-material/dna-discovery-and-structure/a/discovery-of-the-structure-of-dna
