Interesting Science Videos
What is Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining?
Collagen is the major building block of all tissues including tendon, ligament, cornea, cartilage, and bone It is a fibrous, structural protein that made up of a right-handed bundle of three parallel, left-handed polyproline II-type helices. Collagen can undergo extensive proteolytic remodeling during development causing collagen degradation leading to a variety of life-threatening diseases such as Bone cancer (Osteoarthritis), myocardial infarction, glomerulonephritis, and pulmonary fibrosis. It can also be used to detect embryonic bone deformation and skin aging.
Conventional methods are difficult to detect for these kinds of collagen degradations and therefore a designed peptide (Collagen Hybridizing Peptide, CHP), that hybridizes the degraded collagen was made. Collage Hybridizing peptide (CHP) is a synthetic peptide sequence with 6 to 10 repeating units of Gyl-Xaa-Yaa amino acid triplet, mimicking the natural collagen sequence. The CHP peptide has a high content of proline and Hydroxyproline in the Xaa-Yaa position giving it a strong tendency to form the triple helix conformation.
The monomeric peptide chain has the ability to recognize denatured collagen strands in body tissues by forming a hybridized triple helix with the collagen strand. This mechanism is enabled by the triple-helical chain ( Gly-Xaa-Yaa) and hydrogen bond interchains similar to DNA fragments annealing to complementary DNA strands. CHP is very specific with a negligible affinity to intact collagen molecules due to a lack of binding sites. It is also inert towards non-specific binding because of its neutral and hydrophilic nature.
Objectives of Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
To detect and demonstrate the presence of Denatured collagen ligaments
Principle of Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
Collagen Hybridizing Peptide stain is a special stain used in Developmental Biology, Histology, and Histopathology to detect and demonstrate the presence of collagen degraded tissues.
CHP strongly visualizes the cellular matrix degraded by proteolytic migration of inflamed cells within a collagen culture. Local mechanical injuries can be quantified by CHP at a molecular level including assessing the denaturation of the collagen tissues in the extracellular matrix level. Its application with SDS-PAGE allows visualizing the collagen bands without the use of the western blotting technique.
CHP slowly reassembles into triple helices in solution when stored, hence it can not hybridize with unfolded collagen strands. hence it must be separated into monomers by heating before use. The formation of trimers (trimerization) by CHP takes some time even hours when in low concentrations because the heat-dissociated CHP can stay as an active strand for hybridizing the denatured collagen.
Heating the CHP at 80 °C in a water bath after dilution is ideal common protocol is heating the CHP solution (after diluting to the desired concentration) to and quickly quenching it to room temperature followed by immediate application to target collagen substrates, as described below in detail. A heating block and an ice-water bath may be needed in most applications (not provided).
Practically, CHP can be labeled with biotin for avidin/streptavidin-mediated detection.
Reagents
- Peptide powder
- Phosphate buffered water
- Biotin
- Basal Salt
Procedure of Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
- Dissolve the 0.3 mg of peptide powder (Biotin CHP)in 1 mL of pure water or phosphate-buffered saline (1x PBS)
- Mix well and centrifuge, to prepare a stock solution with at least 100 μM of CHP. (Store the stock solution at 4 °C)
- Dilute the stock solution depending on the concentration to use. example; For the 60 μg powder, dissolve in 400 μL water or PBS to get a stock solution with a CHP concentration of 50 μM).
- depending on the tissue of testing, block the sample with 10% serum or 5% BSA especially when co-staining with antibodies. (For certain tissue types, e.g., kidney, it may be necessary to block endogenous biotin using a standard kit for B-CHP staining.)
- Dilute the CHP stock solution in a PBS buffer with an average dilution of the sample.
- Heat the diluted CHP in a water bath with controlled temperatures of 80 °C for 5 min
- Immediately place the heated CHP in a microtube in an ice water bath for 15-90 seconds, to avoid damaging the tissue sample with heat.
- immediately centrifuge the cooled microtube to collect condensation in the tube and pipet the solution to each sample tissue.
- Incubate the tissues with the staining solution at 4 °C for 2 h or overnight for better results.
- Wash the tissue slides in PBS for 5 min in three changes at room temperature.
- Depending on the sample stain;
- CHP and R-CHP can be analyzed with a fluorescence microscope.
- B-CHP can be detected by an avidin/streptavidin-mediated method.
Result and interpretation of Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
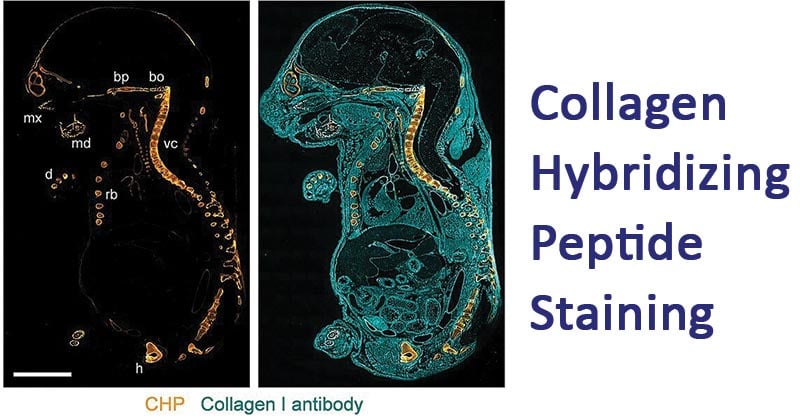
Figure: Localization of CHP binding in a sagittal section of an 18 d.p.c. mouse embryo (E18) double-stained with B-CHP (detected by AlexaFluor647-streptavidin, orange) and an anti-collagen I antibody (detected by AlexaFluor555-labeled donkey anti-rabbit IgG H&L, cyan). mx, maxilla; md, mandibular bone; bp, basisphenoid bone; bo, basioccipital bone; vc, vertebral column; rb, rib; h, hipbone; d, digital bones. Image Source: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b03150
For F-CHP, observe green stained separated porcine ligament cryosections.
For R-CHP, the heated ligaments will appear red, while the intact ligaments appeared blue, and the unheated ligaments dark blue (Black).
For B-CHP, the ligaments appear light brown.
Advantages of Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
- It is specific for monomeric collagen strands that are denatured.
- It is highly sensitive in detecting denatured collagen ligaments
Disadvantages of Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
- The CHP easily coils back to a trimer if it is stored in low concentrations and in very low temperatures
Applications of Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
- CHP probes can be applied for other species of organisms
- CHP can be used to differentiate collagen types
- CHP is used for the detection of inflammation and tissue damage
- CHP is used to detect embryonic bone deformation
- CHP can be used to detect skin aging
- CHP is used to detect osteoarthritis, pulmonary fibrosis, myocardial infarction, glomerulonephritis.
References and Sources
- 3% – https://www.3helix.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/3Helix_CHP_user_guide_2020.07.09.pdf
- 3% – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19344236/
- 3% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collagen_Hybridizing_Peptide
- 2% – https://www.3helix.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/final-CHP_datasheet_201703.pdf
- 2% – https://wikimili.com/en/Collagen_helix
- 2% – https://echelon-inc.com/product/collagen-hybridizing-peptide-biotin-conjugate-chp/
- 2% – https://advancedbiomatrix.com/public/pdf/Other/DFU-CHP.pdf
- 1% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/bone-tissue-engineering
- 1% – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/23193283_The_Spot_Technique_Synthesis_and_Screening_of_Peptide_Macroarrays_on_Cellulose_Membranes
- 1% – https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.7b03150
- <1% – https://www.researchgate.net/topic/Stock-Solution/2
- <1% – https://pediaa.com/what-is-the-difference-between-collagen-protein-and-collagen-peptides/
- <1% – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/jor.24185
- <1% – http://wolfson.huji.ac.il/purification/PDF/ReversePhase/VYDAChandbookRPC.pdf
