Long-Read Sequencing: Principle, Types, Process, Uses
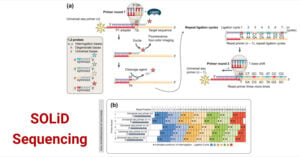
Long-read sequencing (LRS) is a third-generation sequencing method that can sequence longer fragments of nucleotides compared to traditional short-read sequencing methods. It generates genomic data by reading DNA or RNA … Read more