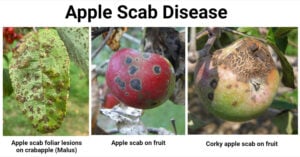
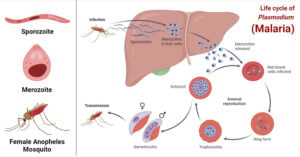
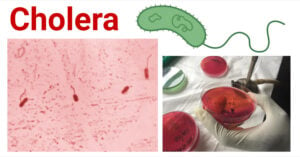
Fusarium Wilt: Causes, Symptoms, Disease Cycle, Control
Fusarium wilt is a soil-borne disease that leads to wilting, yellowing, and sometimes death of various plant species. This disease causes significant crop losses worldwide and is disastrous under warm … Read more